Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines repetitive digital tasks by mimicking human interactions with software, enhancing administrative efficiency within manufacturing operations. Industrial automation focuses on the physical machinery and control systems that automate manufacturing processes, improving production speed, accuracy, and safety. Explore how integrating RPA and industrial automation can revolutionize manufacturing workflows and drive operational excellence.
Why it is important
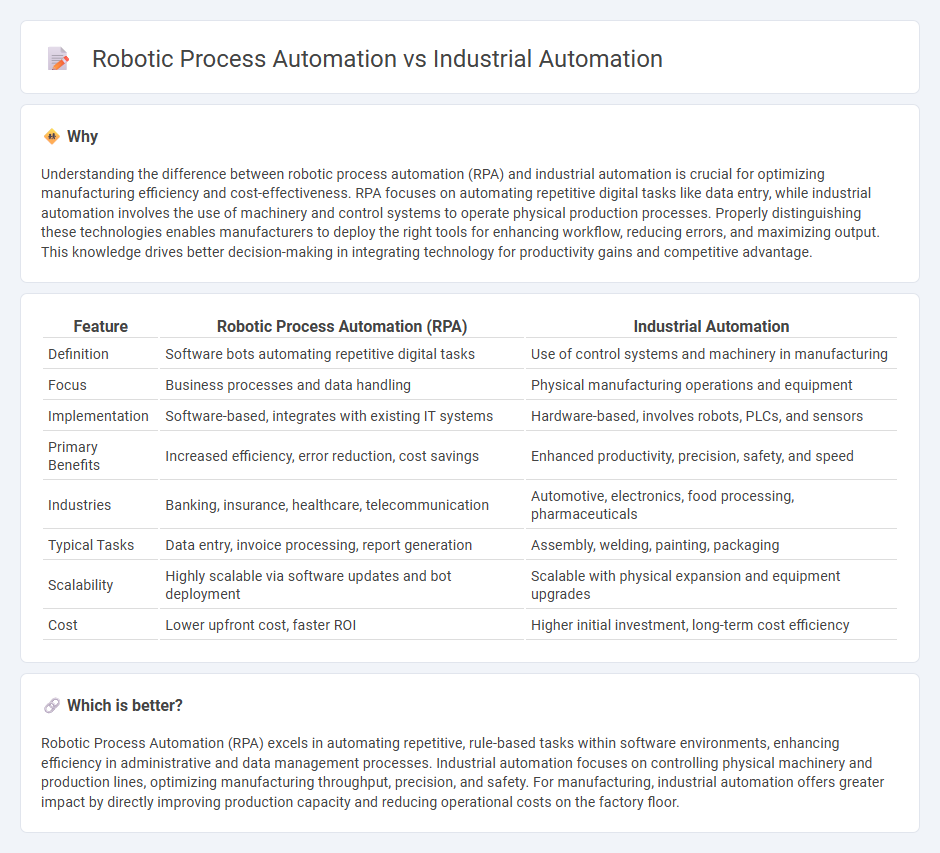
Understanding the difference between robotic process automation (RPA) and industrial automation is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and cost-effectiveness. RPA focuses on automating repetitive digital tasks like data entry, while industrial automation involves the use of machinery and control systems to operate physical production processes. Properly distinguishing these technologies enables manufacturers to deploy the right tools for enhancing workflow, reducing errors, and maximizing output. This knowledge drives better decision-making in integrating technology for productivity gains and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Industrial Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software bots automating repetitive digital tasks | Use of control systems and machinery in manufacturing |
| Focus | Business processes and data handling | Physical manufacturing operations and equipment |
| Implementation | Software-based, integrates with existing IT systems | Hardware-based, involves robots, PLCs, and sensors |
| Primary Benefits | Increased efficiency, error reduction, cost savings | Enhanced productivity, precision, safety, and speed |
| Industries | Banking, insurance, healthcare, telecommunication | Automotive, electronics, food processing, pharmaceuticals |
| Typical Tasks | Data entry, invoice processing, report generation | Assembly, welding, painting, packaging |
| Scalability | Highly scalable via software updates and bot deployment | Scalable with physical expansion and equipment upgrades |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost, faster ROI | Higher initial investment, long-term cost efficiency |
Which is better?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) excels in automating repetitive, rule-based tasks within software environments, enhancing efficiency in administrative and data management processes. Industrial automation focuses on controlling physical machinery and production lines, optimizing manufacturing throughput, precision, and safety. For manufacturing, industrial automation offers greater impact by directly improving production capacity and reducing operational costs on the factory floor.
Connection
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Industrial Automation both streamline manufacturing workflows by integrating software-driven robot control with physical machinery operations, enhancing efficiency and precision. RPA handles repetitive digital tasks such as data entry and process monitoring, while Industrial Automation encompasses the use of robotics, sensors, and control systems to automate hardware equipment and production lines. Their synergy enables seamless coordination between digital processes and physical manufacturing systems, reducing downtime and increasing productivity in smart factories.
Key Terms
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
Industrial automation primarily utilizes Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) to control machinery and processes on factory floors, ensuring real-time, reliable automation of physical equipment. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates rule-based, repetitive tasks in software environments without involving PLCs or direct interactions with hardware. Explore further to understand how PLCs differentiate industrial automation from software-driven RPA solutions.
Human-Machine Interface (HMI)
Industrial automation integrates Human-Machine Interface (HMI) to streamline complex machinery control, emphasizing real-time data visualization and manual override capabilities for enhanced operational safety. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) employs HMI primarily in software environments to facilitate user interactions with automated workflows and monitor digital processes, boosting efficiency in repetitive tasks. Explore how optimizing HMI designs can transform performance in both automation domains.
Software Bots
Industrial automation utilizes machinery and control systems to perform manufacturing tasks, enhancing production efficiency and reducing human intervention. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) leverages software bots to automate repetitive, rule-based digital tasks across business applications, improving accuracy and operational speed. Explore the distinct roles and benefits of software bots in transforming industrial and digital workflows.
Source and External Links
What is Industrial Automation? - Industrial automation uses robotics, machines, and control systems to perform tasks traditionally done by humans, improving productivity, quality, and safety in manufacturing and industrial processes through technologies like PLCs, CNC systems, and industrial sensors.
Industrial Automation: What Is It? - Industrial automation involves control systems, computers, and robots to handle manufacturing processes, with a modern focus on enhancing quality and flexibility rather than just productivity and cost reduction.
What is Industrial Automation? Programmable Logic ... - It defines industrial automation as technology-driven automatic operation of industrial machinery using control devices like PLCs and robotics, which reduces human error and improves reliability and system performance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com