Cloud manufacturing leverages distributed computing resources and real-time data integration to enhance production efficiency and flexibility. Mass customization focuses on producing personalized products at scale by combining flexible processes with customer-specific designs. Explore the differences and benefits of cloud manufacturing versus mass customization to optimize your production strategy.
Why it is important
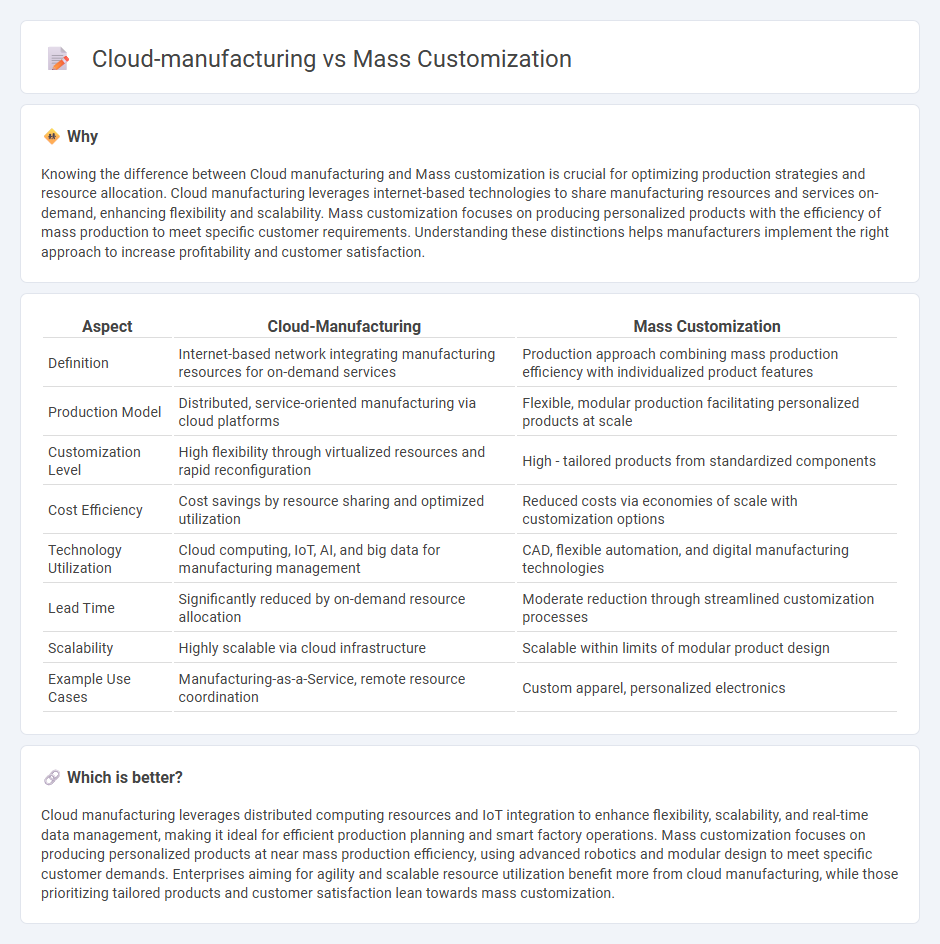
Knowing the difference between Cloud manufacturing and Mass customization is crucial for optimizing production strategies and resource allocation. Cloud manufacturing leverages internet-based technologies to share manufacturing resources and services on-demand, enhancing flexibility and scalability. Mass customization focuses on producing personalized products with the efficiency of mass production to meet specific customer requirements. Understanding these distinctions helps manufacturers implement the right approach to increase profitability and customer satisfaction.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cloud-Manufacturing | Mass Customization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Internet-based network integrating manufacturing resources for on-demand services | Production approach combining mass production efficiency with individualized product features |
| Production Model | Distributed, service-oriented manufacturing via cloud platforms | Flexible, modular production facilitating personalized products at scale |
| Customization Level | High flexibility through virtualized resources and rapid reconfiguration | High - tailored products from standardized components |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost savings by resource sharing and optimized utilization | Reduced costs via economies of scale with customization options |
| Technology Utilization | Cloud computing, IoT, AI, and big data for manufacturing management | CAD, flexible automation, and digital manufacturing technologies |
| Lead Time | Significantly reduced by on-demand resource allocation | Moderate reduction through streamlined customization processes |
| Scalability | Highly scalable via cloud infrastructure | Scalable within limits of modular product design |
| Example Use Cases | Manufacturing-as-a-Service, remote resource coordination | Custom apparel, personalized electronics |
Which is better?
Cloud manufacturing leverages distributed computing resources and IoT integration to enhance flexibility, scalability, and real-time data management, making it ideal for efficient production planning and smart factory operations. Mass customization focuses on producing personalized products at near mass production efficiency, using advanced robotics and modular design to meet specific customer demands. Enterprises aiming for agility and scalable resource utilization benefit more from cloud manufacturing, while those prioritizing tailored products and customer satisfaction lean towards mass customization.
Connection
Cloud manufacturing integrates distributed computing resources, enabling real-time data sharing and collaboration across production networks, which directly facilitates mass customization by allowing flexible, on-demand adjustments to product designs. Mass customization relies on cloud-based platforms to collect customer preferences and dynamically configure manufacturing processes, enhancing efficiency and reducing lead times. This synergy accelerates innovation while meeting personalized market demands through scalable, data-driven production systems.
Key Terms
Personalization
Mass customization leverages flexible manufacturing systems to produce personalized products at scale, blending efficiency with individual customer preferences. Cloud manufacturing utilizes cloud computing resources to enable real-time collaboration, rapid prototyping, and dynamic resource allocation, enhancing the personalization process through interconnected data and services. Explore how these innovative approaches redefine product personalization in modern manufacturing.
Scalability
Mass customization enables scalable production by integrating flexible manufacturing systems that adapt to individual customer preferences without sacrificing efficiency. Cloud-manufacturing enhances scalability by leveraging distributed resources and real-time data sharing to optimize production capacity and reduce lead times. Explore how these innovations transform manufacturing scalability in depth.
Digital Integration
Mass customization leverages digital technologies to tailor products to individual customer specifications while maintaining efficient production through modular design and flexible manufacturing systems. Cloud manufacturing integrates distributed resources and capabilities over cloud platforms, enabling real-time collaboration, resource sharing, and scalability in production processes. Explore the transformative impact of digital integration on manufacturing efficiency and customer-centric innovation.
Source and External Links
Guide to Mass Customization - Mass customization blends the flexibility of custom-made products with the low unit costs of mass production, and is commonly implemented through four distinct approaches such as collaborative and adaptive customization.
Mass Customization: A Complete Guide - Effective mass customization requires understanding customer needs, leveraging technology like 3D printing, automating processes, and ensuring quality control to deliver personalized products efficiently.
Mass Customizations - Definition, How It Works, Types - Mass customization involves capturing individual customer requirements and translating them into products using modular design and product platforms, enabling variety and reduced costs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com