Smart dust revolutionizes manufacturing by deploying microscopic sensors that collect real-time environmental data across production lines, enabling unprecedented precision and automation. Condition monitoring focuses on the continuous tracking of machinery health through vibration analysis, temperature sensors, and acoustic monitoring to predict maintenance needs and prevent downtime. Explore how these cutting-edge technologies transform operational efficiency and reduce costs in advanced manufacturing environments.
Why it is important
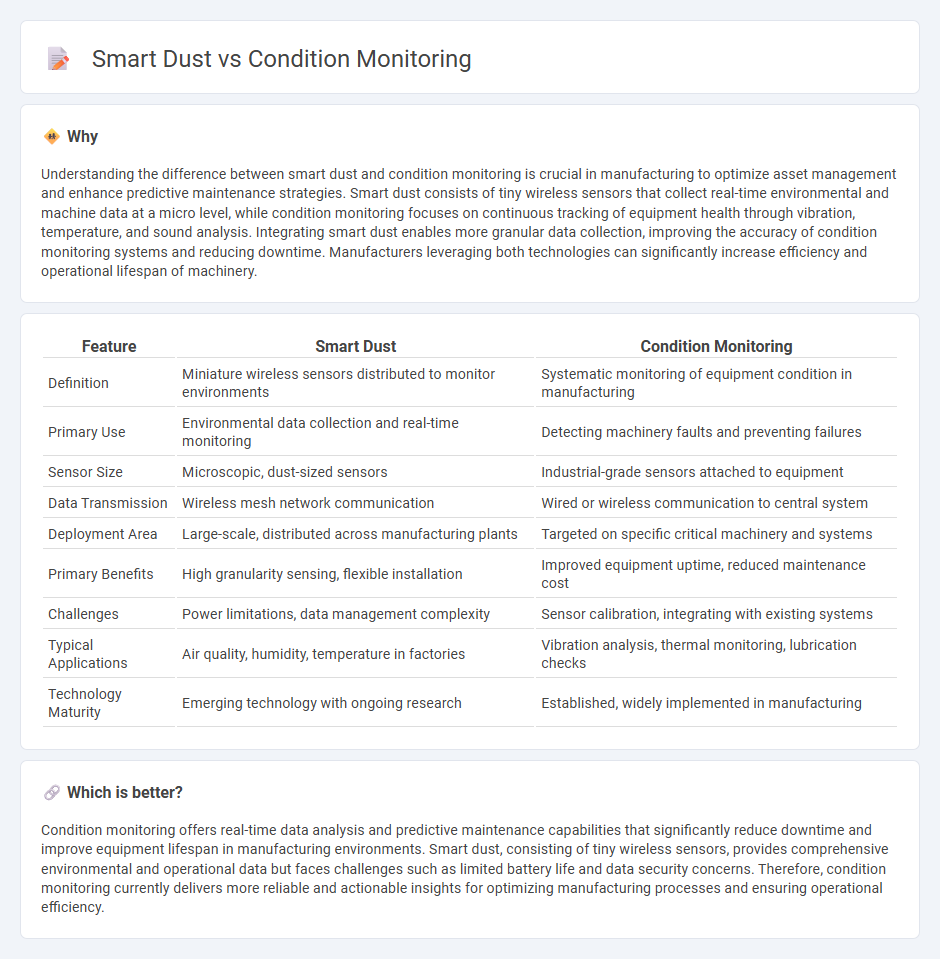
Understanding the difference between smart dust and condition monitoring is crucial in manufacturing to optimize asset management and enhance predictive maintenance strategies. Smart dust consists of tiny wireless sensors that collect real-time environmental and machine data at a micro level, while condition monitoring focuses on continuous tracking of equipment health through vibration, temperature, and sound analysis. Integrating smart dust enables more granular data collection, improving the accuracy of condition monitoring systems and reducing downtime. Manufacturers leveraging both technologies can significantly increase efficiency and operational lifespan of machinery.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Smart Dust | Condition Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Miniature wireless sensors distributed to monitor environments | Systematic monitoring of equipment condition in manufacturing |
| Primary Use | Environmental data collection and real-time monitoring | Detecting machinery faults and preventing failures |
| Sensor Size | Microscopic, dust-sized sensors | Industrial-grade sensors attached to equipment |
| Data Transmission | Wireless mesh network communication | Wired or wireless communication to central system |
| Deployment Area | Large-scale, distributed across manufacturing plants | Targeted on specific critical machinery and systems |
| Primary Benefits | High granularity sensing, flexible installation | Improved equipment uptime, reduced maintenance cost |
| Challenges | Power limitations, data management complexity | Sensor calibration, integrating with existing systems |
| Typical Applications | Air quality, humidity, temperature in factories | Vibration analysis, thermal monitoring, lubrication checks |
| Technology Maturity | Emerging technology with ongoing research | Established, widely implemented in manufacturing |
Which is better?
Condition monitoring offers real-time data analysis and predictive maintenance capabilities that significantly reduce downtime and improve equipment lifespan in manufacturing environments. Smart dust, consisting of tiny wireless sensors, provides comprehensive environmental and operational data but faces challenges such as limited battery life and data security concerns. Therefore, condition monitoring currently delivers more reliable and actionable insights for optimizing manufacturing processes and ensuring operational efficiency.
Connection
Smart dust technology enhances condition monitoring by providing real-time, granular data on equipment performance and environmental conditions within manufacturing facilities. These microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) sensors enable continuous monitoring of temperature, vibration, and humidity, facilitating predictive maintenance and reducing unplanned downtime. Integrating smart dust with advanced analytics optimizes machine reliability, operational efficiency, and overall production quality in manufacturing processes.
Key Terms
Predictive Maintenance
Condition monitoring employs sensors to track machinery performance in real-time, enabling early detection of faults and reducing unplanned downtime. Smart dust consists of tiny wireless sensors that can be deployed in large quantities for distributed data collection, offering granular insights into equipment health for predictive maintenance. Explore how integrating smart dust into condition monitoring systems revolutionizes asset management and enhances predictive maintenance strategies.
Wireless Sensor Networks
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) play a crucial role in condition monitoring by providing real-time data on equipment health, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. Smart dust technology enhances these networks with miniature, autonomous sensors that collect and transmit environmental data with minimal energy consumption. Explore how integrating smart dust into WSNs advances condition monitoring capabilities and transforms industrial applications.
Real-time Data Analytics
Condition monitoring leverages sensors to collect real-time data on equipment performance, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime through continuous analysis of vibration, temperature, and operational metrics. Smart dust consists of tiny, wireless microelectromechanical sensors that provide granular, real-time environmental data across large areas, enhancing precision in monitoring and analytics. Explore advanced applications and benefits of integrating real-time data analytics in these technologies to drive operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
What is Condition Monitoring: The Ultimate Guide - Condition monitoring is a proactive maintenance strategy involving continuous monitoring of equipment parameters like vibration and temperature to detect faults early and optimize maintenance before failures occur.
What is a Condition Monitoring (CM)? - IBM - Condition monitoring uses real-time sensor data on asset health to predict and prevent critical failures, minimizing unplanned downtime and maximizing asset lifespan in industries like manufacturing and transportation.
Condition monitoring - Wikipedia - Condition monitoring tracks machinery condition parameters to identify changes indicative of developing faults, enabling scheduled maintenance and avoiding major damage, commonly applied to rotating equipment with advanced techniques such as vibration analysis and infrared thermography.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com