Edge computing processes data closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth use in manufacturing environments, while Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) extends these capabilities by integrating with cellular networks to enhance connectivity and real-time analytics. MEC supports advanced applications like predictive maintenance and automated quality control by leveraging 5G infrastructure for faster data aggregation and processing at the edge. Explore how leveraging Edge computing and MEC can transform manufacturing operations with improved efficiency and responsiveness.
Why it is important
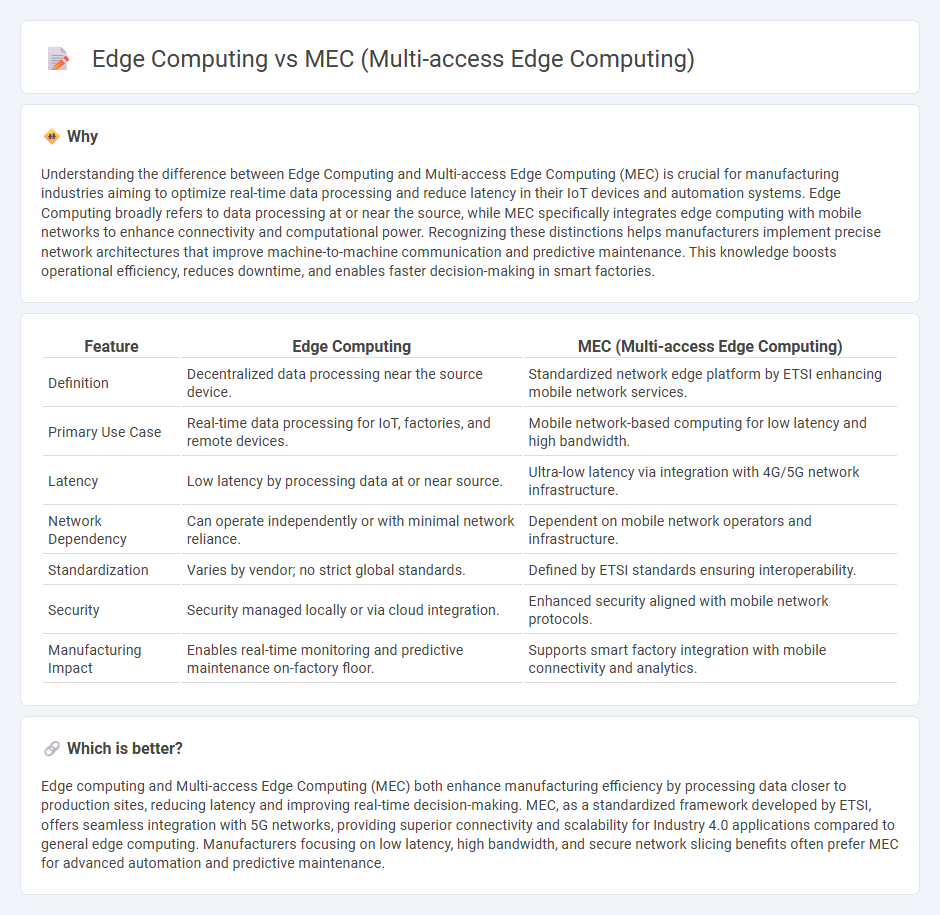
Understanding the difference between Edge Computing and Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) is crucial for manufacturing industries aiming to optimize real-time data processing and reduce latency in their IoT devices and automation systems. Edge Computing broadly refers to data processing at or near the source, while MEC specifically integrates edge computing with mobile networks to enhance connectivity and computational power. Recognizing these distinctions helps manufacturers implement precise network architectures that improve machine-to-machine communication and predictive maintenance. This knowledge boosts operational efficiency, reduces downtime, and enables faster decision-making in smart factories.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Edge Computing | MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decentralized data processing near the source device. | Standardized network edge platform by ETSI enhancing mobile network services. |
| Primary Use Case | Real-time data processing for IoT, factories, and remote devices. | Mobile network-based computing for low latency and high bandwidth. |
| Latency | Low latency by processing data at or near source. | Ultra-low latency via integration with 4G/5G network infrastructure. |
| Network Dependency | Can operate independently or with minimal network reliance. | Dependent on mobile network operators and infrastructure. |
| Standardization | Varies by vendor; no strict global standards. | Defined by ETSI standards ensuring interoperability. |
| Security | Security managed locally or via cloud integration. | Enhanced security aligned with mobile network protocols. |
| Manufacturing Impact | Enables real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance on-factory floor. | Supports smart factory integration with mobile connectivity and analytics. |
Which is better?
Edge computing and Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) both enhance manufacturing efficiency by processing data closer to production sites, reducing latency and improving real-time decision-making. MEC, as a standardized framework developed by ETSI, offers seamless integration with 5G networks, providing superior connectivity and scalability for Industry 4.0 applications compared to general edge computing. Manufacturers focusing on low latency, high bandwidth, and secure network slicing benefits often prefer MEC for advanced automation and predictive maintenance.
Connection
Edge computing and Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) are interconnected technologies enhancing manufacturing by processing data closer to industrial devices, reducing latency and improving real-time decision-making. MEC extends edge computing capabilities by integrating mobile network access, enabling seamless connectivity and faster data analytics for smart factories and automation systems. This synergy supports predictive maintenance, quality control, and efficient supply chain management in manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Latency
MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing) enhances edge computing by integrating mobile network capabilities, significantly reducing latency through localized data processing near end users. Edge computing broadly refers to processing data at or near the data source, improving response times compared to centralized cloud computing but without specific ties to mobile access networks. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how MEC's architecture optimizes latency for real-time applications.
Data Processing Location
MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing) specializes in processing data at the edge of mobile networks, typically within cellular base stations, to deliver ultra-low latency and support real-time applications such as autonomous vehicles and augmented reality. Edge computing encompasses a broader paradigm where data processing occurs near data sources like IoT devices or local edge servers, reducing the need to transmit large data volumes to centralized cloud data centers. Explore further to understand how location-specific data processing impacts network performance and application responsiveness in these edge technologies.
Network Integration
MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing) extends edge computing by specifically integrating with mobile network infrastructure such as 4G/5G, enabling ultra-low latency and context-aware services at the network edge. Edge computing broadly encompasses decentralized data processing closer to users without mandatory telecom network integration, making MEC ideal for operators seeking seamless network collaboration. Explore how MEC's network-centric architecture revolutionizes application performance and service delivery at the edge.
Source and External Links
What is multi-access edge computing? | HPE Juniper Networking US - MEC moves computing and data processing from centralized clouds to the network edge closer to customers, enabling ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and real-time performance by processing data at distributed edge data centers or sites such as cell towers or customer premises.
Multi-access edge computing - Wikipedia - MEC, defined by ETSI, is a network architecture that provides cloud computing capabilities and IT environment at the edge of the cellular or any network, reducing congestion and improving application performance by running processing tasks closer to users, typically at RAN elements or base stations.
What is multi-access edge computing (MEC)? - Red Hat - Multi-access edge computing architecture places cloud and IT services at the network edge to minimize latency, improve service delivery, and enhance user experience, representing an evolution of cloud computing integrated with mobility and edge services.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com