Smart factories leverage advanced IoT technologies and automation to enhance manufacturing efficiency, enabling real-time data-driven decision making and predictive maintenance. Six Sigma focuses on minimizing defects and variability through rigorous statistical analysis and process improvement methodologies, aiming for near-perfect quality levels. Discover how integrating smart factory technologies with Six Sigma principles can revolutionize manufacturing performance.
Why it is important
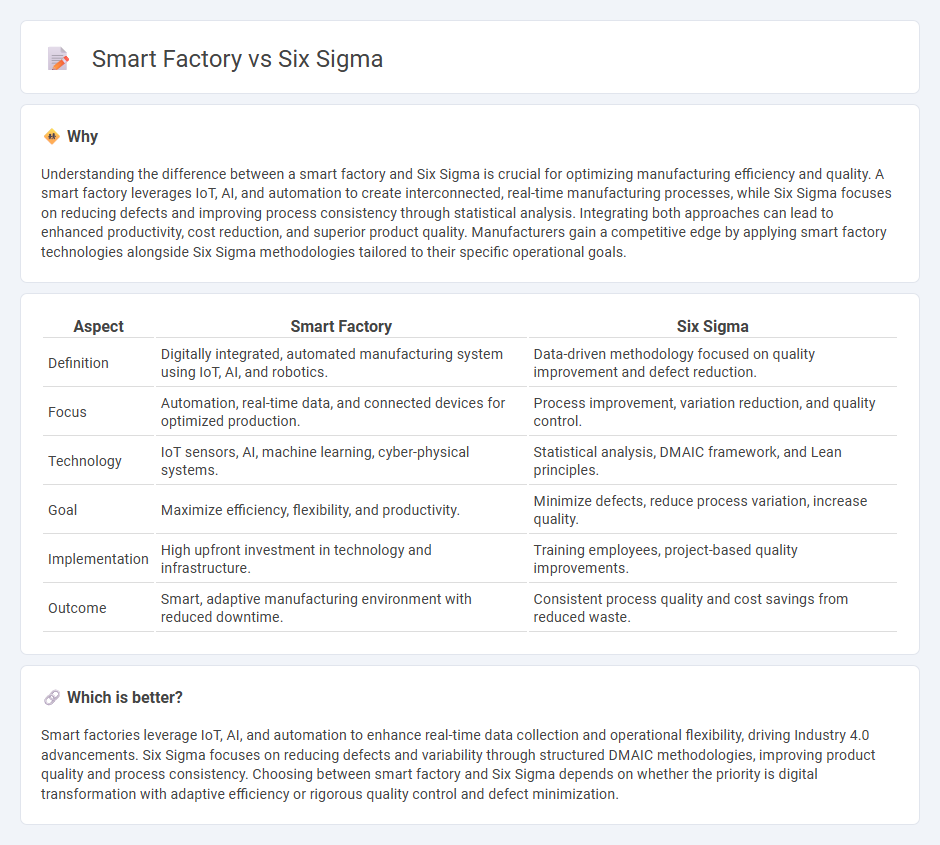
Understanding the difference between a smart factory and Six Sigma is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and quality. A smart factory leverages IoT, AI, and automation to create interconnected, real-time manufacturing processes, while Six Sigma focuses on reducing defects and improving process consistency through statistical analysis. Integrating both approaches can lead to enhanced productivity, cost reduction, and superior product quality. Manufacturers gain a competitive edge by applying smart factory technologies alongside Six Sigma methodologies tailored to their specific operational goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Smart Factory | Six Sigma |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digitally integrated, automated manufacturing system using IoT, AI, and robotics. | Data-driven methodology focused on quality improvement and defect reduction. |
| Focus | Automation, real-time data, and connected devices for optimized production. | Process improvement, variation reduction, and quality control. |
| Technology | IoT sensors, AI, machine learning, cyber-physical systems. | Statistical analysis, DMAIC framework, and Lean principles. |
| Goal | Maximize efficiency, flexibility, and productivity. | Minimize defects, reduce process variation, increase quality. |
| Implementation | High upfront investment in technology and infrastructure. | Training employees, project-based quality improvements. |
| Outcome | Smart, adaptive manufacturing environment with reduced downtime. | Consistent process quality and cost savings from reduced waste. |
Which is better?
Smart factories leverage IoT, AI, and automation to enhance real-time data collection and operational flexibility, driving Industry 4.0 advancements. Six Sigma focuses on reducing defects and variability through structured DMAIC methodologies, improving product quality and process consistency. Choosing between smart factory and Six Sigma depends on whether the priority is digital transformation with adaptive efficiency or rigorous quality control and defect minimization.
Connection
Smart factories integrate advanced IoT sensors and real-time data analytics to optimize manufacturing processes, while Six Sigma methodologies focus on reducing defects and variability through statistical analysis. By applying Six Sigma principles within a smart factory environment, manufacturers can leverage precise data to identify inefficiencies and enhance process control. This synergy drives higher quality production, minimizes waste, and boosts operational efficiency in modern manufacturing.
Key Terms
Process Optimization
Six Sigma emphasizes data-driven process optimization to reduce defects and improve quality by applying DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) methodology. Smart factories integrate IoT, AI, and automation to create real-time adaptive manufacturing environments that enhance productivity and operational efficiency. Explore how combining Six Sigma principles with smart factory technologies can revolutionize process optimization in modern industries.
Data Analytics
Six Sigma leverages statistical data analytics to reduce process variation and enhance quality control, emphasizing precise measurement and data-driven decision making. Smart factories integrate advanced data analytics with IoT, AI, and automation technologies to optimize manufacturing efficiency, predictive maintenance, and real-time process adjustments. Explore how combining Six Sigma methodologies with smart factory data analytics can transform industrial operations.
Automation
Six Sigma emphasizes process improvement and defect reduction through data-driven methodologies, whereas smart factories leverage automation, IoT, and AI to create adaptive, self-optimizing production environments. Automation in smart factories enhances real-time decision-making, predictive maintenance, and operational efficiency beyond traditional Six Sigma approaches. Explore how integrating Six Sigma principles with smart factory automation can drive unparalleled manufacturing excellence.
Source and External Links
What is Lean Six Sigma? - Six Sigma is a disciplined quality improvement method that provides tools to reduce process variation, aiming for near-perfect performance--just 3.4 defects per million opportunities--to improve customer satisfaction, product quality, and profitability.
Six Sigma - Introduced by Motorola engineer Bill Smith in 1986, Six Sigma is a set of data-driven techniques and tools for process improvement, emphasizing measurable financial returns, management leadership, and decision-making based on verifiable data to reduce defects and variation in business and manufacturing processes.
What Is Six Sigma? - Six Sigma is a structured, organization-wide methodology requiring leadership commitment, defined roles (such as belts indicating expertise levels), and team-based projects to systematically eliminate defects and drive continuous improvement through data analysis and process control.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com