Cobotics integrates human-robot collaboration to enhance manufacturing flexibility and safety, optimizing tasks that require precision and adaptability. Automation focuses on fully automated processes aimed at maximizing efficiency and throughput in repetitive, high-volume production environments. Explore the differences between cobotics and automation to determine the best fit for your manufacturing needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cobotics and automation is crucial in manufacturing because cobotics involves collaborative robots designed to work alongside human operators, enhancing flexibility and safety on the production floor. Automation typically refers to fully automated systems that operate independently, improving efficiency but requiring higher initial investment and complex integration. Knowing these distinctions enables manufacturers to choose the right technology for specific tasks, optimizing productivity and cost-efficiency. This knowledge drives better decision-making in implementing innovative manufacturing solutions tailored to workforce skills and production needs.
Comparison Table
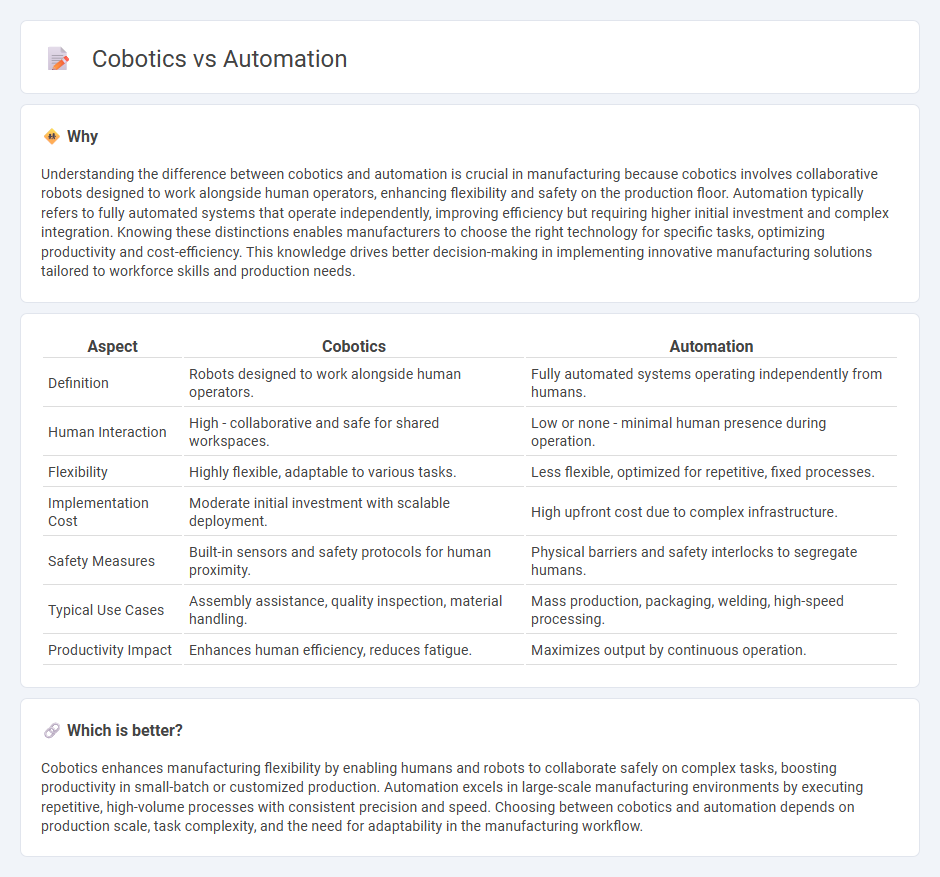
| Aspect | Cobotics | Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Robots designed to work alongside human operators. | Fully automated systems operating independently from humans. |
| Human Interaction | High - collaborative and safe for shared workspaces. | Low or none - minimal human presence during operation. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, adaptable to various tasks. | Less flexible, optimized for repetitive, fixed processes. |
| Implementation Cost | Moderate initial investment with scalable deployment. | High upfront cost due to complex infrastructure. |
| Safety Measures | Built-in sensors and safety protocols for human proximity. | Physical barriers and safety interlocks to segregate humans. |
| Typical Use Cases | Assembly assistance, quality inspection, material handling. | Mass production, packaging, welding, high-speed processing. |
| Productivity Impact | Enhances human efficiency, reduces fatigue. | Maximizes output by continuous operation. |
Which is better?
Cobotics enhances manufacturing flexibility by enabling humans and robots to collaborate safely on complex tasks, boosting productivity in small-batch or customized production. Automation excels in large-scale manufacturing environments by executing repetitive, high-volume processes with consistent precision and speed. Choosing between cobotics and automation depends on production scale, task complexity, and the need for adaptability in the manufacturing workflow.
Connection
Cobotics and automation are intrinsically connected through their shared goal of enhancing manufacturing efficiency by integrating human-robot collaboration and automated systems. Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside human operators to perform repetitive, precision-based tasks, reducing errors and increasing productivity within automated manufacturing environments. This synergy accelerates production cycles, minimizes operational costs, and supports flexible manufacturing processes in Industry 4.0.
Key Terms
Robotics
Robotics integrates automation by using programmable machines to perform repetitive tasks efficiently, while cobotics emphasizes human-robot collaboration, enhancing productivity and safety in shared work environments. Automation in robotics often involves standalone robots operating independently, whereas cobots are designed with sensors and adaptive controls to work alongside human operators seamlessly. Explore how the synergy between automation and cobotics transforms industrial processes and drives innovation in robotics.
Human-robot collaboration
Human-robot collaboration in automation leverages robots to perform repetitive tasks autonomously, enhancing efficiency and precision in industrial processes. Cobotics emphasizes interactive teamwork where collaborative robots, or cobots, work alongside humans, improving safety and flexibility in dynamic environments. Explore the advantages and applications of both technologies to understand their impact on modern manufacturing.
Smart sensors
Smart sensors play a crucial role in both automation and cobotics by enhancing machine accuracy and responsiveness through real-time data collection and analysis. In automation, these sensors enable the independent operation of machines, while in cobotics, they ensure safe and efficient human-robot collaboration by detecting human presence and adjusting robot behavior accordingly. Explore more to understand how smart sensor technology is shaping the future of industrial workflows.
Source and External Links
Automation - Wikipedia - Automation uses technology to reduce human intervention in processes by predetermining decision criteria and embodying those in machines, spanning applications from household devices to large industrial systems for benefits like labor savings, improved quality, and cost reduction.
What Is Automation? - IBM - Automation is the application of technology, programs, or robotics to achieve outcomes with minimal human input, and it is widely used across industries to increase productivity, reduce errors, and optimize business operations.
Understanding automation - Red Hat - Automation is the use of technology to perform tasks with reduced human assistance, particularly in industries with repetitive tasks such as manufacturing, IT, and business processes, and it includes forms like robotic process automation and artificial intelligence.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com