Industrial Internet integrates advanced connectivity and data analytics into manufacturing processes, enhancing real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities. Operational Technology focuses on the hardware and software systems that control and automate physical devices within industrial environments, ensuring process stability and safety. Explore the key differences and benefits of Industrial Internet and Operational Technology to optimize your manufacturing operations.
Why it is important
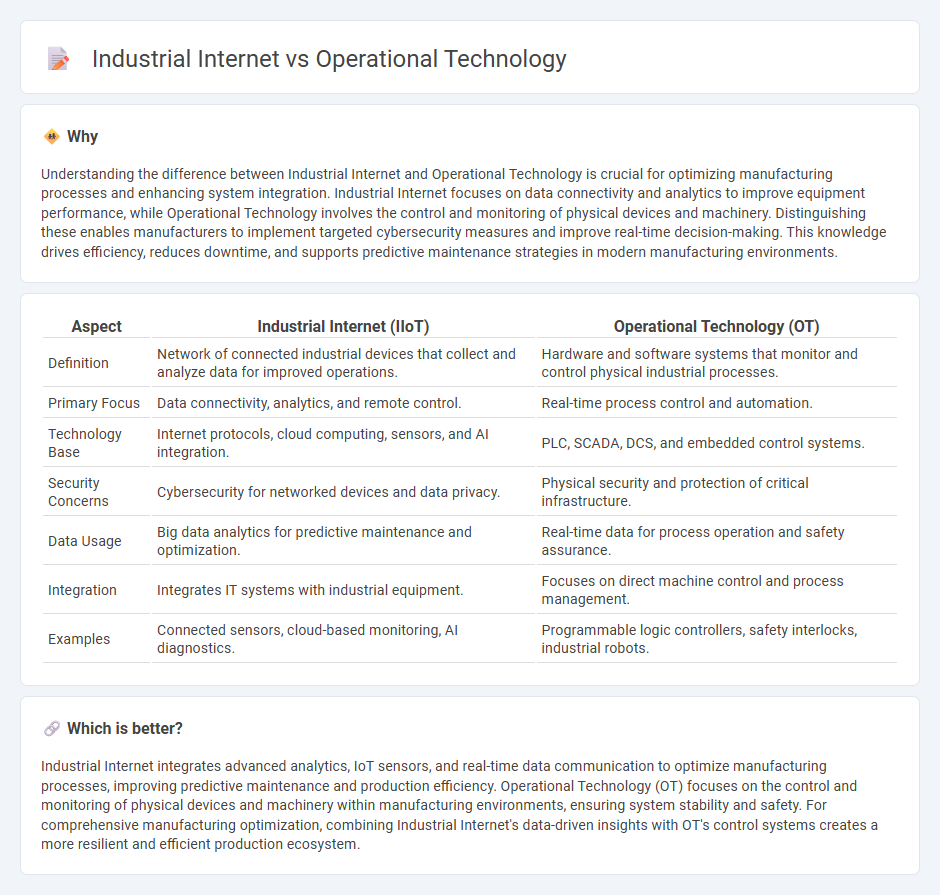
Understanding the difference between Industrial Internet and Operational Technology is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes and enhancing system integration. Industrial Internet focuses on data connectivity and analytics to improve equipment performance, while Operational Technology involves the control and monitoring of physical devices and machinery. Distinguishing these enables manufacturers to implement targeted cybersecurity measures and improve real-time decision-making. This knowledge drives efficiency, reduces downtime, and supports predictive maintenance strategies in modern manufacturing environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Industrial Internet (IIoT) | Operational Technology (OT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network of connected industrial devices that collect and analyze data for improved operations. | Hardware and software systems that monitor and control physical industrial processes. |
| Primary Focus | Data connectivity, analytics, and remote control. | Real-time process control and automation. |
| Technology Base | Internet protocols, cloud computing, sensors, and AI integration. | PLC, SCADA, DCS, and embedded control systems. |
| Security Concerns | Cybersecurity for networked devices and data privacy. | Physical security and protection of critical infrastructure. |
| Data Usage | Big data analytics for predictive maintenance and optimization. | Real-time data for process operation and safety assurance. |
| Integration | Integrates IT systems with industrial equipment. | Focuses on direct machine control and process management. |
| Examples | Connected sensors, cloud-based monitoring, AI diagnostics. | Programmable logic controllers, safety interlocks, industrial robots. |
Which is better?
Industrial Internet integrates advanced analytics, IoT sensors, and real-time data communication to optimize manufacturing processes, improving predictive maintenance and production efficiency. Operational Technology (OT) focuses on the control and monitoring of physical devices and machinery within manufacturing environments, ensuring system stability and safety. For comprehensive manufacturing optimization, combining Industrial Internet's data-driven insights with OT's control systems creates a more resilient and efficient production ecosystem.
Connection
The Industrial Internet integrates advanced sensors, data analytics, and connectivity to optimize manufacturing processes, while Operational Technology (OT) encompasses the hardware and software that directly controls these industrial operations. Together, the Industrial Internet enhances OT systems by enabling real-time data exchange and predictive maintenance, improving production efficiency and reducing downtime. This connection drives smart manufacturing by leveraging Internet of Things (IoT) devices and automation technologies for more adaptive and resilient industrial environments.
Key Terms
SCADA
Operational Technology (OT) encompasses hardware and software systems like SCADA that monitor and control industrial processes, ensuring real-time data acquisition and process automation. The Industrial Internet integrates OT with Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity, enabling advanced analytics, predictive maintenance, and enhanced decision-making through networked SCADA systems. Explore how SCADA bridges traditional OT with Industrial Internet innovations to optimize industrial efficiency and safety.
IIoT
Operational Technology (OT) encompasses hardware and software that manage industrial processes, while Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) specifically refers to interconnected sensors and devices within those systems that enable data exchange and analytics. IIoT enhances traditional OT by integrating advanced connectivity and real-time data insights to optimize efficiency, predictive maintenance, and automation. Explore the evolving landscape of IIoT to understand its transformative impact on industrial automation and operational efficiency.
Cyber-Physical Systems
Operational Technology (OT) encompasses hardware and software that directly monitor and control physical devices and processes in industrial environments, ensuring real-time system reliability and safety. The Industrial Internet integrates internet connectivity and advanced data analytics into Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS), enabling enhanced automation, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making across manufacturing and critical infrastructure. Explore the evolving landscape of Cyber-Physical Systems to understand how OT and the Industrial Internet converge, transforming industrial operations.
Source and External Links
Operational technology - Operational Technology (OT) is hardware and software that directly monitors and controls industrial equipment and processes, including systems like PLCs, SCADA, and DCS, distinct from traditional IT systems in industrial environments.
What Is Operational Technology (OT)? | Definition from ... - OT refers to hardware and software that monitors and controls physical devices, primarily used in industrial control systems, and faces growing integration with IT systems, raising security challenges due to its critical role in infrastructure.
Modern Operational Technology (OT) Components ... - OT comprises hardware and software designed to monitor, control, and manage industrial operations including ICS and SCADA systems, with a focus on security to protect critical infrastructure from cyber threats.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com