Lights out factories operate with minimal human intervention, relying entirely on automated systems to manage production processes around the clock, increasing efficiency and reducing operational costs. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) focuses on automating specific repetitive tasks within manufacturing workflows, enhancing precision and accelerating data processing. Explore the distinctions and benefits of these transformative manufacturing technologies to optimize your production strategy.
Why it is important
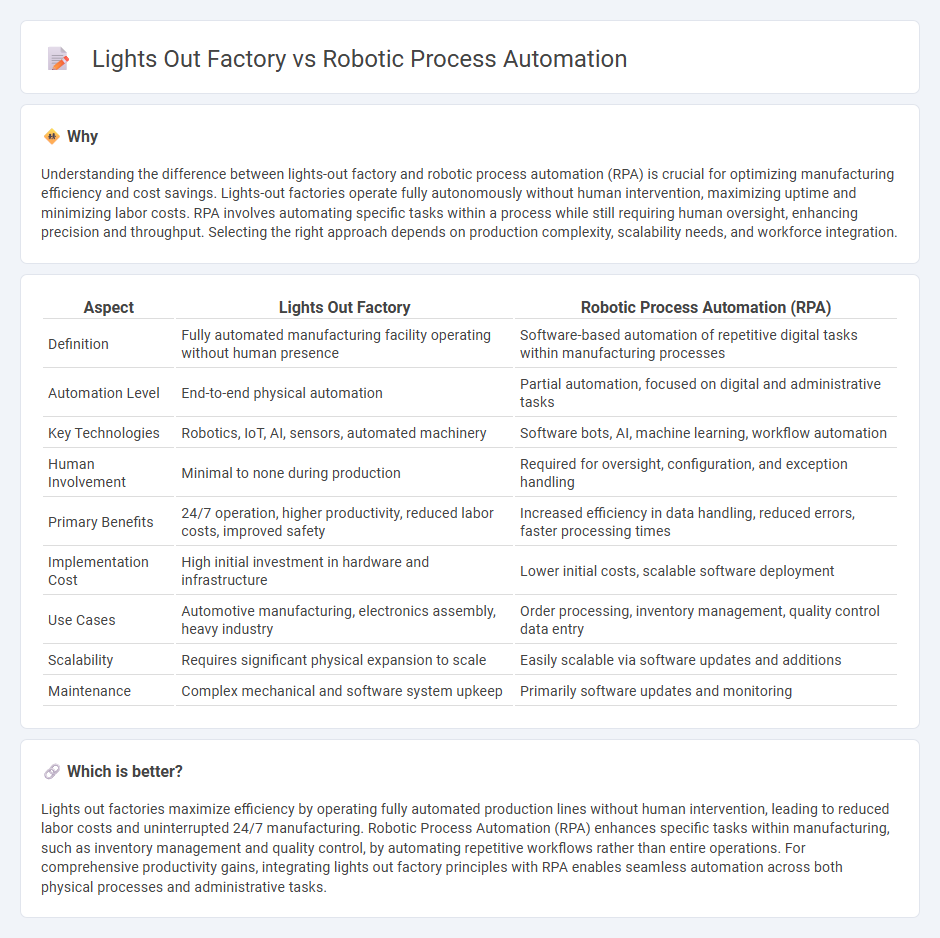
Understanding the difference between lights-out factory and robotic process automation (RPA) is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and cost savings. Lights-out factories operate fully autonomously without human intervention, maximizing uptime and minimizing labor costs. RPA involves automating specific tasks within a process while still requiring human oversight, enhancing precision and throughput. Selecting the right approach depends on production complexity, scalability needs, and workforce integration.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Lights Out Factory | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated manufacturing facility operating without human presence | Software-based automation of repetitive digital tasks within manufacturing processes |
| Automation Level | End-to-end physical automation | Partial automation, focused on digital and administrative tasks |
| Key Technologies | Robotics, IoT, AI, sensors, automated machinery | Software bots, AI, machine learning, workflow automation |
| Human Involvement | Minimal to none during production | Required for oversight, configuration, and exception handling |
| Primary Benefits | 24/7 operation, higher productivity, reduced labor costs, improved safety | Increased efficiency in data handling, reduced errors, faster processing times |
| Implementation Cost | High initial investment in hardware and infrastructure | Lower initial costs, scalable software deployment |
| Use Cases | Automotive manufacturing, electronics assembly, heavy industry | Order processing, inventory management, quality control data entry |
| Scalability | Requires significant physical expansion to scale | Easily scalable via software updates and additions |
| Maintenance | Complex mechanical and software system upkeep | Primarily software updates and monitoring |
Which is better?
Lights out factories maximize efficiency by operating fully automated production lines without human intervention, leading to reduced labor costs and uninterrupted 24/7 manufacturing. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances specific tasks within manufacturing, such as inventory management and quality control, by automating repetitive workflows rather than entire operations. For comprehensive productivity gains, integrating lights out factory principles with RPA enables seamless automation across both physical processes and administrative tasks.
Connection
Lights out factories leverage robotic process automation (RPA) to enable fully automated manufacturing operations without human intervention, drastically increasing efficiency and reducing errors. RPA controls machines and equipment through software robots that perform repetitive tasks with high precision, facilitating continuous production in lights out environments. Integration of RPA technologies in lights out factories accelerates production cycles and minimizes operational costs by optimizing resource utilization and scheduling.
Key Terms
Automation
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines repetitive, rule-based tasks in business processes by using software bots to increase efficiency and reduce human error. Lights out factories represent fully automated manufacturing environments where machines operate continuously without human intervention, maximizing production scalability and cost savings. Explore how these automation technologies transform operations and drive productivity gains.
Human intervention
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) relies on human intervention for monitoring, exception handling, and process updates, ensuring flexibility in dynamic workflows. Lights out factories operate with minimal to no human involvement, emphasizing fully automated manufacturing environments driven by interconnected machines and AI systems. Explore deeper insights into how these automation strategies balance human oversight and operational efficiency.
Unattended operations
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based tasks within business processes, enabling unattended software operations that improve efficiency and reduce human error. Lights out factories operate fully autonomously, employing advanced robotics and control systems to perform manufacturing tasks without human intervention, aiming for continuous, 24/7 production. Discover how these technologies drive unattended operations to transform productivity and operational excellence.
Source and External Links
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)? - Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is software technology that uses software robots to automate repetitive business tasks that humans typically perform, such as data extraction, form filling, and moving files, combining APIs and UI interactions to execute processes autonomously and increase efficiency by freeing humans for higher-value work.
What is Robotic Process Automation - RPA Software - RPA technology enables companies to build and manage software robots that emulate human interactions with digital systems, automating workflows to reduce errors and costs, speed up processes, and allow employees to focus on more strategic and creative work.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) - RPA automates repetitive, rule-based tasks such as document processing, invoice handling, customer support, HR onboarding, and supply chain operations by deploying bots that improve business productivity and accuracy across various industries.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com