Generative design leverages advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence to create optimized structures by adding material only where necessary, resulting in lightweight and efficient components. In contrast, subtractive manufacturing removes material from a solid block through processes like milling or cutting, often leading to higher material waste and longer production times. Explore how these manufacturing techniques revolutionize product development and cost efficiency.
Why it is important
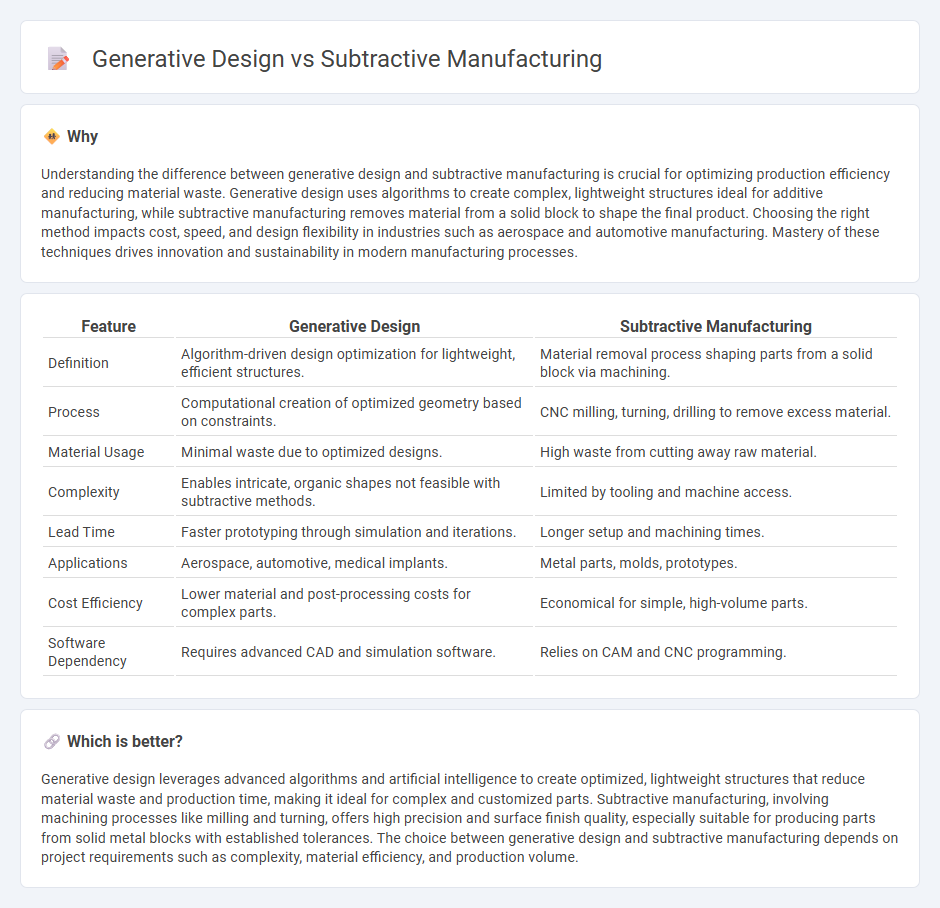
Understanding the difference between generative design and subtractive manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and reducing material waste. Generative design uses algorithms to create complex, lightweight structures ideal for additive manufacturing, while subtractive manufacturing removes material from a solid block to shape the final product. Choosing the right method impacts cost, speed, and design flexibility in industries such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing. Mastery of these techniques drives innovation and sustainability in modern manufacturing processes.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Generative Design | Subtractive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Algorithm-driven design optimization for lightweight, efficient structures. | Material removal process shaping parts from a solid block via machining. |
| Process | Computational creation of optimized geometry based on constraints. | CNC milling, turning, drilling to remove excess material. |
| Material Usage | Minimal waste due to optimized designs. | High waste from cutting away raw material. |
| Complexity | Enables intricate, organic shapes not feasible with subtractive methods. | Limited by tooling and machine access. |
| Lead Time | Faster prototyping through simulation and iterations. | Longer setup and machining times. |
| Applications | Aerospace, automotive, medical implants. | Metal parts, molds, prototypes. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower material and post-processing costs for complex parts. | Economical for simple, high-volume parts. |
| Software Dependency | Requires advanced CAD and simulation software. | Relies on CAM and CNC programming. |
Which is better?
Generative design leverages advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence to create optimized, lightweight structures that reduce material waste and production time, making it ideal for complex and customized parts. Subtractive manufacturing, involving machining processes like milling and turning, offers high precision and surface finish quality, especially suitable for producing parts from solid metal blocks with established tolerances. The choice between generative design and subtractive manufacturing depends on project requirements such as complexity, material efficiency, and production volume.
Connection
Generative design creates optimized 3D models by using algorithms to explore multiple design possibilities, which are then realized through subtractive manufacturing techniques like CNC machining. Subtractive manufacturing removes material from raw stock based on CAD models generated by generative design, enabling precise production of complex geometries. This integration enhances manufacturing efficiency, reduces waste, and accelerates product development cycles.
Key Terms
Material removal
Subtractive manufacturing involves the precise removal of material from a solid block using tools like CNC machines or lasers to achieve the desired shape, optimizing waste reduction and maintaining structural integrity. In contrast, generative design leverages algorithms to create efficient material layouts, minimizing excess and enabling innovative, lightweight structures that would be difficult to fabricate through traditional subtractive methods. Explore more about how these processes complement each other to revolutionize modern manufacturing strategies.
Topology optimization
Topology optimization leverages generative design to create efficient, lightweight structures by iteratively refining material distribution based on load and stress constraints. Subtractive manufacturing removes material from a solid block, often facing limitations in achieving complex geometries that topology optimization presents. Explore how topology optimization pushes the boundaries of design freedom beyond traditional subtractive methods.
CAD modeling
Subtractive manufacturing relies on removing material from a solid block using CNC machines, creating precise CAD models optimized for tool paths and machining constraints. Generative design utilizes AI algorithms to produce CAD models by simulating multiple design iterations based on performance goals, minimizing material use and maximizing structural efficiency. Explore how these CAD modeling approaches influence product innovation and manufacturing efficiency.
Source and External Links
Additive vs. Subtractive Manufacturing - Formlabs - Subtractive manufacturing creates objects by removing material from solid blocks or bars using processes like cutting, drilling, and grinding, typically through computer-controlled CNC machines for high precision in metals and plastics.
Subtractive Manufacturing vs. Additive Manufacturing | Xometry Pro - In subtractive manufacturing, parts are shaped by progressively removing material from a starting block or sheet, which allows for tight tolerances, excellent surface finish, and effective creation of threaded features and holes, mainly using CNC machining.
Subtractive Manufacturing: Past, Present, and Future - Subtractive manufacturing encompasses any process where material is cut, shaped, or finished to achieve a desired configuration, remaining fundamental in industry for detail and finish work, and increasingly combined with additive methods in hybrid manufacturing systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com