Condition monitoring involves continuous tracking of equipment performance using sensors and data analytics to detect anomalies and prevent failures. Root cause analysis focuses on identifying the underlying reasons for equipment malfunctions after a problem has occurred to implement corrective actions. Explore these critical manufacturing strategies to enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between condition monitoring and root cause analysis is crucial in manufacturing to optimize equipment reliability and reduce downtime. Condition monitoring detects early signs of equipment degradation through real-time data, enabling proactive maintenance. Root cause analysis investigates failures to identify underlying issues, preventing recurrence and improving process efficiency. Integrating both enhances production continuity and minimizes costly breakdowns.
Comparison Table
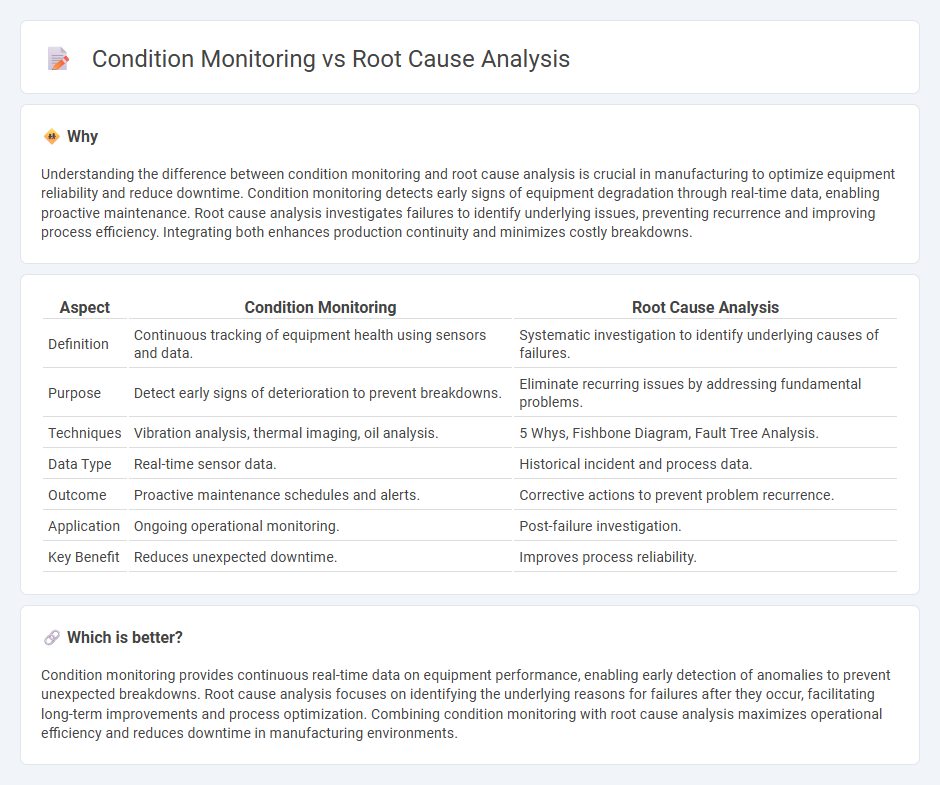
| Aspect | Condition Monitoring | Root Cause Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous tracking of equipment health using sensors and data. | Systematic investigation to identify underlying causes of failures. |
| Purpose | Detect early signs of deterioration to prevent breakdowns. | Eliminate recurring issues by addressing fundamental problems. |
| Techniques | Vibration analysis, thermal imaging, oil analysis. | 5 Whys, Fishbone Diagram, Fault Tree Analysis. |
| Data Type | Real-time sensor data. | Historical incident and process data. |
| Outcome | Proactive maintenance schedules and alerts. | Corrective actions to prevent problem recurrence. |
| Application | Ongoing operational monitoring. | Post-failure investigation. |
| Key Benefit | Reduces unexpected downtime. | Improves process reliability. |
Which is better?
Condition monitoring provides continuous real-time data on equipment performance, enabling early detection of anomalies to prevent unexpected breakdowns. Root cause analysis focuses on identifying the underlying reasons for failures after they occur, facilitating long-term improvements and process optimization. Combining condition monitoring with root cause analysis maximizes operational efficiency and reduces downtime in manufacturing environments.
Connection
Condition monitoring provides real-time data on equipment performance and operational health, enabling early detection of anomalies. Root cause analysis utilizes this information to systematically identify underlying issues responsible for faults or failures. Integrating both techniques enhances predictive maintenance strategies, reduces downtime, and improves overall manufacturing efficiency.
Key Terms
Fault Diagnosis
Root cause analysis identifies the underlying reasons for equipment failure by systematically investigating faults, while condition monitoring continuously tracks machine health through real-time data collection, sensors, and performance metrics. Fault diagnosis leverages insights from both methods to detect and address issues early, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Learn more about integrating root cause analysis and condition monitoring for effective fault diagnosis.
Failure Modes
Root cause analysis identifies underlying causes of equipment failures by examining failure modes, aiming to prevent recurrence through corrective actions. Condition monitoring continuously tracks equipment health indicators such as vibration, temperature, and lubrication to detect early signs of failure modes in real-time. Explore more to understand how integrating both approaches enhances failure mode detection and maintenance strategies.
Predictive Maintenance
Root cause analysis identifies the underlying causes of equipment failures by examining historical data and failure patterns, while condition monitoring continuously tracks real-time sensor data such as vibration, temperature, and pressure to predict imminent faults. Predictive maintenance leverages condition monitoring to anticipate issues before breakdowns occur, reducing downtime and optimizing asset performance. Explore how integrating root cause analysis with advanced condition monitoring enhances predictive maintenance strategies for improved operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
Root Cause Analysis Explained: Definition, Examples, and Methods - Root cause analysis (RCA) is a systematic process to identify the underlying causes of problems to devise effective solutions rather than merely addressing symptoms, emphasizing a methodical approach to find concrete cause-effect evidence and prevent issues in the future.
Root Cause Analysis: A Quick Guide - ProjectManager - RCA uses problem-solving techniques such as the "Five Whys," which involves repeatedly asking "why" to peel back layers of a problem until the root cause is uncovered, enabling teams to understand and address fundamental issues affecting projects and workflows.
What is Root Cause Analysis (RCA)? - ASQ - RCA encompasses various methodologies like causal factor analysis, change analysis, barrier analysis, and cause tree analysis to methodically gather evidence and identify the root causes of incidents for more informed corrective actions and risk prevention.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com