Cobots enhance manufacturing by working safely alongside human operators, increasing precision and flexibility in assembly tasks. AGVs optimize material transport within facilities, reducing labor costs and improving workflow efficiency through automated navigation systems. Discover how integrating cobots and AGVs transforms manufacturing processes for greater productivity and innovation.
Why it is important
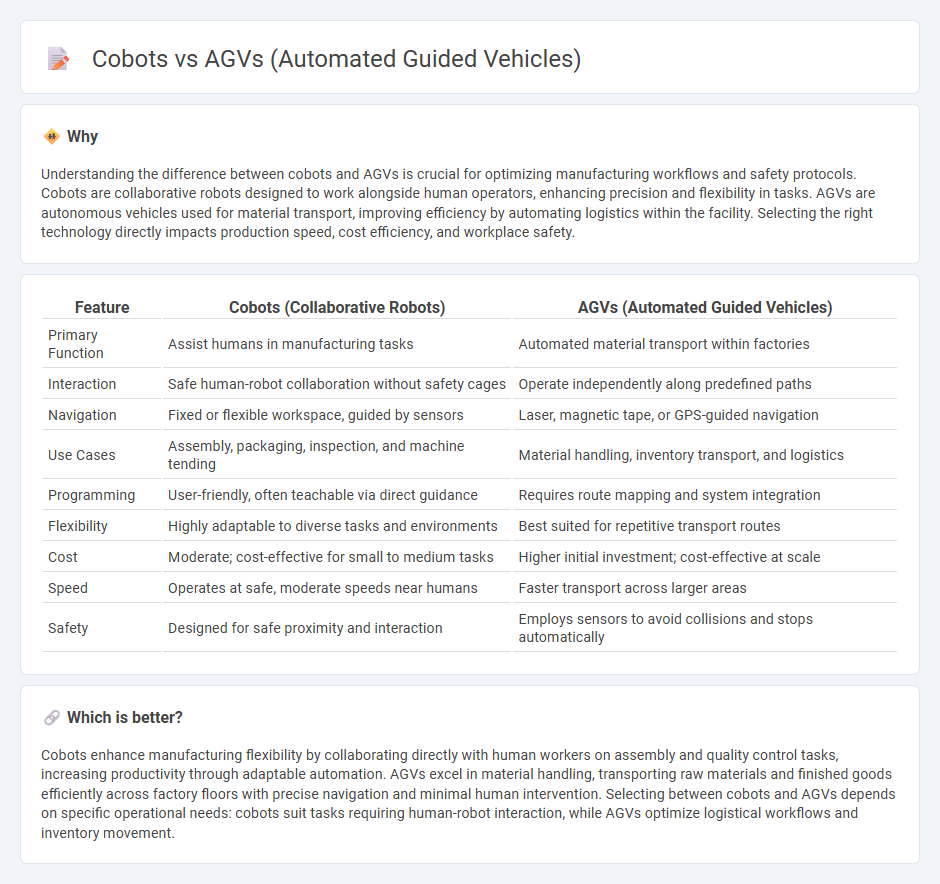
Understanding the difference between cobots and AGVs is crucial for optimizing manufacturing workflows and safety protocols. Cobots are collaborative robots designed to work alongside human operators, enhancing precision and flexibility in tasks. AGVs are autonomous vehicles used for material transport, improving efficiency by automating logistics within the facility. Selecting the right technology directly impacts production speed, cost efficiency, and workplace safety.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Cobots (Collaborative Robots) | AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Assist humans in manufacturing tasks | Automated material transport within factories |
| Interaction | Safe human-robot collaboration without safety cages | Operate independently along predefined paths |
| Navigation | Fixed or flexible workspace, guided by sensors | Laser, magnetic tape, or GPS-guided navigation |
| Use Cases | Assembly, packaging, inspection, and machine tending | Material handling, inventory transport, and logistics |
| Programming | User-friendly, often teachable via direct guidance | Requires route mapping and system integration |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable to diverse tasks and environments | Best suited for repetitive transport routes |
| Cost | Moderate; cost-effective for small to medium tasks | Higher initial investment; cost-effective at scale |
| Speed | Operates at safe, moderate speeds near humans | Faster transport across larger areas |
| Safety | Designed for safe proximity and interaction | Employs sensors to avoid collisions and stops automatically |
Which is better?
Cobots enhance manufacturing flexibility by collaborating directly with human workers on assembly and quality control tasks, increasing productivity through adaptable automation. AGVs excel in material handling, transporting raw materials and finished goods efficiently across factory floors with precise navigation and minimal human intervention. Selecting between cobots and AGVs depends on specific operational needs: cobots suit tasks requiring human-robot interaction, while AGVs optimize logistical workflows and inventory movement.
Connection
Cobots and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are interconnected in manufacturing by enhancing operational efficiency and flexibility through collaborative automation and autonomous material transport. Integration of cobots with AGVs enables seamless coordination for tasks like assembly, inspection, and logistics, reducing downtime and labor costs. Real-time data exchange between cobots and AGVs ensures synchronized workflows, boosting productivity and safety on the factory floor.
Key Terms
Autonomy
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and collaborative robots (cobots) differ significantly in autonomy levels; AGVs follow predefined paths using sensors and markers to navigate, enabling steady, repetitive task execution with minimal human intervention. Cobots exhibit advanced autonomous capabilities with adaptive learning algorithms and real-time decision-making to safely interact with humans and dynamically respond to changing environments. Discover more about how autonomy shapes the future of AGVs and cobots in modern industrial applications.
Human-robot collaboration
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) streamline material handling through autonomous navigation, reducing manual labor and enhancing operational efficiency in warehouses and manufacturing. Cobots, or collaborative robots, work alongside human operators, providing assistance on complex tasks with safety features tailored for close human-robot interaction. Explore in-depth the evolving dynamics of human-robot collaboration and how AGVs and cobots are transforming workplace productivity.
Material handling
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) streamline material handling by autonomously transporting goods within warehouses, enhancing efficiency through predefined navigation routes and reducing labor costs. Cobots, or collaborative robots, assist human workers by performing tasks such as picking, packing, and sorting, offering flexibility for complex material handling operations. Explore further to understand how integrating AGVs and cobots can optimize your supply chain processes.
Source and External Links
What Are Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)? - Spectra by MHI - AGVs are autonomous, driverless materials-handling machines that move goods in warehouses, factories, and hospitals, using internal navigation systems guided by sensors or lasers combined with fleet control software to improve efficiency and address labor shortages.
Fundamentals of Automated Guided Vehicles - Cyngn - An AGV is a standalone robotic vehicle autonomously transporting materials on fixed routes using guidance like magnetic strips or wires, typically in manufacturing or warehouse environments, and differs from AMRs by its less flexible navigation.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGV) | Meaning, Types & Use-Cases - AGVs follow pre-defined paths using technologies such as magnetic tape, wires, or laser navigation, equipped with sensors for obstacle detection and communicate with central control systems for coordinated autonomous material handling in industrial settings.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com