Generative design leverages AI algorithms to create optimized manufacturing plans by analyzing multiple variables simultaneously, resulting in innovative and efficient product designs. In contrast, manual drafting relies on human expertise and traditional tools, often limiting complexity and increasing time requirements. Explore how these methods impact manufacturing workflows and product quality in greater detail.
Why it is important
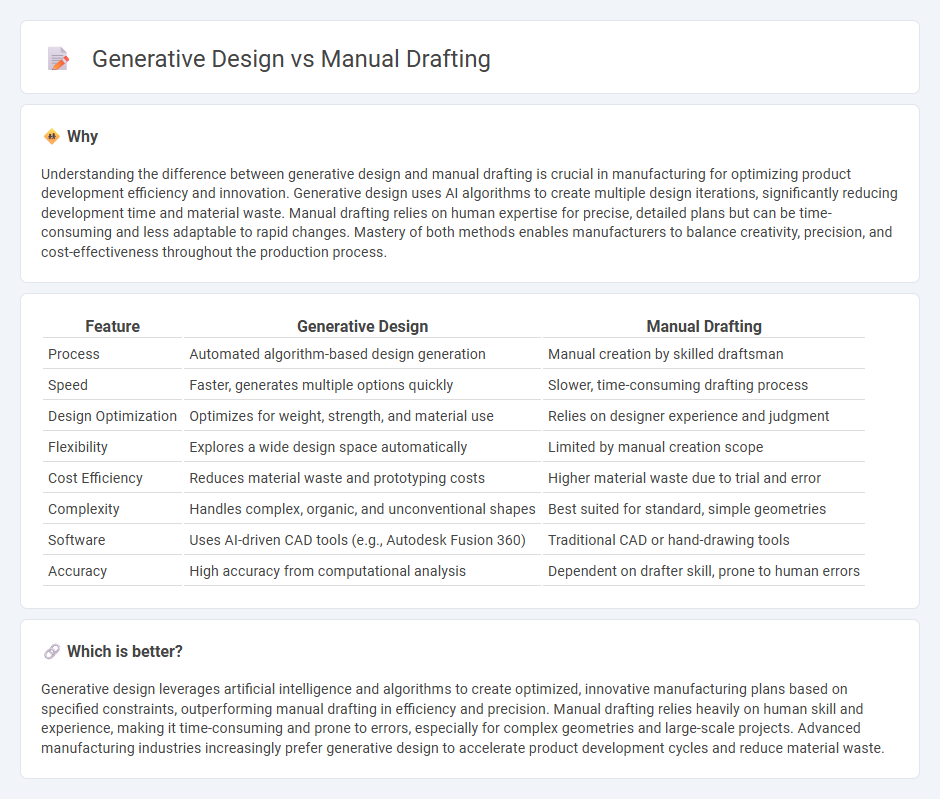
Understanding the difference between generative design and manual drafting is crucial in manufacturing for optimizing product development efficiency and innovation. Generative design uses AI algorithms to create multiple design iterations, significantly reducing development time and material waste. Manual drafting relies on human expertise for precise, detailed plans but can be time-consuming and less adaptable to rapid changes. Mastery of both methods enables manufacturers to balance creativity, precision, and cost-effectiveness throughout the production process.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Generative Design | Manual Drafting |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Automated algorithm-based design generation | Manual creation by skilled draftsman |
| Speed | Faster, generates multiple options quickly | Slower, time-consuming drafting process |
| Design Optimization | Optimizes for weight, strength, and material use | Relies on designer experience and judgment |
| Flexibility | Explores a wide design space automatically | Limited by manual creation scope |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces material waste and prototyping costs | Higher material waste due to trial and error |
| Complexity | Handles complex, organic, and unconventional shapes | Best suited for standard, simple geometries |
| Software | Uses AI-driven CAD tools (e.g., Autodesk Fusion 360) | Traditional CAD or hand-drawing tools |
| Accuracy | High accuracy from computational analysis | Dependent on drafter skill, prone to human errors |
Which is better?
Generative design leverages artificial intelligence and algorithms to create optimized, innovative manufacturing plans based on specified constraints, outperforming manual drafting in efficiency and precision. Manual drafting relies heavily on human skill and experience, making it time-consuming and prone to errors, especially for complex geometries and large-scale projects. Advanced manufacturing industries increasingly prefer generative design to accelerate product development cycles and reduce material waste.
Connection
Generative design leverages advanced algorithms to produce optimized manufacturing blueprints, while manual drafting involves human-created technical drawings essential for precise fabrication processes. Integrating generative design outputs with manual drafting enhances customization and accuracy in manufacturing workflows. This connection streamlines product development, reduces material waste, and accelerates time-to-market for engineered components.
Key Terms
Human intervention
Manual drafting relies heavily on direct human intervention, requiring designers to create detailed plans and make iterative adjustments based on experience and intuition. Generative design leverages algorithms to explore numerous design permutations, reducing repetitive tasks but still necessitating human expertise to guide parameters and assess outcomes. Explore how blending human judgment with AI-driven tools transforms modern design workflows.
Algorithm-driven
Algorithm-driven generative design leverages computational algorithms to create optimized solutions by exploring a vast design space beyond human capability, enhancing efficiency and innovation compared to manual drafting. This technology enables rapid iteration, precision, and data-informed decision-making by using parameters and constraints to generate multiple design alternatives automatically. Explore further to understand how algorithmic approaches transform traditional design processes and unlock new potentials in creativity and productivity.
Iterative optimization
Manual drafting relies heavily on human expertise and repetitive adjustments to achieve design improvements, often resulting in longer development cycles and increased risk of errors. Generative design uses algorithms and iterative optimization processes to explore multiple design alternatives rapidly, optimizing for specific constraints and performance goals with minimal manual input. Discover how generative design can revolutionize your workflow and enhance efficiency through advanced iterative optimization techniques.
Source and External Links
Manual drafting techniques - Designing Buildings Wiki - Manual drafting involves creating drawings by hand, using tools like a drafting table, parallel motion board, and various papers such as vellum or tracing paper, with the board angled to aid drawing accuracy and posture.
Manual Drafting Tools and Equipment - ISBE - Manual drafting uses pencils, templates, T-squares, and other tools which must be properly maintained to ensure clean, accurate drawings, with attention paid to pencil lead thickness and cleanliness.
HAND DRAFTING - MAKER LESSONS - Hand drafting is fundamental for architects and engineers to effectively communicate designs, develop spatial reasoning, and improve technical skills through tools like T-squares, triangles, and compasses, emphasizing detail and design understanding.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com