Cloud manufacturing leverages centralized cloud computing resources to streamline production processes and optimize resource allocation across multiple facilities. Distributed manufacturing decentralizes production by utilizing a network of interconnected, often localized, manufacturing units to enhance flexibility and reduce lead times. Explore the advantages and applications of both models to determine the ideal manufacturing strategy.
Why it is important
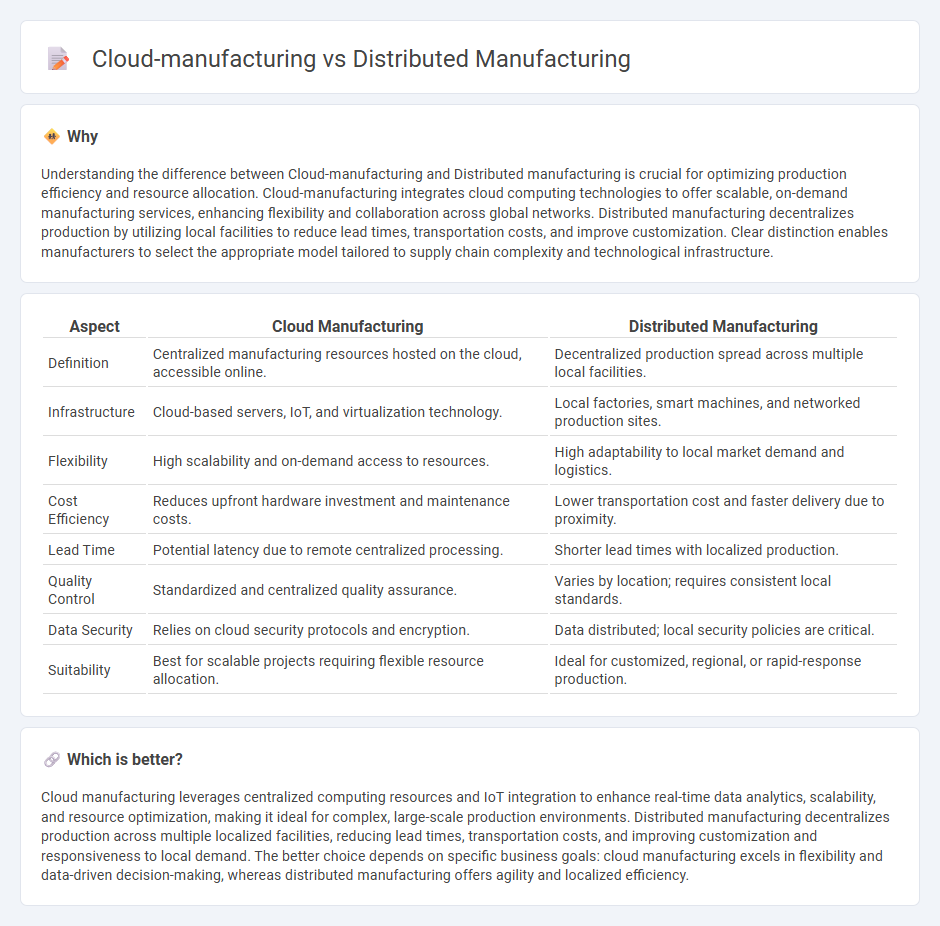
Understanding the difference between Cloud-manufacturing and Distributed manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and resource allocation. Cloud-manufacturing integrates cloud computing technologies to offer scalable, on-demand manufacturing services, enhancing flexibility and collaboration across global networks. Distributed manufacturing decentralizes production by utilizing local facilities to reduce lead times, transportation costs, and improve customization. Clear distinction enables manufacturers to select the appropriate model tailored to supply chain complexity and technological infrastructure.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cloud Manufacturing | Distributed Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Centralized manufacturing resources hosted on the cloud, accessible online. | Decentralized production spread across multiple local facilities. |
| Infrastructure | Cloud-based servers, IoT, and virtualization technology. | Local factories, smart machines, and networked production sites. |
| Flexibility | High scalability and on-demand access to resources. | High adaptability to local market demand and logistics. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces upfront hardware investment and maintenance costs. | Lower transportation cost and faster delivery due to proximity. |
| Lead Time | Potential latency due to remote centralized processing. | Shorter lead times with localized production. |
| Quality Control | Standardized and centralized quality assurance. | Varies by location; requires consistent local standards. |
| Data Security | Relies on cloud security protocols and encryption. | Data distributed; local security policies are critical. |
| Suitability | Best for scalable projects requiring flexible resource allocation. | Ideal for customized, regional, or rapid-response production. |
Which is better?
Cloud manufacturing leverages centralized computing resources and IoT integration to enhance real-time data analytics, scalability, and resource optimization, making it ideal for complex, large-scale production environments. Distributed manufacturing decentralizes production across multiple localized facilities, reducing lead times, transportation costs, and improving customization and responsiveness to local demand. The better choice depends on specific business goals: cloud manufacturing excels in flexibility and data-driven decision-making, whereas distributed manufacturing offers agility and localized efficiency.
Connection
Cloud manufacturing leverages internet-based platforms to enable real-time data sharing and resource allocation across multiple production sites, seamlessly integrating with distributed manufacturing systems that spatially disperse production processes to improve flexibility and reduce lead times. This connection enhances operational efficiency by facilitating decentralized decision-making, optimizing supply chain management, and enabling rapid customization through synchronized digital workflows. The synergy between cloud manufacturing and distributed manufacturing drives innovation in smart factories, supporting scalable, resilient, and cost-effective manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Decentralization
Distributed manufacturing decentralizes production by leveraging localized factories and 3D printing technologies, reducing dependency on a single central facility and enabling faster response to regional demand. Cloud manufacturing integrates networked resources, software, and services into a unified platform, allowing real-time coordination and flexible allocation of manufacturing tasks across multiple geographic locations. Explore how these decentralized models transform production efficiency and supply chain resilience.
Resource virtualization
Distributed manufacturing leverages geographically dispersed production facilities, enabling local resource utilization and reducing transportation costs. Cloud manufacturing, on the other hand, emphasizes resource virtualization by integrating and managing manufacturing resources as shared services through cloud computing platforms, enhancing scalability and flexibility. Explore the transformative impact of resource virtualization on manufacturing efficiency and agility by diving deeper into these paradigms.
Networked collaboration
Distributed manufacturing leverages localized production facilities interconnected through digital networks, enabling rapid response to market demands and reduced transportation costs. Cloud manufacturing centralizes resources and services on virtual platforms, facilitating real-time collaboration and resource sharing among geographically dispersed partners. Explore more about how networked collaboration transforms manufacturing efficiency and innovation.
Source and External Links
Distributed manufacturing benefits: Revolutionizing production - Distributed manufacturing uses a network of geographically dispersed, digitally connected facilities to produce goods closer to consumers, enabling faster delivery, lower transportation costs, and greater customization to local needs.
Distributed Manufacturing: The Way of the Future? - Distributed manufacturing spreads production across many local sites, using technologies like 3D printing and modular design to make products on-demand near where they will be used, reducing waste and long-distance shipping.
What Is Distributed Manufacturing? - MRPeasy Blog - In distributed manufacturing, goods are made in multiple small facilities over a wide area rather than one central plant, allowing for local customization, shorter lead times, and a more resilient, flexible supply chain.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com