Digital twinning creates virtual replicas of physical manufacturing processes, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive analytics. Smart factories integrate IoT, AI, and automation to optimize production efficiency and flexibility across the entire plant. Discover how these transformative technologies are shaping the future of manufacturing.
Why it is important
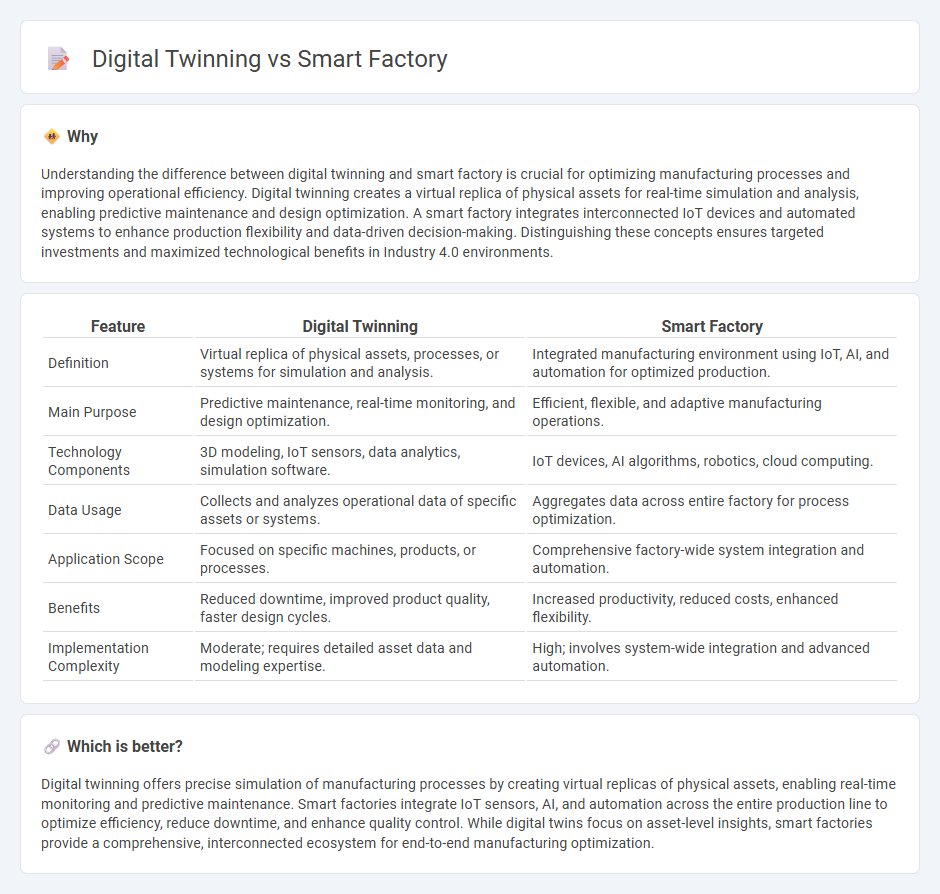
Understanding the difference between digital twinning and smart factory is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes and improving operational efficiency. Digital twinning creates a virtual replica of physical assets for real-time simulation and analysis, enabling predictive maintenance and design optimization. A smart factory integrates interconnected IoT devices and automated systems to enhance production flexibility and data-driven decision-making. Distinguishing these concepts ensures targeted investments and maximized technological benefits in Industry 4.0 environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Twinning | Smart Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual replica of physical assets, processes, or systems for simulation and analysis. | Integrated manufacturing environment using IoT, AI, and automation for optimized production. |
| Main Purpose | Predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and design optimization. | Efficient, flexible, and adaptive manufacturing operations. |
| Technology Components | 3D modeling, IoT sensors, data analytics, simulation software. | IoT devices, AI algorithms, robotics, cloud computing. |
| Data Usage | Collects and analyzes operational data of specific assets or systems. | Aggregates data across entire factory for process optimization. |
| Application Scope | Focused on specific machines, products, or processes. | Comprehensive factory-wide system integration and automation. |
| Benefits | Reduced downtime, improved product quality, faster design cycles. | Increased productivity, reduced costs, enhanced flexibility. |
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate; requires detailed asset data and modeling expertise. | High; involves system-wide integration and advanced automation. |
Which is better?
Digital twinning offers precise simulation of manufacturing processes by creating virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Smart factories integrate IoT sensors, AI, and automation across the entire production line to optimize efficiency, reduce downtime, and enhance quality control. While digital twins focus on asset-level insights, smart factories provide a comprehensive, interconnected ecosystem for end-to-end manufacturing optimization.
Connection
Digital twinning enhances smart factory operations by creating virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This integration improves production efficiency, reduces downtime, and optimizes resource allocation through data-driven insights. Smart factories leverage digital twins to simulate workflows and test process changes before implementation, ensuring seamless automation and agile manufacturing.
Key Terms
Automation
Smart factories integrate advanced automation systems with IoT, AI, and robotics to optimize manufacturing processes and increase efficiency. Digital twinning creates virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and simulation-based decision-making. Explore how these technologies revolutionize automation to enhance operational excellence and drive Industry 4.0 innovation.
Real-time data
Smart factories leverage real-time data to optimize manufacturing processes, improve operational efficiency, and enable predictive maintenance through IoT sensors and AI analytics. Digital twinning creates virtual replicas of physical assets or systems, continuously updated with real-time data to simulate, monitor, and enhance performance in a dynamic environment. Explore how integrating real-time data in smart factories and digital twins transforms industrial automation and decision-making.
Virtual simulation
Smart factories integrate IoT, AI, and automation to optimize production efficiency and enable real-time decision-making, while digital twinning employs virtual simulation for precise replication and analysis of physical processes. Virtual simulation within digital twinning allows manufacturers to test scenarios, predict outcomes, and improve system performance without disrupting actual operations. Explore the transformative impact of virtual simulation in smart manufacturing to unlock innovative efficiencies.
Source and External Links
What Is a Smart Factory? An Expert Guide - NetSuite - A smart factory is a highly automated, digitally connected manufacturing environment that integrates advanced technologies like AI, robotics, and machine learning to enable autonomous, flexible production and continuous process improvement, leading to higher efficiency, quality, and reduced costs.
What is a smart factory? Understanding the future of manufacturing - A smart factory digitizes all manufacturing areas, using sensors, cloud computing, AI, and machine learning to analyze data and continuously improve production processes, forming a core part of Industry 4.0 with intelligent automation.
Smart Factory Guide | L2L - Smart factories connect machines, people, and processes through digital technologies to optimize production efficiency, asset management, safety, and quality, generating business value and competitiveness through data-driven insights and IIoT integration.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com