Dark factories leverage fully automated systems operating without human presence to maximize efficiency and reduce labor costs, while Industry 4.0 integrates cyber-physical systems, IoT, and real-time data analytics to create smart, interconnected manufacturing environments. Emphasizing digital twins, predictive maintenance, and autonomous robotics, Industry 4.0 transforms traditional production lines into adaptive, intelligent systems. Discover the critical differences and advancements shaping the future of manufacturing by exploring how dark factories and Industry 4.0 redefine industrial processes.
Why it is important
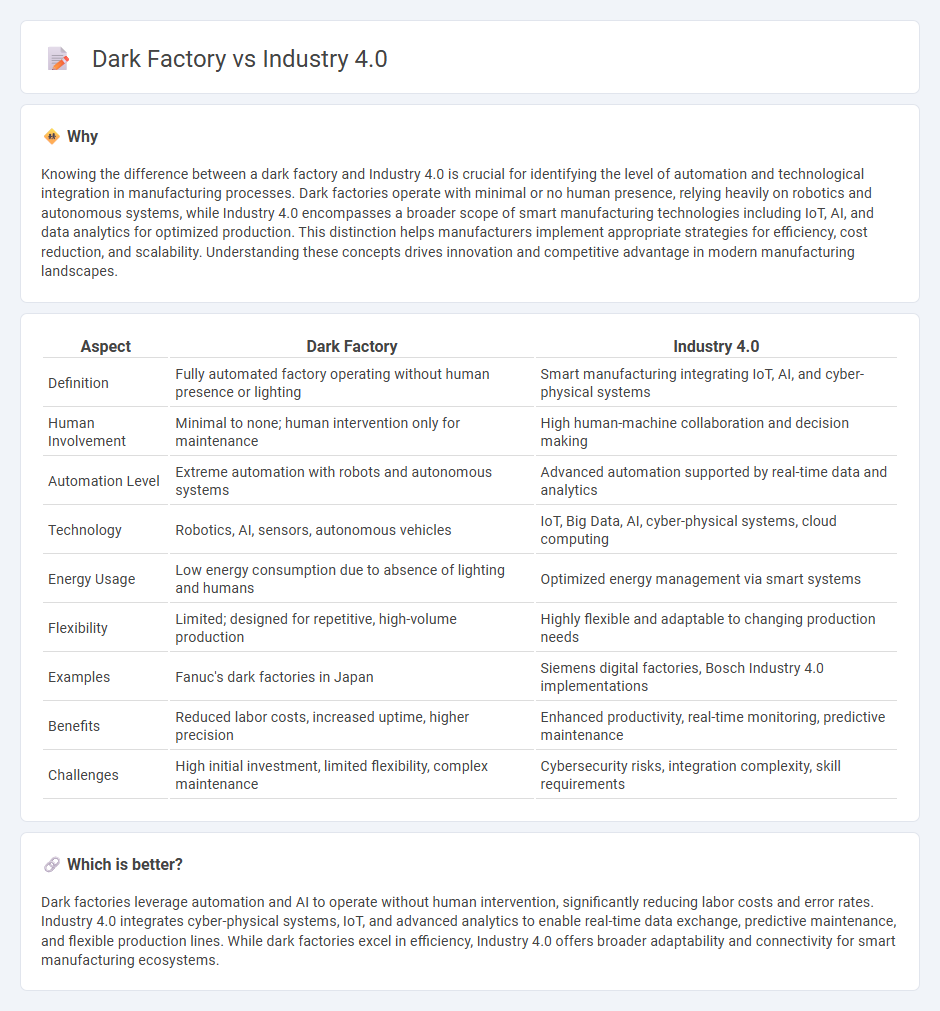
Knowing the difference between a dark factory and Industry 4.0 is crucial for identifying the level of automation and technological integration in manufacturing processes. Dark factories operate with minimal or no human presence, relying heavily on robotics and autonomous systems, while Industry 4.0 encompasses a broader scope of smart manufacturing technologies including IoT, AI, and data analytics for optimized production. This distinction helps manufacturers implement appropriate strategies for efficiency, cost reduction, and scalability. Understanding these concepts drives innovation and competitive advantage in modern manufacturing landscapes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Factory | Industry 4.0 |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated factory operating without human presence or lighting | Smart manufacturing integrating IoT, AI, and cyber-physical systems |
| Human Involvement | Minimal to none; human intervention only for maintenance | High human-machine collaboration and decision making |
| Automation Level | Extreme automation with robots and autonomous systems | Advanced automation supported by real-time data and analytics |
| Technology | Robotics, AI, sensors, autonomous vehicles | IoT, Big Data, AI, cyber-physical systems, cloud computing |
| Energy Usage | Low energy consumption due to absence of lighting and humans | Optimized energy management via smart systems |
| Flexibility | Limited; designed for repetitive, high-volume production | Highly flexible and adaptable to changing production needs |
| Examples | Fanuc's dark factories in Japan | Siemens digital factories, Bosch Industry 4.0 implementations |
| Benefits | Reduced labor costs, increased uptime, higher precision | Enhanced productivity, real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance |
| Challenges | High initial investment, limited flexibility, complex maintenance | Cybersecurity risks, integration complexity, skill requirements |
Which is better?
Dark factories leverage automation and AI to operate without human intervention, significantly reducing labor costs and error rates. Industry 4.0 integrates cyber-physical systems, IoT, and advanced analytics to enable real-time data exchange, predictive maintenance, and flexible production lines. While dark factories excel in efficiency, Industry 4.0 offers broader adaptability and connectivity for smart manufacturing ecosystems.
Connection
Dark factories leverage Industry 4.0 technologies such as IoT sensors, AI-driven automation, and advanced robotics to operate autonomously without human presence, enhancing efficiency and reducing operational costs. Industry 4.0's integration of cyber-physical systems and real-time data analytics enables predictive maintenance and optimized production workflows in fully automated manufacturing environments. These smart factory advancements transform traditional manufacturing into highly responsive, self-monitoring dark factories that maximize productivity and minimize downtime.
Key Terms
Automation
Industry 4.0 integrates advanced automation technologies such as IoT, AI, and robotics to create smart, interconnected manufacturing systems. Dark factories take this a step further by operating fully automated production lines without human presence, enhancing efficiency and reducing operational costs. Explore the key differences and benefits of automation in both concepts to optimize your manufacturing processes.
Cyber-physical systems
Industry 4.0 integrates cyber-physical systems (CPS) to enhance automation, data exchange, and real-time monitoring in smart factories. Dark factories operate primarily with CPS, enabling fully automated production lines without human intervention, optimizing efficiency and reducing operational costs. Explore how cyber-physical systems are transforming manufacturing through Industry 4.0 and dark factory implementations.
Lights-out manufacturing
Industry 4.0 revolutionizes manufacturing through smart factories integrating IoT, AI, and automation to enhance productivity and flexibility. Dark factories, a subset of this evolution, operate entirely without human presence by utilizing advanced robotics and AI systems for lights-out manufacturing. Explore the transformative benefits and challenges of lights-out manufacturing to understand its impact on the future of production.
Source and External Links
Industry 4.0 vs 5.0: What's the Difference? - Rutgers University - Industry 4.0, also called the Fourth Industrial Revolution, features cyber-physical systems and digital industrial technology to create smart, integrated factories using data-driven insights for versatile manufacturing solutions.
What is Industry 4.0? - IBM - Industry 4.0 or smart manufacturing leverages IoT, AI, cloud computing, and advanced sensors to enable real-time decision making, enhanced productivity, predictive maintenance, and highly automated, efficient factory processes.
What is Industry 4.0--the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)? - Epicor - Industry 4.0 integrates connectivity, automation, machine learning, and real-time data across manufacturing and supply chains to revolutionize operations and growth through smart digital ecosystems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com