Cobotics integrates collaborative robots into manufacturing workflows to enhance precision, safety, and efficiency, especially in repetitive or hazardous tasks. Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, enables the creation of complex parts layer-by-layer, reducing material waste and accelerating prototyping processes. Explore how combining cobotics and additive manufacturing transforms modern production methods.
Why it is important
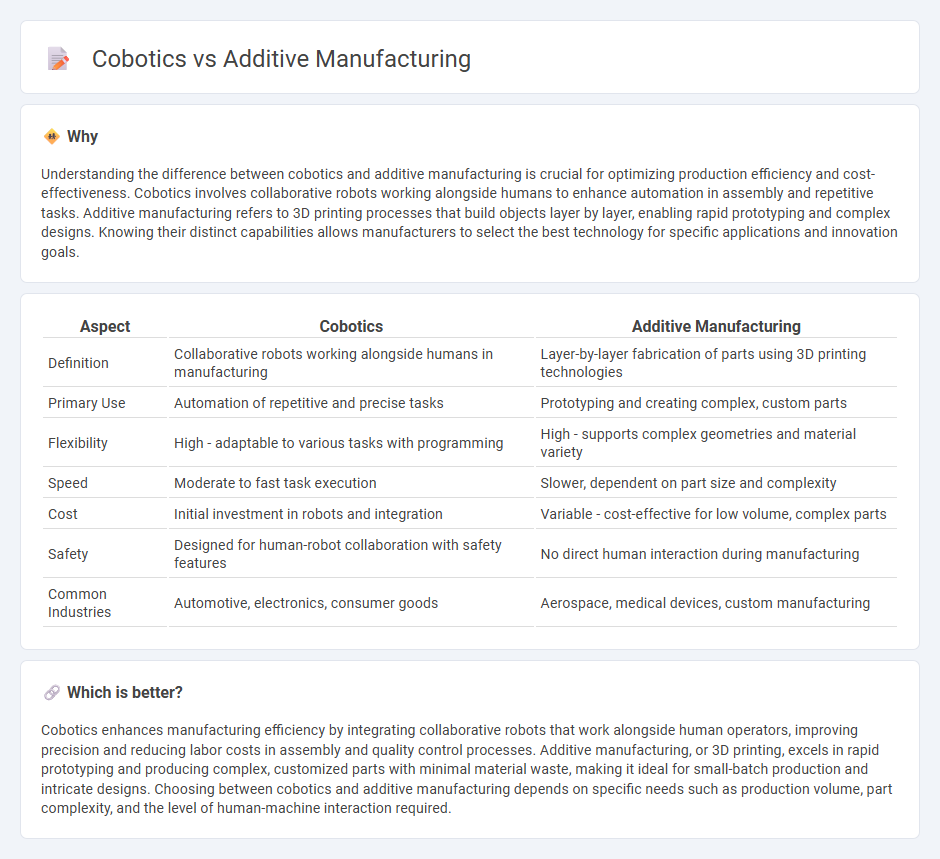
Understanding the difference between cobotics and additive manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Cobotics involves collaborative robots working alongside humans to enhance automation in assembly and repetitive tasks. Additive manufacturing refers to 3D printing processes that build objects layer by layer, enabling rapid prototyping and complex designs. Knowing their distinct capabilities allows manufacturers to select the best technology for specific applications and innovation goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cobotics | Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborative robots working alongside humans in manufacturing | Layer-by-layer fabrication of parts using 3D printing technologies |
| Primary Use | Automation of repetitive and precise tasks | Prototyping and creating complex, custom parts |
| Flexibility | High - adaptable to various tasks with programming | High - supports complex geometries and material variety |
| Speed | Moderate to fast task execution | Slower, dependent on part size and complexity |
| Cost | Initial investment in robots and integration | Variable - cost-effective for low volume, complex parts |
| Safety | Designed for human-robot collaboration with safety features | No direct human interaction during manufacturing |
| Common Industries | Automotive, electronics, consumer goods | Aerospace, medical devices, custom manufacturing |
Which is better?
Cobotics enhances manufacturing efficiency by integrating collaborative robots that work alongside human operators, improving precision and reducing labor costs in assembly and quality control processes. Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, excels in rapid prototyping and producing complex, customized parts with minimal material waste, making it ideal for small-batch production and intricate designs. Choosing between cobotics and additive manufacturing depends on specific needs such as production volume, part complexity, and the level of human-machine interaction required.
Connection
Cobotics enhances additive manufacturing by enabling human-robot collaboration that improves precision and efficiency in 3D printing processes. Collaborative robots assist in tasks such as material handling and post-processing, reducing production time and minimizing errors. These integrated technologies drive innovation in manufacturing by increasing flexibility and enabling customized, small-batch production.
Key Terms
3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
3D printing, a core technology in additive manufacturing, builds objects layer by layer from digital models, enabling rapid prototyping and complex geometries unattainable by traditional methods. Cobotics integrates collaborative robots with human workers to enhance precision, efficiency, and safety in manufacturing environments, often supporting additive processes by handling post-print tasks like assembly and inspection. Explore the evolving synergy between 3D printing and cobotics to unlock new productivity and innovation opportunities in advanced manufacturing.
Human-Robot Collaboration (Cobotics)
Human-robot collaboration (cobotics) enhances manufacturing by enabling robots and humans to work safely side-by-side, increasing productivity and flexibility in complex tasks. Additive manufacturing, while revolutionizing production through layer-by-layer material addition for custom and rapid prototyping, relies primarily on machine autonomy rather than direct human-robot interaction. Explore how cobotics transforms assembly processes and complements additive manufacturing to drive innovation in Industry 4.0.
Automation
Additive manufacturing automates the production process by creating complex parts layer by layer, significantly reducing material waste and enabling rapid prototyping with high precision. Cobotics enhances automation by integrating collaborative robots that work safely alongside humans, optimizing tasks such as assembly, quality control, and material handling. Explore how these technologies complement each other to revolutionize industrial automation.
Source and External Links
Additive manufacturing, explained | MIT Sloan - Additive manufacturing creates objects by building them layer by layer from digital designs, commonly known as 3D printing, and has evolved from rapid prototyping in the 1980s to producing functional products today using diverse materials like polymers, metals, ceramics, and biomaterials.
Additive manufacturing | NIST - Additive manufacturing (AM), or 3D printing, fabricates complex 3D products layer-by-layer from digital designs, producing less waste and enabling applications like aerospace lightweighting and customized biomedical implants, using materials such as metals, plastics, and ceramics.
What Is Additive Manufacturing? | 3D Printing Simulation Software - Additive manufacturing builds three-dimensional objects by layering materials from CAD models with various technologies including powder bed fusion, material extrusion, binder jetting, photopolymerization, and direct energy deposition, each suited to different materials and production needs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com