Robotic process automation (RPA) enhances manufacturing efficiency by automating repetitive tasks through software robots, minimizing human error and reducing operational costs. Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste, optimizing workflows, and improving productivity through continuous improvement and value stream mapping. Explore the differences and applications of RPA and Lean manufacturing to optimize your production processes and boost operational excellence.
Why it is important
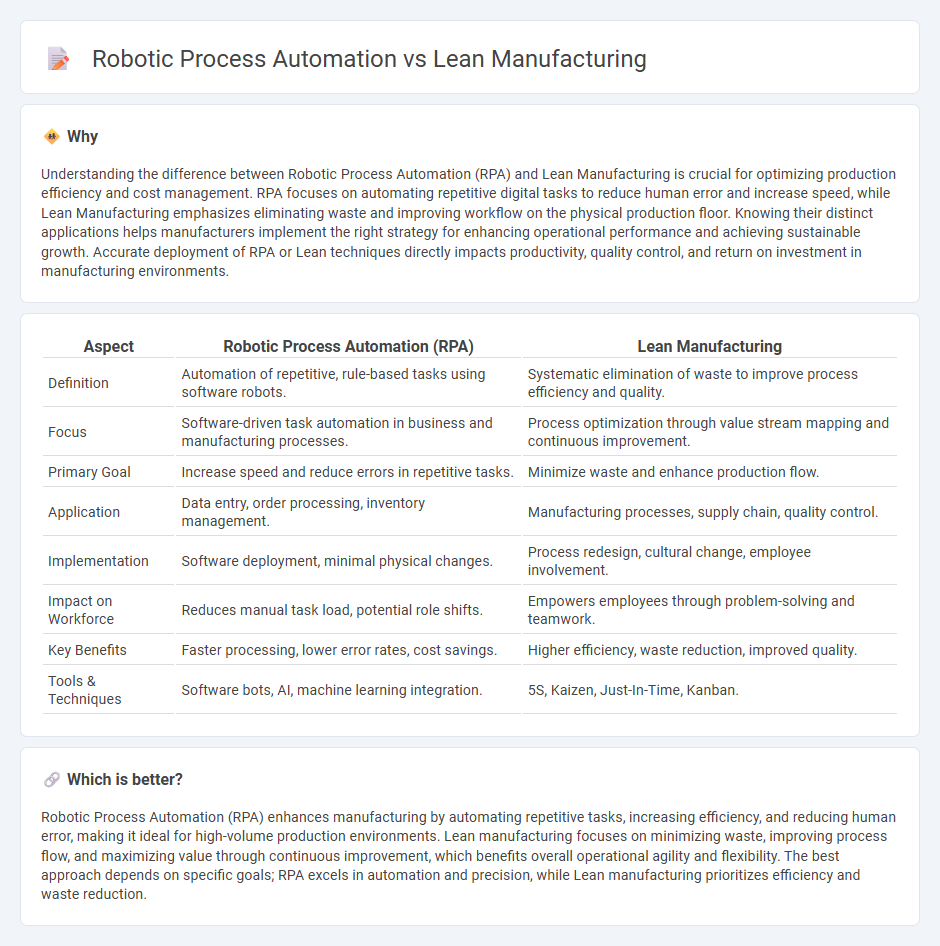
Understanding the difference between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Lean Manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and cost management. RPA focuses on automating repetitive digital tasks to reduce human error and increase speed, while Lean Manufacturing emphasizes eliminating waste and improving workflow on the physical production floor. Knowing their distinct applications helps manufacturers implement the right strategy for enhancing operational performance and achieving sustainable growth. Accurate deployment of RPA or Lean techniques directly impacts productivity, quality control, and return on investment in manufacturing environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automation of repetitive, rule-based tasks using software robots. | Systematic elimination of waste to improve process efficiency and quality. |
| Focus | Software-driven task automation in business and manufacturing processes. | Process optimization through value stream mapping and continuous improvement. |
| Primary Goal | Increase speed and reduce errors in repetitive tasks. | Minimize waste and enhance production flow. |
| Application | Data entry, order processing, inventory management. | Manufacturing processes, supply chain, quality control. |
| Implementation | Software deployment, minimal physical changes. | Process redesign, cultural change, employee involvement. |
| Impact on Workforce | Reduces manual task load, potential role shifts. | Empowers employees through problem-solving and teamwork. |
| Key Benefits | Faster processing, lower error rates, cost savings. | Higher efficiency, waste reduction, improved quality. |
| Tools & Techniques | Software bots, AI, machine learning integration. | 5S, Kaizen, Just-In-Time, Kanban. |
Which is better?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances manufacturing by automating repetitive tasks, increasing efficiency, and reducing human error, making it ideal for high-volume production environments. Lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste, improving process flow, and maximizing value through continuous improvement, which benefits overall operational agility and flexibility. The best approach depends on specific goals; RPA excels in automation and precision, while Lean manufacturing prioritizes efficiency and waste reduction.
Connection
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances Lean manufacturing by streamlining repetitive tasks, reducing human error, and increasing overall process efficiency. Lean principles focus on waste elimination and continuous improvement, which aligns with RPA's ability to automate manual workflows, thereby accelerating production cycles. Integrating RPA within Lean manufacturing frameworks leads to optimized resource utilization and improved quality control in manufacturing operations.
Key Terms
Waste Reduction
Lean manufacturing targets waste reduction by eliminating non-value-added activities through continuous improvement and streamlined processes, focusing on time, materials, and energy efficiency. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) reduces waste by automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, minimizing human errors and accelerating workflow in digital environments. Explore detailed strategies and benefits of combining Lean manufacturing and RPA for enhanced waste reduction outcomes.
Process Automation
Lean manufacturing emphasizes eliminating waste and optimizing workflows to improve efficiency in physical production processes, reducing lead times and costs. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) targets automating repetitive, rule-based tasks in digital workflows, enhancing accuracy and speed in administrative and back-office functions. Explore how combining lean principles with RPA can transform process automation across industries.
Continuous Improvement
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction and efficiency through methods like Kaizen and Just-In-Time production to drive continuous improvement in physical workflows. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances business processes by automating repetitive tasks, enabling faster cycle times and error reduction in digital operations. Explore detailed insights to understand how integrating Lean principles with RPA can maximize continuous improvement in diverse industries.
Source and External Links
Lean manufacturing - Wikipedia - Lean manufacturing is a method focused on reducing production and supplier response times by eliminating waste in seven areas such as overproduction, excess inventory, and defects; it is closely related to just-in-time manufacturing and originated from Toyota's production system.
What is Lean Manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - Lean manufacturing aims to minimize waste that does not add customer value while maximizing productivity, with principles like continuous improvement (Kaizen), and has been adopted by companies across various industries beyond automotive.
What is Lean Manufacturing and the 5 Principles Used? - TWI - Lean manufacturing is based on five core principles: value, value stream, flow, pull, and perfection, focusing on maximizing productivity by streamlining processes and removing waste across production and service sectors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com