Circular manufacturing minimizes waste by reusing materials through continuous production cycles, enhancing resource efficiency and sustainability compared to linear manufacturing, which follows a take-make-dispose model leading to higher environmental impact. This sustainable approach reduces raw material consumption and promotes product lifecycle extension through recycling and refurbishing. Explore how circular manufacturing innovations are transforming industry practices for a greener future.
Why it is important
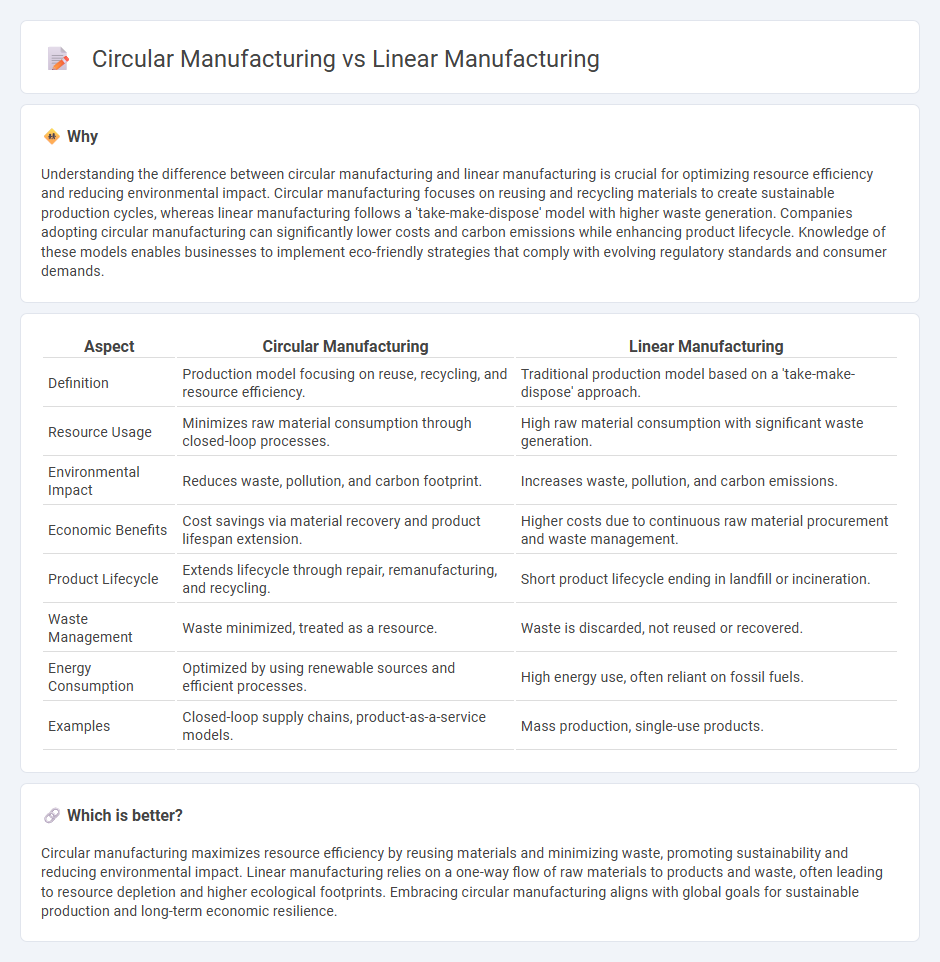
Understanding the difference between circular manufacturing and linear manufacturing is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Circular manufacturing focuses on reusing and recycling materials to create sustainable production cycles, whereas linear manufacturing follows a 'take-make-dispose' model with higher waste generation. Companies adopting circular manufacturing can significantly lower costs and carbon emissions while enhancing product lifecycle. Knowledge of these models enables businesses to implement eco-friendly strategies that comply with evolving regulatory standards and consumer demands.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Manufacturing | Linear Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Production model focusing on reuse, recycling, and resource efficiency. | Traditional production model based on a 'take-make-dispose' approach. |
| Resource Usage | Minimizes raw material consumption through closed-loop processes. | High raw material consumption with significant waste generation. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste, pollution, and carbon footprint. | Increases waste, pollution, and carbon emissions. |
| Economic Benefits | Cost savings via material recovery and product lifespan extension. | Higher costs due to continuous raw material procurement and waste management. |
| Product Lifecycle | Extends lifecycle through repair, remanufacturing, and recycling. | Short product lifecycle ending in landfill or incineration. |
| Waste Management | Waste minimized, treated as a resource. | Waste is discarded, not reused or recovered. |
| Energy Consumption | Optimized by using renewable sources and efficient processes. | High energy use, often reliant on fossil fuels. |
| Examples | Closed-loop supply chains, product-as-a-service models. | Mass production, single-use products. |
Which is better?
Circular manufacturing maximizes resource efficiency by reusing materials and minimizing waste, promoting sustainability and reducing environmental impact. Linear manufacturing relies on a one-way flow of raw materials to products and waste, often leading to resource depletion and higher ecological footprints. Embracing circular manufacturing aligns with global goals for sustainable production and long-term economic resilience.
Connection
Circular manufacturing and linear manufacturing are connected through material flow and resource management, where circular manufacturing aims to close the loop by reusing and recycling materials from linear manufacturing processes. Linear manufacturing follows a traditional 'take-make-dispose' model, generating waste that circular manufacturing seeks to minimize by integrating reclaiming and remanufacturing strategies. This connection enhances sustainability by reducing environmental impact and promoting resource efficiency across production cycles.
Key Terms
Resource Efficiency
Linear manufacturing relies on a take-make-dispose model, leading to significant resource depletion and waste generation, whereas circular manufacturing enhances resource efficiency by prioritizing reuse, recycling, and regenerative processes. Circular systems reduce raw material extraction and minimize environmental impact through closed-loop supply chains and sustainable product design. Explore how circular manufacturing strategies optimize resource use and drive sustainable innovation.
Waste Management
Linear manufacturing generates significant waste by following a 'take-make-dispose' model, leading to resource depletion and increased landfill burden. Circular manufacturing minimizes waste through recycling, reusing materials, and designing products for longevity, thereby promoting sustainable resource management. Explore how adopting circular strategies can revolutionize waste management and reduce environmental impact.
Product Lifecycle
Linear manufacturing follows a straightforward product lifecycle that moves from raw material extraction to production, usage, and disposal, often resulting in significant waste and resource depletion. Circular manufacturing prioritizes product design, reuse, refurbishment, and recycling to extend the product lifecycle, reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainability. Explore how circular manufacturing transforms product lifecycle strategies to improve resource efficiency and lower carbon footprints.
Source and External Links
Linear Meaning & Definition for Manufacturers - Eyelit Technologies - Linear manufacturing is an organized, sequential process where each step depends on the previous one, optimizing efficiency by minimizing waste and streamlining production lines, commonly used in industries like automotive, food, and electronics for standardized products.
Linear Manufacturing: Home - Linear Manufacturing is an AS9100:2016-ISO 9001:2015 certified full-service electronics contract manufacturer based in Colorado Springs, offering engineering, design, and rapid prototyping services across multiple market segments including aerospace and medical devices.
Linear Manufacturing - US Manufacturing Report, by Sustainment - Linear Manufacturing specializes in PCB assembly, engineering design, and turnkey electronics manufacturing solutions focused on aerospace, military, medical, oil and gas, and communications industries, emphasizing production in the USA.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com