Industrial edge computing enhances manufacturing efficiency by processing data locally on devices near production lines, reducing latency compared to traditional PLC systems that rely heavily on centralized control. Unlike PLCs that focus primarily on control and automation tasks, edge computing integrates advanced analytics, real-time monitoring, and AI-driven decision-making to optimize manufacturing workflows. Explore how industrial edge computing can revolutionize factory operations beyond the capabilities of conventional PLC solutions.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between industrial edge computing and PLC systems is crucial for optimizing manufacturing operations, as edge computing enables real-time data processing and advanced analytics at or near the production site, enhancing decision-making and efficiency. PLCs serve as reliable, dedicated controllers for automating machinery, while edge computing extends capabilities by integrating IoT, AI, and cloud connectivity for predictive maintenance and quality control. Selecting the appropriate technology directly impacts production uptime, resource management, and scalability in smart factories. Knowledge of these distinctions supports strategic investments in Industry 4.0 technologies to drive innovation and competitiveness.
Comparison Table
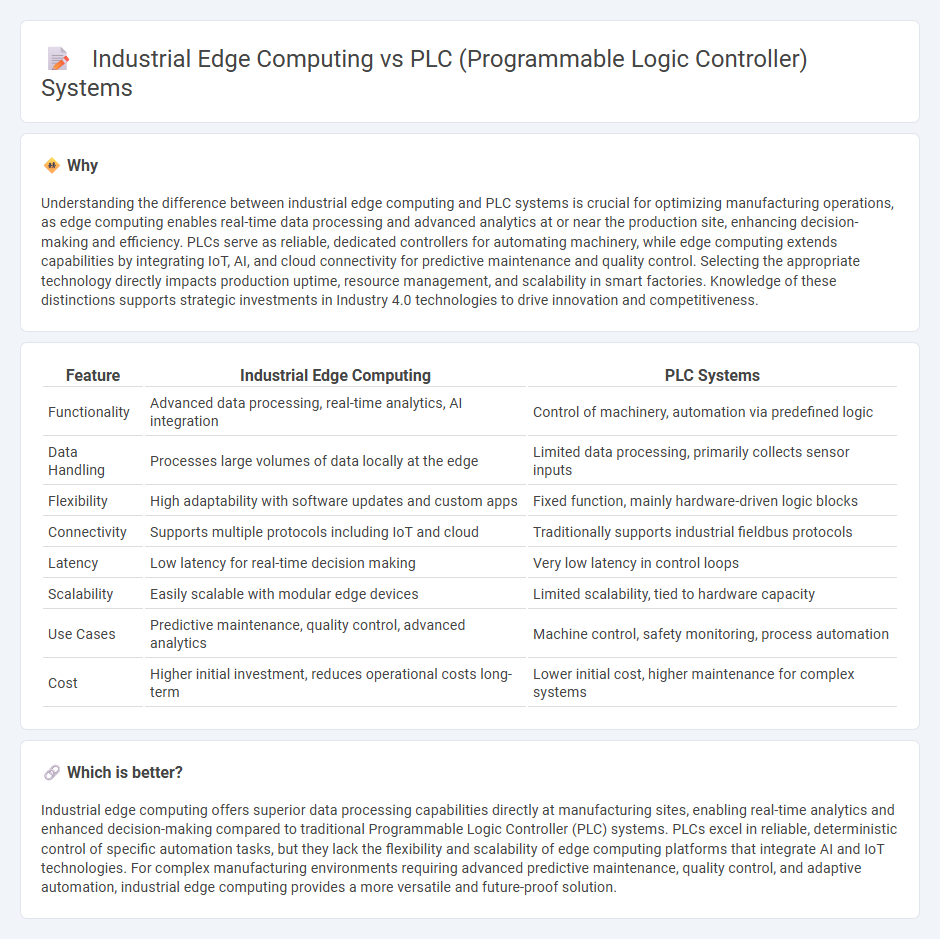
| Feature | Industrial Edge Computing | PLC Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Advanced data processing, real-time analytics, AI integration | Control of machinery, automation via predefined logic |
| Data Handling | Processes large volumes of data locally at the edge | Limited data processing, primarily collects sensor inputs |
| Flexibility | High adaptability with software updates and custom apps | Fixed function, mainly hardware-driven logic blocks |
| Connectivity | Supports multiple protocols including IoT and cloud | Traditionally supports industrial fieldbus protocols |
| Latency | Low latency for real-time decision making | Very low latency in control loops |
| Scalability | Easily scalable with modular edge devices | Limited scalability, tied to hardware capacity |
| Use Cases | Predictive maintenance, quality control, advanced analytics | Machine control, safety monitoring, process automation |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, reduces operational costs long-term | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance for complex systems |
Which is better?
Industrial edge computing offers superior data processing capabilities directly at manufacturing sites, enabling real-time analytics and enhanced decision-making compared to traditional Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) systems. PLCs excel in reliable, deterministic control of specific automation tasks, but they lack the flexibility and scalability of edge computing platforms that integrate AI and IoT technologies. For complex manufacturing environments requiring advanced predictive maintenance, quality control, and adaptive automation, industrial edge computing provides a more versatile and future-proof solution.
Connection
Industrial edge computing enhances manufacturing efficiency by processing data directly from Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) systems on-site, reducing latency and enabling real-time decision-making. PLCs collect and control sensor and machine data, which edge computing platforms analyze locally to optimize operations and predict maintenance needs. This integration supports smarter automation workflows, improves production reliability, and lowers operational costs in industrial environments.
Key Terms
Real-time control
PLC systems provide robust real-time control by executing pre-programmed logic directly on hardware, ensuring deterministic and low-latency responses essential for industrial automation. Industrial edge computing extends these capabilities by integrating advanced data processing, AI, and analytics closer to the source, enabling real-time decision-making beyond simple control tasks. Explore how combining PLC reliability with edge computing intelligence can revolutionize industrial automation efficiency.
Data processing location
PLC systems process data locally within the control unit, enabling real-time automation and quick response to machine-level events. Industrial edge computing extends data processing closer to the source at edge devices, facilitating advanced analytics and reducing latency without relying solely on centralized cloud resources. Explore the distinctions in data processing strategies between PLCs and industrial edge computing to optimize your manufacturing operations.
Connectivity
PLC systems offer reliable, real-time control with dedicated connectivity protocols such as Modbus and Profibus, ensuring seamless device communication within industrial environments. Industrial edge computing enhances connectivity by integrating advanced networking capabilities, supporting IoT protocols and enabling data processing closer to machines for faster decision-making. Explore more to understand how connectivity shapes efficiency in modern industrial automation.
Source and External Links
What is PLC ? Programmable Logic Controller - Unitronics - A PLC is a ruggedized computer used in industrial automation to receive inputs from sensors, process data according to programmed logic, and control outputs such as relays and drives, enabling automation of machines or entire production lines.
What is a PLC? - AMCI - A Programmable Logic Controller is an industrial computer control system that monitors inputs, runs a user-defined program, and controls outputs, with its modular design allowing versatile input/output configurations for manufacturing and process automation.
What Is a Programmable Logic Controller? | UTI - A PLC is a rugged digital computer built for industrial environments that automates control of machinery by monitoring sensors, processing inputs, and controlling outputs such as motors or conveyor belts to ensure efficient operation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com