Smart dust consists of tiny, wireless sensors capable of detecting environmental changes at a microscopic scale, enabling real-time data collection in manufacturing processes. Robotics involves programmable machines designed for automated tasks, enhancing precision, efficiency, and safety across production lines. Explore how these innovations revolutionize manufacturing through increased automation and intelligent monitoring.
Why it is important
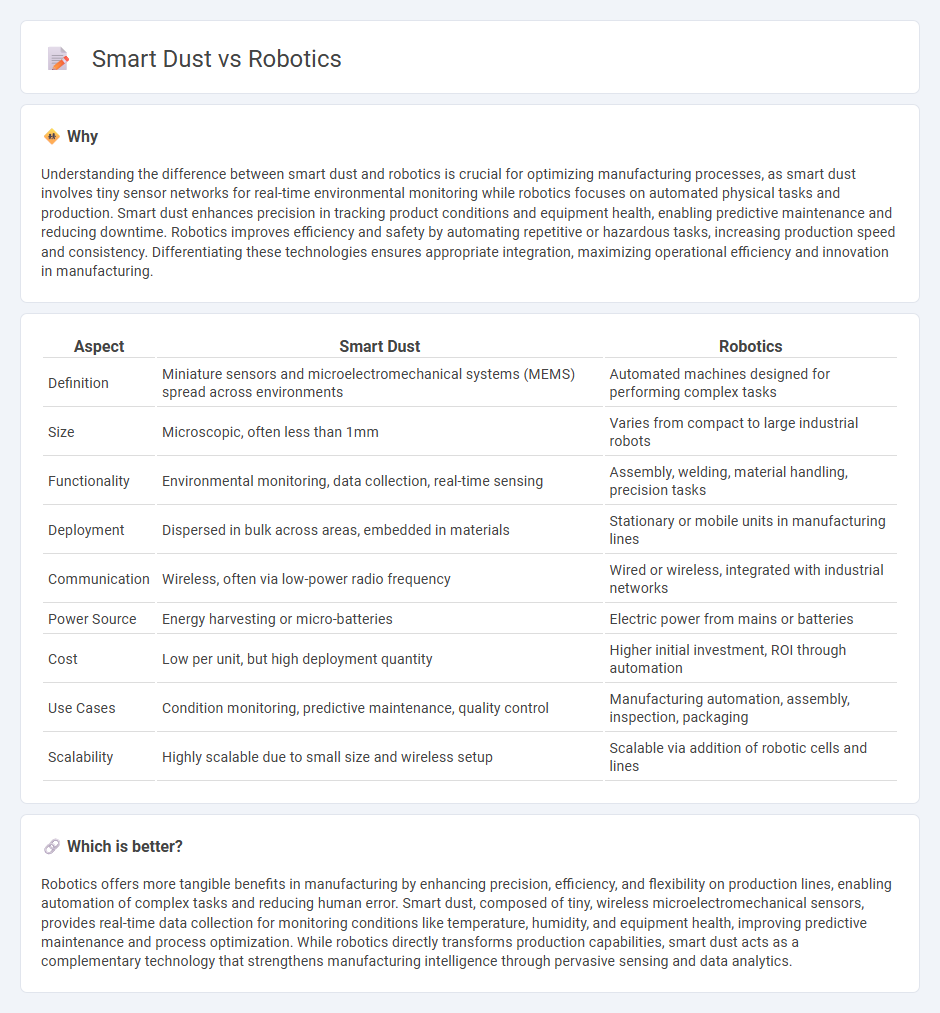
Understanding the difference between smart dust and robotics is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes, as smart dust involves tiny sensor networks for real-time environmental monitoring while robotics focuses on automated physical tasks and production. Smart dust enhances precision in tracking product conditions and equipment health, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. Robotics improves efficiency and safety by automating repetitive or hazardous tasks, increasing production speed and consistency. Differentiating these technologies ensures appropriate integration, maximizing operational efficiency and innovation in manufacturing.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Smart Dust | Robotics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Miniature sensors and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) spread across environments | Automated machines designed for performing complex tasks |
| Size | Microscopic, often less than 1mm | Varies from compact to large industrial robots |
| Functionality | Environmental monitoring, data collection, real-time sensing | Assembly, welding, material handling, precision tasks |
| Deployment | Dispersed in bulk across areas, embedded in materials | Stationary or mobile units in manufacturing lines |
| Communication | Wireless, often via low-power radio frequency | Wired or wireless, integrated with industrial networks |
| Power Source | Energy harvesting or micro-batteries | Electric power from mains or batteries |
| Cost | Low per unit, but high deployment quantity | Higher initial investment, ROI through automation |
| Use Cases | Condition monitoring, predictive maintenance, quality control | Manufacturing automation, assembly, inspection, packaging |
| Scalability | Highly scalable due to small size and wireless setup | Scalable via addition of robotic cells and lines |
Which is better?
Robotics offers more tangible benefits in manufacturing by enhancing precision, efficiency, and flexibility on production lines, enabling automation of complex tasks and reducing human error. Smart dust, composed of tiny, wireless microelectromechanical sensors, provides real-time data collection for monitoring conditions like temperature, humidity, and equipment health, improving predictive maintenance and process optimization. While robotics directly transforms production capabilities, smart dust acts as a complementary technology that strengthens manufacturing intelligence through pervasive sensing and data analytics.
Connection
Smart dust, composed of tiny sensors, integrates with advanced robotics to enhance manufacturing processes through real-time monitoring and data collection. Robotics equipped with smart dust technology enable precision tracking of equipment status, optimizes workflow efficiency, and detects anomalies early, reducing downtime. This synergy supports predictive maintenance and facilitates adaptive automation, driving Industry 4.0 advancements in manufacturing.
Key Terms
Automation
Robotics and smart dust represent two revolutionary approaches to automation, with robotics emphasizing physical machines performing complex tasks and smart dust leveraging distributed microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) for environmental monitoring. Robotics excels in industrial automation, enhancing manufacturing precision and efficiency through programmable machines, while smart dust offers unprecedented potential in real-time data collection at a microscopic scale across vast environments. Explore further to understand how these technologies are transforming automation across diverse industries.
Miniaturization
Robotics advancements emphasize the development of compact, multifunctional machines capable of performing complex tasks, while smart dust prioritizes extreme miniaturization of sensors and communication devices to create vast, distributed networks. Miniaturization in robotics often involves integrating mechanical joints, sensors, and processors within small-scale robots, enabling enhanced mobility and interaction with environments. Explore further to understand how these technologies revolutionize automation and sensing applications.
Wireless Communication
Robotics and smart dust both rely heavily on wireless communication to enable real-time data exchange and remote control, but robotics typically uses higher bandwidth protocols such as Wi-Fi and LTE to support complex sensor arrays and actuators. Smart dust, consisting of tiny microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), utilizes ultra-low-power wireless communication like Zigbee or Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) to maximize battery life and operate in dense sensor networks. Explore more about the specific wireless technologies driving advancements in robotics and smart dust applications.
Source and External Links
Robotics: What Are Robots? - Robotics is the interdisciplinary field that designs, constructs, and operates machines (robots) to automate or replace human actions, with modern robots increasingly using artificial intelligence for complex tasks.
Robotics - Robotics integrates engineering, computer science, and other disciplines to create robots capable of assisting humans, especially in hazardous, repetitive, or static environments, with ongoing advancements in autonomy and navigation.
Robotics | Definition, Applications, & Facts - Robotics involves the design and use of robots to perform tasks traditionally done by humans, spanning industries from manufacturing to exploration, and increasingly incorporates artificial intelligence for senses and decision-making.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com