Adaptive machining utilizes real-time data and advanced sensors to dynamically adjust cutting parameters, enhancing precision and reducing material waste, unlike traditional machining which relies on fixed settings and manual adjustments. This technology-driven approach improves efficiency, extends tool life, and accommodates complex geometries with minimal human intervention. Explore how adaptive machining transforms production processes and optimizes manufacturing outcomes.
Why it is important
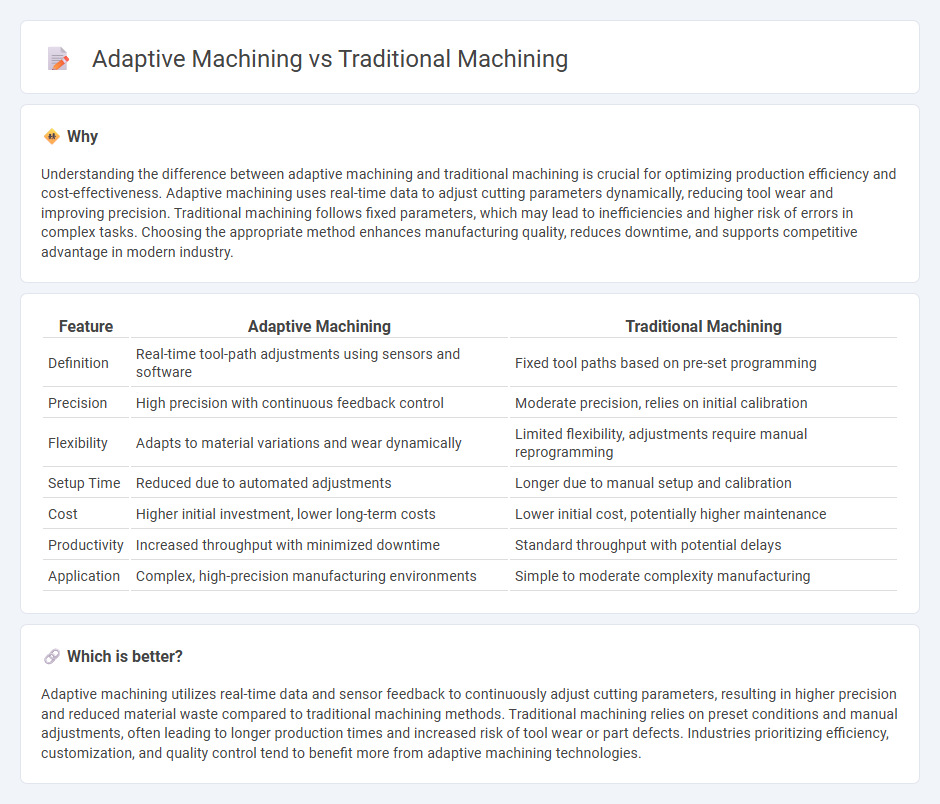
Understanding the difference between adaptive machining and traditional machining is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Adaptive machining uses real-time data to adjust cutting parameters dynamically, reducing tool wear and improving precision. Traditional machining follows fixed parameters, which may lead to inefficiencies and higher risk of errors in complex tasks. Choosing the appropriate method enhances manufacturing quality, reduces downtime, and supports competitive advantage in modern industry.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Adaptive Machining | Traditional Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time tool-path adjustments using sensors and software | Fixed tool paths based on pre-set programming |
| Precision | High precision with continuous feedback control | Moderate precision, relies on initial calibration |
| Flexibility | Adapts to material variations and wear dynamically | Limited flexibility, adjustments require manual reprogramming |
| Setup Time | Reduced due to automated adjustments | Longer due to manual setup and calibration |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower long-term costs | Lower initial cost, potentially higher maintenance |
| Productivity | Increased throughput with minimized downtime | Standard throughput with potential delays |
| Application | Complex, high-precision manufacturing environments | Simple to moderate complexity manufacturing |
Which is better?
Adaptive machining utilizes real-time data and sensor feedback to continuously adjust cutting parameters, resulting in higher precision and reduced material waste compared to traditional machining methods. Traditional machining relies on preset conditions and manual adjustments, often leading to longer production times and increased risk of tool wear or part defects. Industries prioritizing efficiency, customization, and quality control tend to benefit more from adaptive machining technologies.
Connection
Adaptive machining and traditional machining are interconnected through their shared use of fundamental manufacturing processes such as milling, turning, and drilling. Adaptive machining enhances traditional techniques by integrating real-time sensor data and CNC programming to adjust cutting parameters dynamically, improving precision and efficiency. This synergy allows manufacturers to optimize tool paths and reduce material waste while maintaining the reliability and simplicity of conventional machining methods.
Key Terms
Material Removal Rate
Adaptive machining significantly increases the Material Removal Rate (MRR) compared to traditional machining by optimizing cutting parameters in real-time, reducing tool wear and maximizing productivity. Traditional machining maintains fixed cutting conditions, often resulting in inefficient material removal and longer cycle times. Explore the benefits of adaptive machining to enhance your manufacturing efficiency and throughput.
Tool Path Optimization
Traditional machining relies on fixed tool paths based on initial programming, often resulting in longer cycle times and increased tool wear. Adaptive machining employs dynamic tool path optimization, continuously adjusting cutting parameters in real-time to enhance efficiency, reduce machining time, and extend tool life. Discover how adaptive machining transforms manufacturing by optimizing tool paths for superior performance.
Real-Time Feedback
Traditional machining operates on pre-set parameters without adjustments during the process, often leading to inefficiencies and increased tool wear. Adaptive machining integrates real-time feedback systems using sensor data to modify cutting conditions dynamically, improving precision and reducing material waste. Discover how real-time feedback revolutionizes machining by enhancing productivity and product quality.
Source and External Links
Machining - Wikipedia - Traditional machining involves manual operations like turning, boring, drilling, and threading where the workpiece or tool moves in direct contact, typically using machines like lathes and mills.
CNC vs. Traditional Machining Compared - Adept Corporation - Traditional machining uses manually controlled tools such as lathes and drills, relying on operator skill for real-time adjustments, and is favored for bespoke or artistic projects due to its lower initial cost and direct control.
Types of Machining Operations: Classifications and Differences - Conventional (traditional) machining is characterized by direct contact between the cutting tool and workpiece to remove excess material, including processes like turning and milling where the tool or workpiece rotates.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com