Dark factories operate autonomously with minimal human presence, leveraging advanced robotics and IoT for continuous production, while Robotic Process Automation (RPA) focuses on automating repetitive digital tasks within business processes. Dark factories enhance manufacturing throughput and reduce labor costs by integrating physical automation, whereas RPA improves efficiency by streamlining administrative workflows and data handling. Explore the transformative impacts of dark factories and RPA on modern manufacturing processes.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dark factories and robotic process automation (RPA) is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and cost. Dark factories operate fully automated production without human presence, leveraging advanced robotics and AI, leading to 24/7 productivity with minimal errors. RPA involves software bots automating repetitive digital tasks, improving administrative efficiency rather than physical manufacturing processes. Accurate differentiation helps businesses implement targeted automation strategies that maximize production output and streamline operational workflows.
Comparison Table
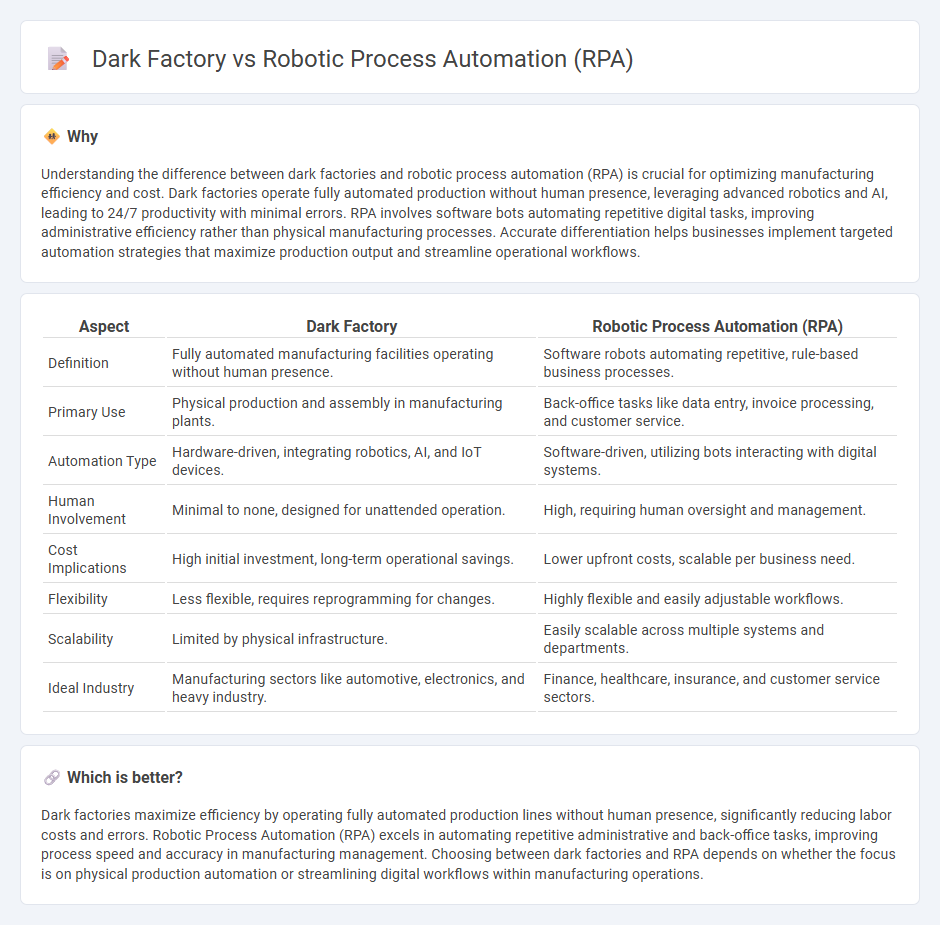
| Aspect | Dark Factory | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated manufacturing facilities operating without human presence. | Software robots automating repetitive, rule-based business processes. |
| Primary Use | Physical production and assembly in manufacturing plants. | Back-office tasks like data entry, invoice processing, and customer service. |
| Automation Type | Hardware-driven, integrating robotics, AI, and IoT devices. | Software-driven, utilizing bots interacting with digital systems. |
| Human Involvement | Minimal to none, designed for unattended operation. | High, requiring human oversight and management. |
| Cost Implications | High initial investment, long-term operational savings. | Lower upfront costs, scalable per business need. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, requires reprogramming for changes. | Highly flexible and easily adjustable workflows. |
| Scalability | Limited by physical infrastructure. | Easily scalable across multiple systems and departments. |
| Ideal Industry | Manufacturing sectors like automotive, electronics, and heavy industry. | Finance, healthcare, insurance, and customer service sectors. |
Which is better?
Dark factories maximize efficiency by operating fully automated production lines without human presence, significantly reducing labor costs and errors. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) excels in automating repetitive administrative and back-office tasks, improving process speed and accuracy in manufacturing management. Choosing between dark factories and RPA depends on whether the focus is on physical production automation or streamlining digital workflows within manufacturing operations.
Connection
Dark factories utilize robotic process automation (RPA) to enable fully automated production lines without human intervention, significantly increasing efficiency and reducing labor costs. By integrating RPA, these factories achieve continuous operations with real-time monitoring and minimal downtime, optimizing manufacturing throughput. The synergy between dark factories and RPA fosters smart manufacturing environments driven by advanced AI, IoT sensors, and data analytics for predictive maintenance and quality control.
Key Terms
Automation
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) leverages software robots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks across digital systems, enhancing efficiency in front-office and back-office processes. In contrast, a Dark Factory employs fully automated physical manufacturing systems operating autonomously without human intervention or lighting, optimizing production speed and consistency. Explore how these distinct automation strategies transform operational workflows and industrial productivity.
Human intervention
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) relies on human intervention for designing, monitoring, and managing automated workflows, making it suitable for tasks requiring frequent updates and oversight. In contrast, a dark factory operates with minimal to no human presence, utilizing fully autonomous machines and robots to maintain continuous production. Explore the distinctions between these technologies to understand their impact on workforce dynamics and operational efficiency.
Lights-out manufacturing
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines repetitive digital tasks by automating rule-based workflows across software applications, enhancing efficiency in administrative processes. Dark factories, or lights-out manufacturing facilities, operate fully automated production lines without human intervention, leveraging advanced robotics, AI, and IoT to optimize manufacturing output and reduce operational costs. Explore how integrating RPA with lights-out manufacturing drives unprecedented productivity and innovation in smart factories.
Source and External Links
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)? - IBM - RPA is software robotics that uses intelligent automation to perform repetitive office tasks like data extraction and form filling, combining API and UI interactions to automate tasks across systems and enhance digital transformation efforts.
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)? | Laserfiche Blog - RPA uses bots to mimic human interactions with software interfaces to automate repetitive tasks, improving accuracy and efficiency while freeing employees to focus on strategic work.
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)? - OpenText - RPA software robots mimic human UI actions to automate repetitive, high-volume, rules-based tasks across industries, increasing productivity and reducing errors without changing underlying IT systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com