Microfactories focus on compact, flexible production units designed for localized manufacturing with lower capital investment and faster deployment. Smart factories leverage advanced automation, IoT, and AI to enable highly efficient, scalable, and interconnected production systems within larger industrial environments. Explore the differences and benefits of microfactories and smart factories to optimize your manufacturing strategy.
Why it is important
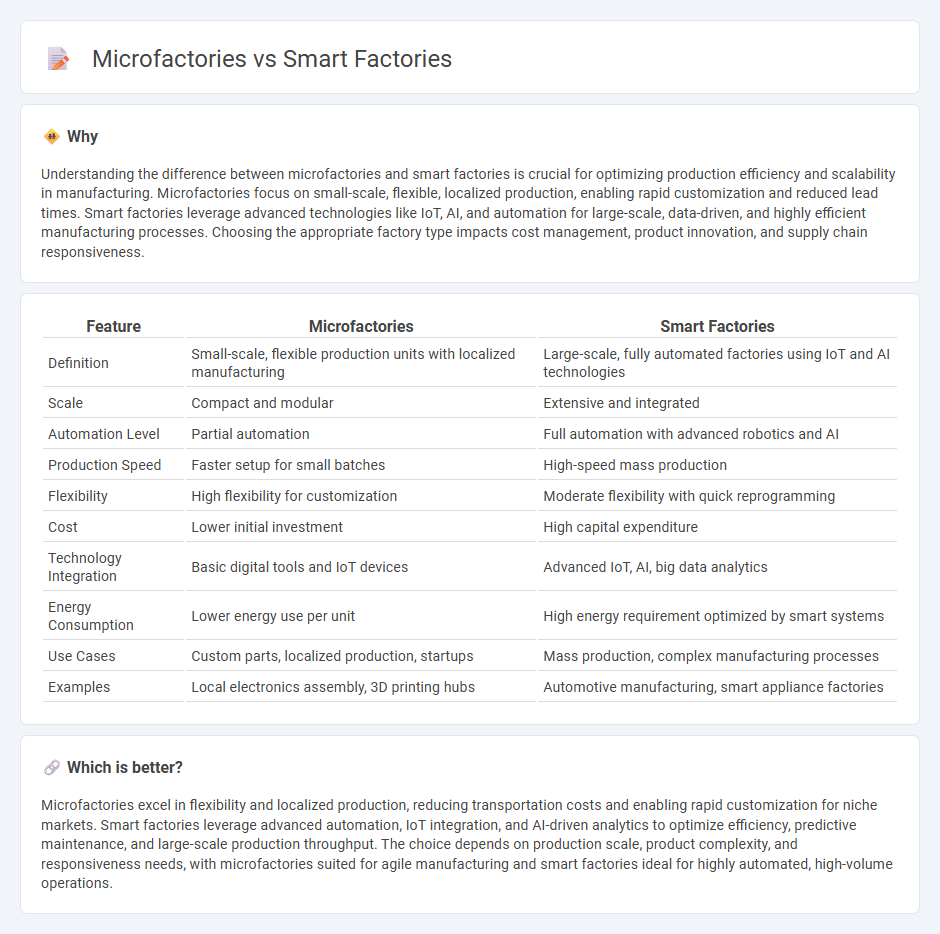
Understanding the difference between microfactories and smart factories is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and scalability in manufacturing. Microfactories focus on small-scale, flexible, localized production, enabling rapid customization and reduced lead times. Smart factories leverage advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and automation for large-scale, data-driven, and highly efficient manufacturing processes. Choosing the appropriate factory type impacts cost management, product innovation, and supply chain responsiveness.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Microfactories | Smart Factories |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small-scale, flexible production units with localized manufacturing | Large-scale, fully automated factories using IoT and AI technologies |
| Scale | Compact and modular | Extensive and integrated |
| Automation Level | Partial automation | Full automation with advanced robotics and AI |
| Production Speed | Faster setup for small batches | High-speed mass production |
| Flexibility | High flexibility for customization | Moderate flexibility with quick reprogramming |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | High capital expenditure |
| Technology Integration | Basic digital tools and IoT devices | Advanced IoT, AI, big data analytics |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy use per unit | High energy requirement optimized by smart systems |
| Use Cases | Custom parts, localized production, startups | Mass production, complex manufacturing processes |
| Examples | Local electronics assembly, 3D printing hubs | Automotive manufacturing, smart appliance factories |
Which is better?
Microfactories excel in flexibility and localized production, reducing transportation costs and enabling rapid customization for niche markets. Smart factories leverage advanced automation, IoT integration, and AI-driven analytics to optimize efficiency, predictive maintenance, and large-scale production throughput. The choice depends on production scale, product complexity, and responsiveness needs, with microfactories suited for agile manufacturing and smart factories ideal for highly automated, high-volume operations.
Connection
Microfactories leverage advanced automation and IoT technologies to enable localized, flexible production, while smart factories utilize interconnected systems and data analytics for optimized large-scale manufacturing processes. Both concepts rely on real-time data integration and digital communication networks to enhance efficiency, reduce downtime, and enable adaptive production workflows. The synergy between microfactories and smart factories drives Industry 4.0 by combining scalability with customization through intelligent manufacturing ecosystems.
Key Terms
Automation
Smart factories utilize advanced automation technologies, including robotics, IoT sensors, and AI-driven systems, to optimize production efficiency and reduce human intervention. Microfactories emphasize localized, flexible automation to enable rapid customization and smaller batch production with lower operational costs. Explore how the strategic deployment of automation in these factory models transforms manufacturing agility and scalability.
Scale of Production
Smart factories typically operate on a large scale, integrating extensive automation, IoT devices, and advanced analytics to optimize mass production processes. Microfactories focus on small-scale, flexible manufacturing, enabling rapid prototyping, customization, and localized production with lower overhead costs. Explore the detailed differences in production scale and capabilities between smart factories and microfactories to understand their unique advantages.
Flexibility
Smart factories leverage advanced automation and IoT technologies to enhance production flexibility by enabling real-time data analysis and adaptive manufacturing processes. Microfactories prioritize modular design and localized production, allowing for rapid reconfiguration and customization to meet specific market demands. Explore how these innovative approaches transform manufacturing agility and responsiveness.
Source and External Links
9 Benefits of Smart Factories - Manufacturing Today - Smart factories integrate IoT, AI, and machine learning to increase efficiency, improve quality control, and enable flexible, customized production, greatly transforming manufacturing operations.
What Is a Smart Factory? An Expert Guide - NetSuite - A smart factory is a highly automated, digitally connected environment where integrated technologies collect and analyze data in real time to enable self-optimizing and autonomous manufacturing processes.
What is Smart Factory and Smart Manufacturing? - Oracle - Smart factories use interconnected systems to generate real-time data for improving production processes, quality, and maintenance by predicting machine health and automating supply replenishment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com