Lattice structure design offers enhanced strength-to-weight ratios and superior energy absorption compared to traditional honeycomb structures, making it ideal for advanced manufacturing applications. Honeycomb structures excel in uniform load distribution and ease of fabrication, widely used in aerospace and automotive industries. Explore the distinctive advantages of lattice and honeycomb designs to optimize manufacturing performance and material efficiency.
Why it is important
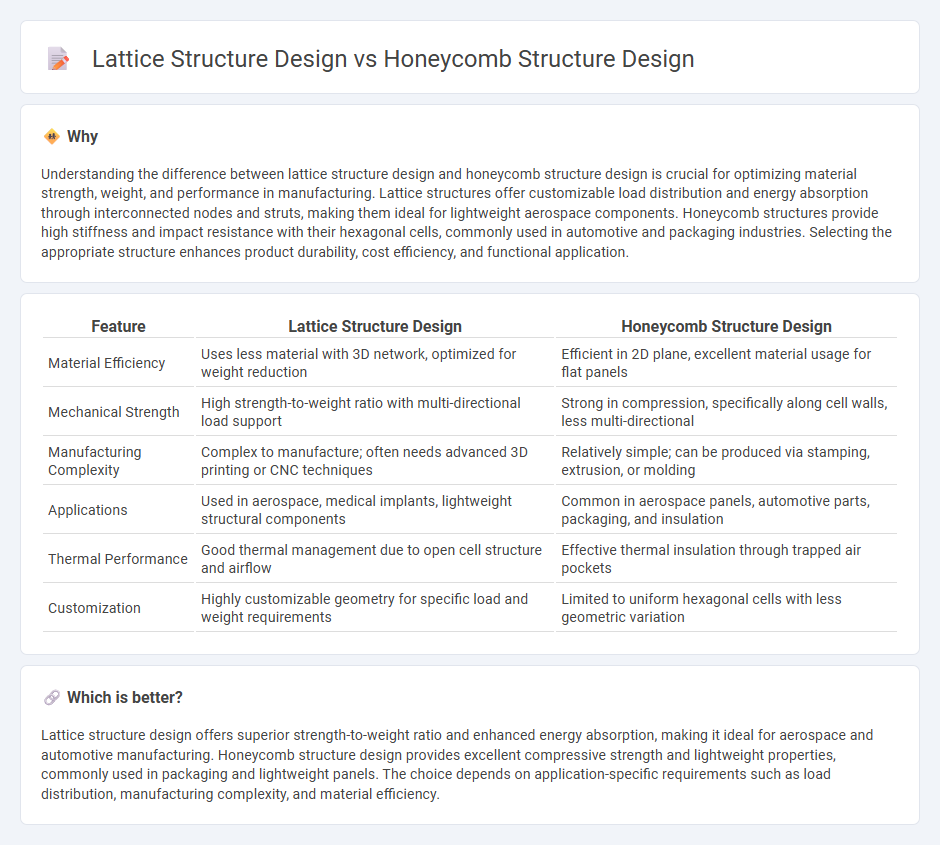
Understanding the difference between lattice structure design and honeycomb structure design is crucial for optimizing material strength, weight, and performance in manufacturing. Lattice structures offer customizable load distribution and energy absorption through interconnected nodes and struts, making them ideal for lightweight aerospace components. Honeycomb structures provide high stiffness and impact resistance with their hexagonal cells, commonly used in automotive and packaging industries. Selecting the appropriate structure enhances product durability, cost efficiency, and functional application.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Lattice Structure Design | Honeycomb Structure Design |
|---|---|---|
| Material Efficiency | Uses less material with 3D network, optimized for weight reduction | Efficient in 2D plane, excellent material usage for flat panels |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength-to-weight ratio with multi-directional load support | Strong in compression, specifically along cell walls, less multi-directional |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Complex to manufacture; often needs advanced 3D printing or CNC techniques | Relatively simple; can be produced via stamping, extrusion, or molding |
| Applications | Used in aerospace, medical implants, lightweight structural components | Common in aerospace panels, automotive parts, packaging, and insulation |
| Thermal Performance | Good thermal management due to open cell structure and airflow | Effective thermal insulation through trapped air pockets |
| Customization | Highly customizable geometry for specific load and weight requirements | Limited to uniform hexagonal cells with less geometric variation |
Which is better?
Lattice structure design offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced energy absorption, making it ideal for aerospace and automotive manufacturing. Honeycomb structure design provides excellent compressive strength and lightweight properties, commonly used in packaging and lightweight panels. The choice depends on application-specific requirements such as load distribution, manufacturing complexity, and material efficiency.
Connection
Lattice structure design and honeycomb structure design are connected through their emphasis on maximizing strength-to-weight ratios and material efficiency in manufacturing. Both designs utilize repeated geometric patterns to distribute loads evenly and enhance structural rigidity while minimizing material usage. These optimized structures are widely applied in aerospace, automotive, and construction industries to improve performance and reduce manufacturing costs.
Key Terms
Weight-to-strength ratio
Honeycomb structures exhibit exceptional weight-to-strength ratios due to their hexagonal cells, offering high stiffness and energy absorption with minimal material use. Lattice structures provide customizable mechanical properties through varied node connectivity and strut thickness, optimizing load distribution and weight reduction for specific applications. Explore detailed comparisons to determine the ideal structure for your engineering project.
Material efficiency
Honeycomb structure design offers superior material efficiency by using hexagonal cells that provide high strength-to-weight ratios with minimal material usage, ideal for aerospace and automotive applications. Lattice structure design utilizes interconnected struts forming a network of nodes, allowing for customizable stiffness and weight distribution but generally requires more complex manufacturing processes. Explore further to understand which design optimizes your specific material efficiency needs.
Load distribution
Honeycomb structures provide superior load distribution through their hexagonal cells, efficiently dispersing stress and reducing material weight while maintaining strength. Lattice structures, composed of interconnected struts, offer customizable load paths and enhanced energy absorption by distributing forces along multiple axes. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which design optimally suits specific load distribution requirements.
Source and External Links
Honeycomb: The Architect's Secret Weapon For Versatile Structures - Honeycomb structures use hexagonal cells mimicking nature to provide high strength, lightweight, and rigidity, offering customization and versatility in architectural and engineering designs.
Honeycomb structure - Wikipedia - Honeycomb structures consist of hollow hexagonal cells which, when sandwiched between two skins, produce panels with excellent rigidity at minimal weight and strong compression strength due to efficient wall support.
Innovative Honeycomb Designs for Enhanced Manufacturability, Performance, and Functionality - Advanced honeycomb designs include hierarchical and graded structures that optimize material properties like energy absorption, stiffness, and strength for specific performance needs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com