Dark factories leverage automation and robotics to operate without human intervention, reducing labor costs and increasing production efficiency. Smart factories integrate IoT sensors, AI, and real-time data analytics to enhance adaptability, predictive maintenance, and energy management. Explore the latest advancements in manufacturing technologies to understand how these factory models transform industrial processes.
Why it is important
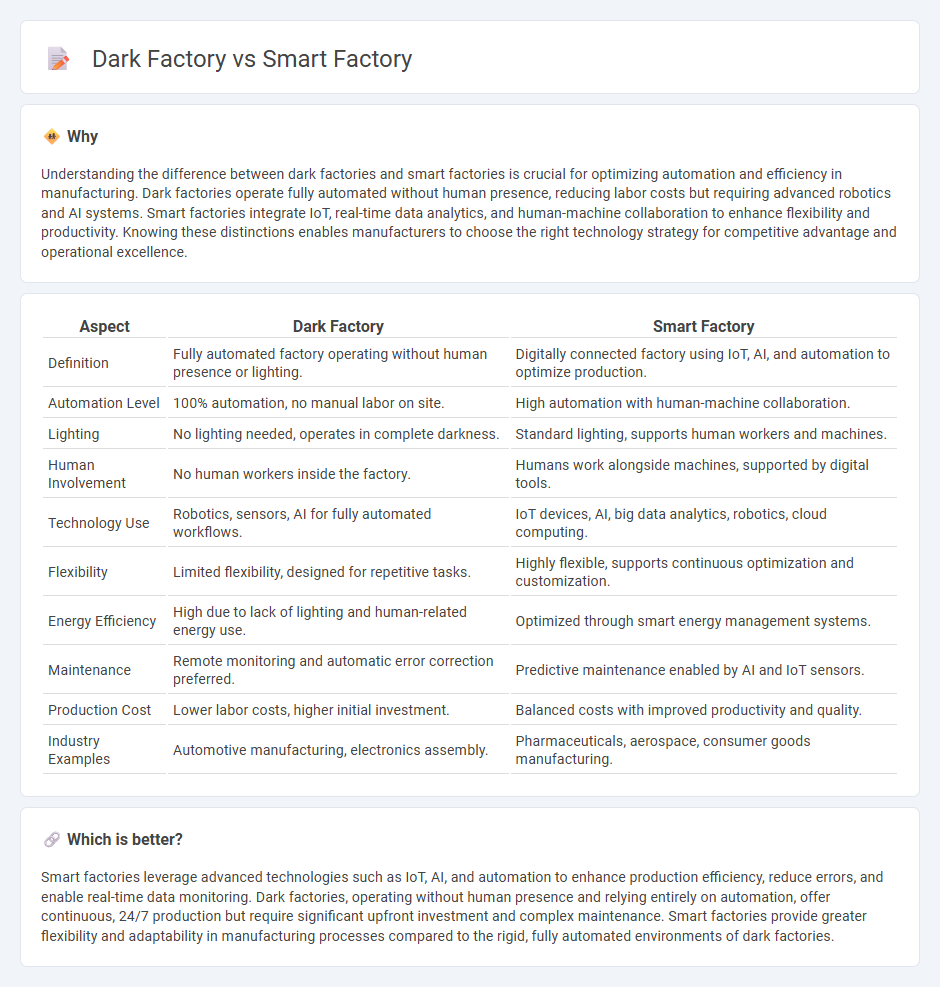
Understanding the difference between dark factories and smart factories is crucial for optimizing automation and efficiency in manufacturing. Dark factories operate fully automated without human presence, reducing labor costs but requiring advanced robotics and AI systems. Smart factories integrate IoT, real-time data analytics, and human-machine collaboration to enhance flexibility and productivity. Knowing these distinctions enables manufacturers to choose the right technology strategy for competitive advantage and operational excellence.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Factory | Smart Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated factory operating without human presence or lighting. | Digitally connected factory using IoT, AI, and automation to optimize production. |
| Automation Level | 100% automation, no manual labor on site. | High automation with human-machine collaboration. |
| Lighting | No lighting needed, operates in complete darkness. | Standard lighting, supports human workers and machines. |
| Human Involvement | No human workers inside the factory. | Humans work alongside machines, supported by digital tools. |
| Technology Use | Robotics, sensors, AI for fully automated workflows. | IoT devices, AI, big data analytics, robotics, cloud computing. |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility, designed for repetitive tasks. | Highly flexible, supports continuous optimization and customization. |
| Energy Efficiency | High due to lack of lighting and human-related energy use. | Optimized through smart energy management systems. |
| Maintenance | Remote monitoring and automatic error correction preferred. | Predictive maintenance enabled by AI and IoT sensors. |
| Production Cost | Lower labor costs, higher initial investment. | Balanced costs with improved productivity and quality. |
| Industry Examples | Automotive manufacturing, electronics assembly. | Pharmaceuticals, aerospace, consumer goods manufacturing. |
Which is better?
Smart factories leverage advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and automation to enhance production efficiency, reduce errors, and enable real-time data monitoring. Dark factories, operating without human presence and relying entirely on automation, offer continuous, 24/7 production but require significant upfront investment and complex maintenance. Smart factories provide greater flexibility and adaptability in manufacturing processes compared to the rigid, fully automated environments of dark factories.
Connection
Dark factories leverage advanced automation and IoT technologies to operate with minimal or no human intervention, creating an environment where manufacturing processes are fully autonomous. Smart factories integrate cyber-physical systems, AI, and real-time data analytics to optimize production efficiency and flexibility. The connection between dark and smart factories lies in their reliance on digitalization and intelligent systems to enhance manufacturing productivity and reduce human labor.
Key Terms
Automation
Smart factories utilize advanced automation technologies such as IoT sensors, AI-driven process management, and robotics to optimize production efficiency while maintaining human supervision. Dark factories operate fully automated systems with minimal or no human presence, leveraging AI, robotics, and machine learning to perform continuous manufacturing under controlled conditions without lighting. Explore the transformative impact of automation on manufacturing by learning more about smart and dark factory innovations.
Human Intervention
Smart factories integrate advanced automation with significant human intervention for monitoring, maintenance, and decision-making, enabling flexibility and adaptability in production processes. Dark factories operate fully autonomously without human presence, relying on AI, robotics, and IoT to run 24/7 for optimized efficiency and minimal errors. Discover how these approaches impact operational efficiency and workforce dynamics in modern manufacturing.
Real-time Data Integration
Smart factories utilize real-time data integration to optimize production processes, enabling dynamic adjustments and predictive maintenance through IoT sensors and advanced analytics. Dark factories operate with full automation and minimal human presence, relying heavily on synchronized real-time data flows to maintain uninterrupted operations and quality control. Explore how cutting-edge real-time data integration transforms manufacturing efficiency and innovation.
Source and External Links
What is a smart factory? How to build ... - A smart factory is a digitally connected facility enabling smart manufacturing through technologies like AI, IIoT, big data, and cloud computing to continuously improve production processes in real time as part of Industry 4.0.
Smart Factory Guide | L2L - A smart factory connects machines, people, and processes via digital tech to improve efficiency, quality, safety, and cost, representing a cyber-physical system under Industry 4.0 that drives competitive advantages.
The Smart Factory @ Wichita - Deloitte's Smart Factory @ Wichita is an immersive experience showcasing end-to-end smart production lines, enabling companies to explore and accelerate digital manufacturing transformation for sustainable innovation and growth.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com