Biofabrication involves creating complex biological structures using living cells and biomaterials, primarily for medical and tissue engineering applications. Microfabrication focuses on the precision engineering of microscale components often used in electronics and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). Explore the advancements and unique applications of biofabrication and microfabrication to understand their impact on manufacturing innovation.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between biofabrication and microfabrication is crucial in manufacturing as biofabrication involves creating biological materials and tissues, while microfabrication focuses on producing microscale devices and structures from non-biological materials. Mastery of these distinctions enables optimized material selection, process design, and application targeting in fields like medical devices, tissue engineering, and electronics. Precise knowledge of biofabrication techniques supports advances in regenerative medicine, whereas microfabrication drives innovation in semiconductor and MEMS production. Recognizing their unique methodologies and end-use applications maximizes efficiency and product functionality in manufacturing workflows.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Biofabrication | Microfabrication |
|---|---|---|
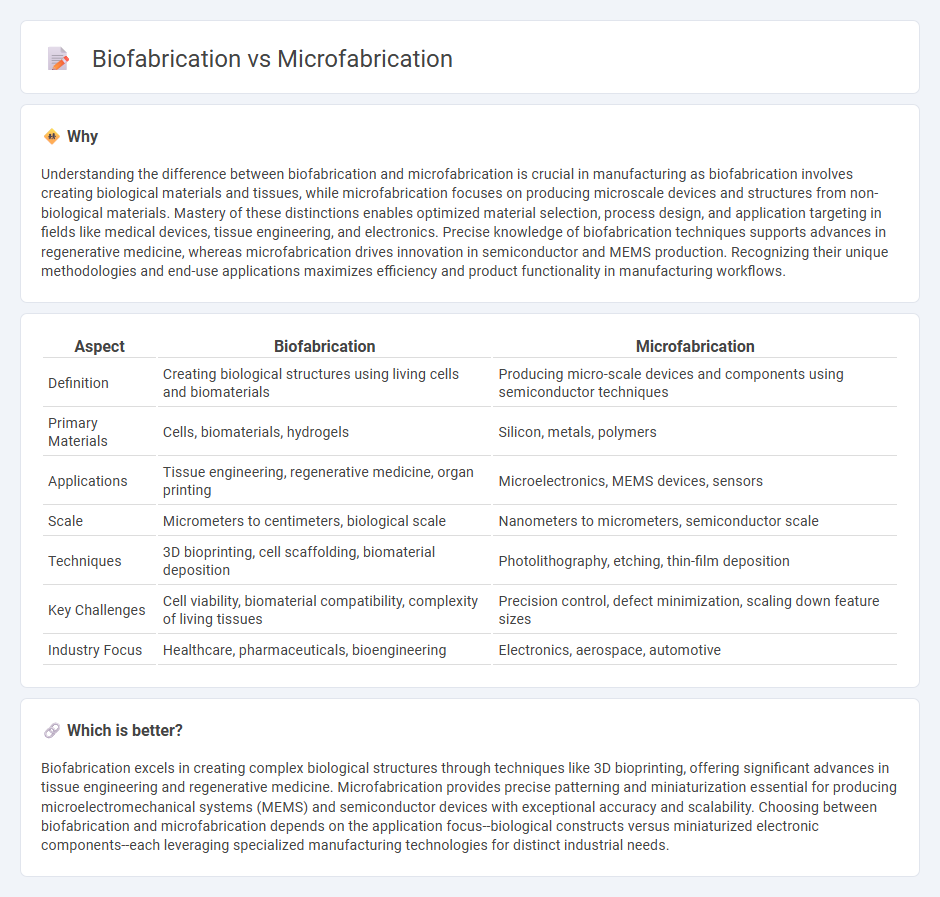
| Definition | Creating biological structures using living cells and biomaterials | Producing micro-scale devices and components using semiconductor techniques |
| Primary Materials | Cells, biomaterials, hydrogels | Silicon, metals, polymers |
| Applications | Tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, organ printing | Microelectronics, MEMS devices, sensors |
| Scale | Micrometers to centimeters, biological scale | Nanometers to micrometers, semiconductor scale |
| Techniques | 3D bioprinting, cell scaffolding, biomaterial deposition | Photolithography, etching, thin-film deposition |
| Key Challenges | Cell viability, biomaterial compatibility, complexity of living tissues | Precision control, defect minimization, scaling down feature sizes |
| Industry Focus | Healthcare, pharmaceuticals, bioengineering | Electronics, aerospace, automotive |
Which is better?
Biofabrication excels in creating complex biological structures through techniques like 3D bioprinting, offering significant advances in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Microfabrication provides precise patterning and miniaturization essential for producing microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and semiconductor devices with exceptional accuracy and scalability. Choosing between biofabrication and microfabrication depends on the application focus--biological constructs versus miniaturized electronic components--each leveraging specialized manufacturing technologies for distinct industrial needs.
Connection
Biofabrication integrates biological materials with microfabrication techniques to create complex, functional tissue structures at a microscale. Microfabrication provides precise control over the spatial arrangement and architecture of cells and biomaterials, enabling the production of highly detailed biological constructs. This synergy drives advancements in regenerative medicine, drug testing, and customized implants by replicating natural tissue environments with high fidelity.
Key Terms
Lithography
Lithography is a cornerstone technique in microfabrication, essential for creating intricate patterns on semiconductor wafers with nanometer precision, enabling the production of microchips and MEMS devices. In biofabrication, lithography adapts to layer bio-compatible materials and guide cellular organization for tissue engineering and biomodeling, often incorporating soft lithography methods. Explore the evolving applications of lithography in both micro- and biofabrication to understand its critical role in advancing technology and biomedicine.
Bioprinting
Microfabrication techniques enable the creation of precise microscale structures primarily using materials like silicon and polymers, essential for MEMS and microfluidic devices. Biofabrication, with a focus on bioprinting, involves the layer-by-layer deposition of living cells and biomaterials to engineer complex tissue constructs for regenerative medicine and drug testing. Explore the latest advancements in bioprinting technologies to understand their transformative potential in healthcare.
Cleanroom
Cleanrooms play a critical role in both microfabrication and biofabrication by providing controlled environments with low levels of contaminants essential for precise optical lithography, deposition, and etching in semiconductor device manufacturing. In biofabrication, cleanrooms ensure sterile conditions necessary for cell culture, tissue engineering, and the fabrication of biomaterials, preventing microbial contamination and preserving biological integrity. Discover how advanced cleanroom technologies enhance productivity and quality in both fields.
Source and External Links
Microfabrication - Microfabrication is the process of creating miniature structures at micrometer scales and smaller, widely used in integrated circuit fabrication, MEMS, microfluidics, solar cells, and sensors, employing key techniques such as microlithography, thin films, doping, etching, and bonding.
Microfabrication in biology and medicine - Microfabrication applies integrated-circuit manufacturing technologies to produce microscopic objects with applications in molecular biology, cell biology, medical devices, and biosensors, enabling enhanced or novel device capabilities.
Boston Micro Fabrication - Boston Micro Fabrication specializes in ultra-high resolution additive manufacturing using Projection Micro Stereolithography (PuSL), enabling precise 3D printing of microstructures with resolutions as fine as 2 microns and extremely tight tolerances.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com