Microfactories offer compact, flexible production units that enable localized manufacturing with reduced lead times and tailored output. Continuous flow manufacturing focuses on streamlining production lines to maximize efficiency, minimize waste, and maintain consistent product quality through uninterrupted processes. Explore the advantages and applications of microfactories and continuous flow manufacturing to optimize your production strategy.
Why it is important
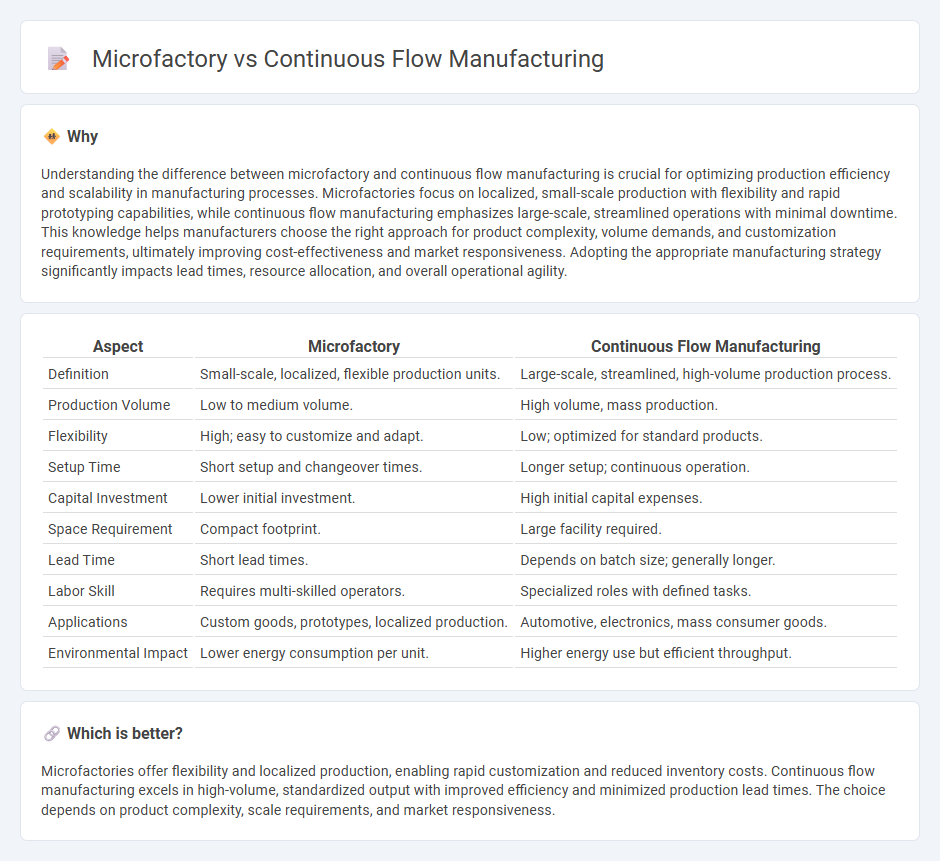
Understanding the difference between microfactory and continuous flow manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and scalability in manufacturing processes. Microfactories focus on localized, small-scale production with flexibility and rapid prototyping capabilities, while continuous flow manufacturing emphasizes large-scale, streamlined operations with minimal downtime. This knowledge helps manufacturers choose the right approach for product complexity, volume demands, and customization requirements, ultimately improving cost-effectiveness and market responsiveness. Adopting the appropriate manufacturing strategy significantly impacts lead times, resource allocation, and overall operational agility.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microfactory | Continuous Flow Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small-scale, localized, flexible production units. | Large-scale, streamlined, high-volume production process. |
| Production Volume | Low to medium volume. | High volume, mass production. |
| Flexibility | High; easy to customize and adapt. | Low; optimized for standard products. |
| Setup Time | Short setup and changeover times. | Longer setup; continuous operation. |
| Capital Investment | Lower initial investment. | High initial capital expenses. |
| Space Requirement | Compact footprint. | Large facility required. |
| Lead Time | Short lead times. | Depends on batch size; generally longer. |
| Labor Skill | Requires multi-skilled operators. | Specialized roles with defined tasks. |
| Applications | Custom goods, prototypes, localized production. | Automotive, electronics, mass consumer goods. |
| Environmental Impact | Lower energy consumption per unit. | Higher energy use but efficient throughput. |
Which is better?
Microfactories offer flexibility and localized production, enabling rapid customization and reduced inventory costs. Continuous flow manufacturing excels in high-volume, standardized output with improved efficiency and minimized production lead times. The choice depends on product complexity, scale requirements, and market responsiveness.
Connection
Microfactories leverage continuous flow manufacturing principles by organizing production into streamlined, modular units that minimize waste and reduce lead times. Continuous flow manufacturing enhances microfactory efficiency through just-in-time production, enabling rapid response to market demands and customization. Both approaches focus on maximizing productivity and flexibility by optimizing space, labor, and material movement within compact manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Production Line
Continuous flow manufacturing emphasizes streamlined, sequential production lines designed to minimize downtime and maximize output by maintaining a steady movement of materials through each station. Microfactories prioritize compact, flexible production lines that integrate advanced automation and modular setups to quickly adapt to changes and produce smaller batches efficiently. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which production line approach best fits your manufacturing goals.
Scale
Continuous flow manufacturing emphasizes large-scale production with streamlined processes to maximize output and efficiency, ideal for high-volume demands. Microfactories prioritize flexibility and localized production, operating on a smaller scale to rapidly adapt to market changes and reduce logistical costs. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which approach best suits your manufacturing scale needs.
Flexibility
Continuous flow manufacturing excels in producing high volumes with minimal interruption, optimizing efficiency in standardized processes. Microfactories prioritize flexibility by accommodating small batch sizes and rapid product changes, ideal for customized manufacturing and local production. Explore how these approaches can transform your manufacturing strategy for enhanced adaptability.
Source and External Links
Continuous-Flow Manufacturing (CFM) | Propel Glossary - Continuous-flow manufacturing is a process where materials move constantly through the production line, opposing batch production by maintaining seamless, uninterrupted production and often incorporating just-in-time and automation principles.
Continuous Flow Production: A Complete Guide - Ease.io - This method involves nonstop production with zero downtime, using precisely coordinated process flow, advanced equipment, and integrated quality control systems to ensure consistent, high-quality output.
Continuous Flow Manufacturing: A Guide to Streamlined Production - Implementing continuous flow manufacturing requires analyzing current processes, mapping value streams, optimizing factory layout, and providing employee training to enable smooth, efficient material flow throughout production stages.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com