Mass customization combines the efficiency of serial production with personalized product designs tailored to individual customer preferences, leveraging flexible manufacturing systems and advanced digital technologies. Serial production focuses on high-volume, standardized output through assembly line methods, optimizing cost-effectiveness and consistency for mass markets. Explore how integrating mass customization can transform traditional manufacturing strategies and enhance competitive advantage.
Why it is important
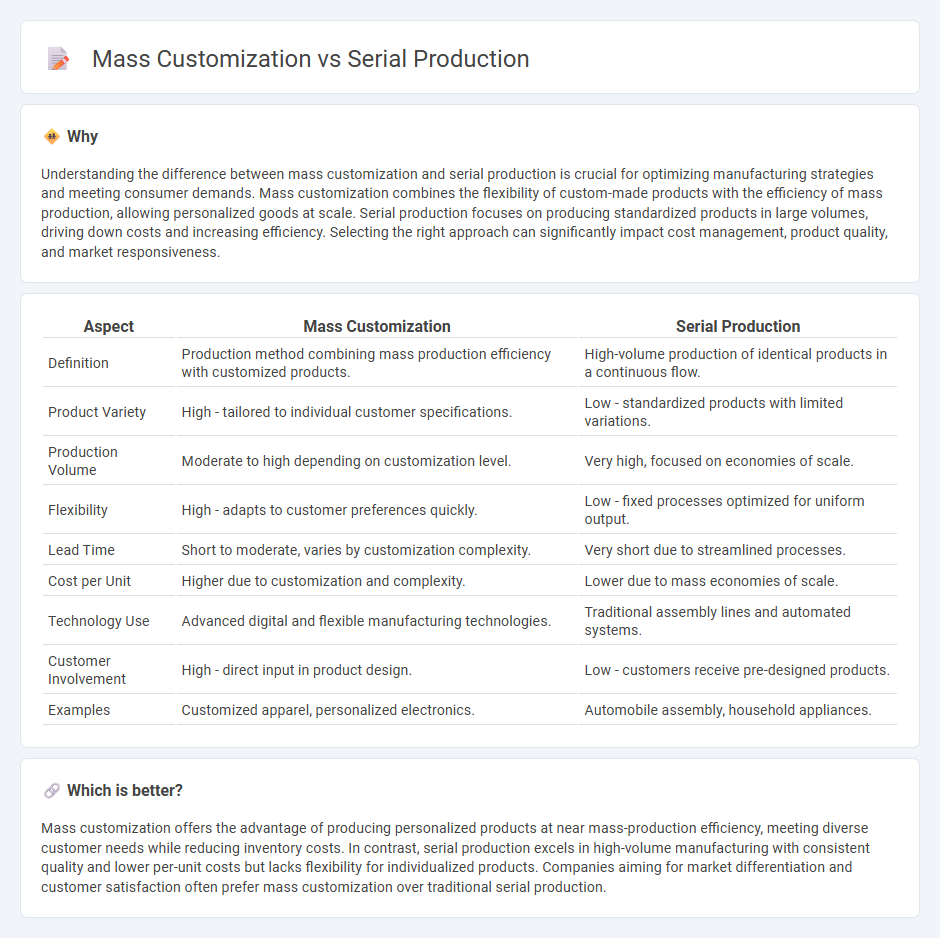
Understanding the difference between mass customization and serial production is crucial for optimizing manufacturing strategies and meeting consumer demands. Mass customization combines the flexibility of custom-made products with the efficiency of mass production, allowing personalized goods at scale. Serial production focuses on producing standardized products in large volumes, driving down costs and increasing efficiency. Selecting the right approach can significantly impact cost management, product quality, and market responsiveness.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Mass Customization | Serial Production |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Production method combining mass production efficiency with customized products. | High-volume production of identical products in a continuous flow. |
| Product Variety | High - tailored to individual customer specifications. | Low - standardized products with limited variations. |
| Production Volume | Moderate to high depending on customization level. | Very high, focused on economies of scale. |
| Flexibility | High - adapts to customer preferences quickly. | Low - fixed processes optimized for uniform output. |
| Lead Time | Short to moderate, varies by customization complexity. | Very short due to streamlined processes. |
| Cost per Unit | Higher due to customization and complexity. | Lower due to mass economies of scale. |
| Technology Use | Advanced digital and flexible manufacturing technologies. | Traditional assembly lines and automated systems. |
| Customer Involvement | High - direct input in product design. | Low - customers receive pre-designed products. |
| Examples | Customized apparel, personalized electronics. | Automobile assembly, household appliances. |
Which is better?
Mass customization offers the advantage of producing personalized products at near mass-production efficiency, meeting diverse customer needs while reducing inventory costs. In contrast, serial production excels in high-volume manufacturing with consistent quality and lower per-unit costs but lacks flexibility for individualized products. Companies aiming for market differentiation and customer satisfaction often prefer mass customization over traditional serial production.
Connection
Mass customization combines the efficiency of serial production with the flexibility to tailor products to individual customer needs, leveraging automation and modular design principles. Serial production provides the high-volume, standardized processes necessary to maintain cost-effectiveness while enabling variations through customizable components. This integration enhances supply chain responsiveness and drives innovation in manufacturing by balancing personalization with scalable output.
Key Terms
Standardization
Serial production emphasizes standardization by producing large quantities of identical products, ensuring consistent quality and cost efficiency through uniform processes. Mass customization balances standardization with personalization by using flexible manufacturing systems to tailor products while maintaining standardized core components. Discover how these approaches optimize production strategies and meet diverse market demands.
Flexibility
Serial production emphasizes standardized processes with limited flexibility, producing large volumes of identical products efficiently. Mass customization integrates flexible manufacturing systems, leveraging advanced technologies like computer-aided design and robotics to tailor products to individual customer specifications while maintaining cost-effectiveness. Explore how balancing flexibility in production can optimize both efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Lead Time
Serial production typically involves longer lead times due to standardized processes and batch manufacturing, which are designed to maximize efficiency and reduce costs through volume. Mass customization shortens lead time by integrating flexible production systems and advanced technologies that allow for rapid customization according to individual customer specifications. Explore more to understand how lead time optimization varies between serial production and mass customization methods.
Source and External Links
Serial Production - iSAX - Serial production is a manufacturing process producing several similar products simultaneously or in immediate succession, serving as an intermediate stage between one-off production and mass production, suitable for limited quantities and smaller demand.
Serial production of plastic parts - Knauf Industries Automotive - Serial production involves producing batches of identical goods that move through production stations, distinguished from mass production by the presence of downtime between batches.
Mass production - Wikipedia - Mass production, also called series production, is the continuous production of large quantities of standardized products, often on assembly lines, and is one of the main manufacturing methods alongside batch and job production.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com