Human augmentation enhances worker capabilities through advanced technologies like exoskeletons and neural interfaces, improving precision and reducing fatigue in manufacturing processes. Robotic automation employs AI-driven machines and robotic arms to perform repetitive tasks, increasing efficiency and consistency on production lines. Explore the evolving synergy between human augmentation and robotic automation to revolutionize manufacturing productivity.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between human augmentation and robotic automation is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and workforce integration. Human augmentation enhances workers' capabilities using technology, improving precision and reducing fatigue. Robotic automation replaces repetitive tasks with machines, boosting production speed and consistency. Differentiating these strategies enables manufacturers to balance productivity gains with workforce development and cost management.
Comparison Table
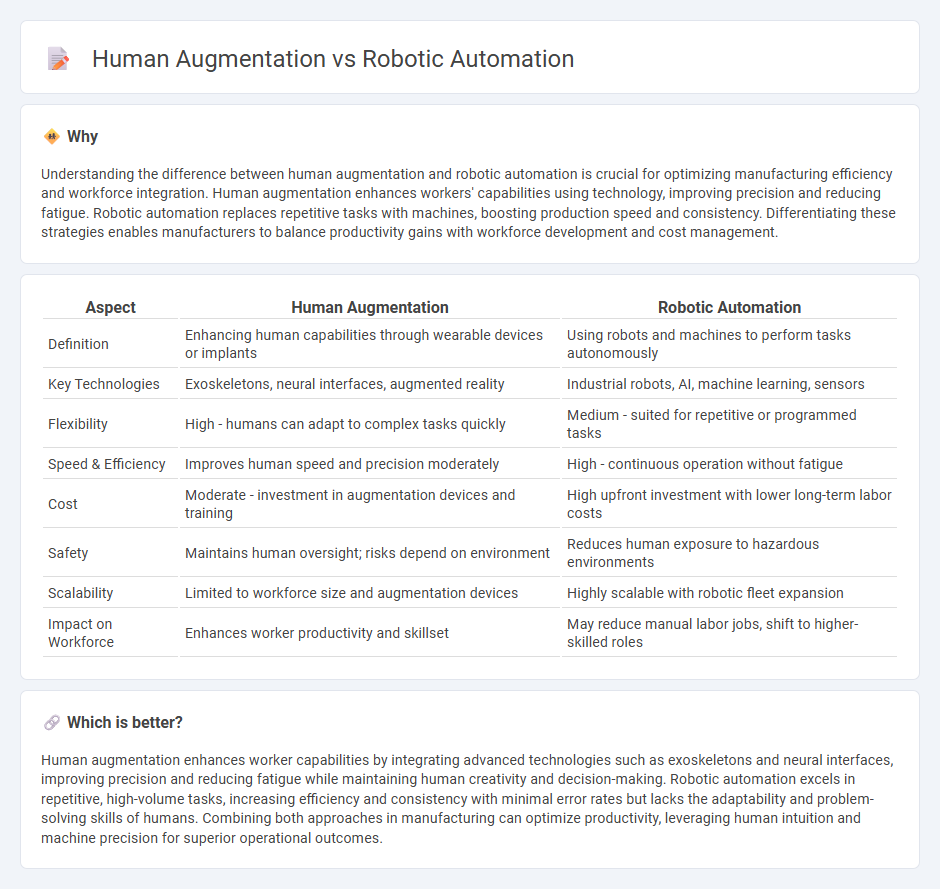
| Aspect | Human Augmentation | Robotic Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Enhancing human capabilities through wearable devices or implants | Using robots and machines to perform tasks autonomously |
| Key Technologies | Exoskeletons, neural interfaces, augmented reality | Industrial robots, AI, machine learning, sensors |
| Flexibility | High - humans can adapt to complex tasks quickly | Medium - suited for repetitive or programmed tasks |
| Speed & Efficiency | Improves human speed and precision moderately | High - continuous operation without fatigue |
| Cost | Moderate - investment in augmentation devices and training | High upfront investment with lower long-term labor costs |
| Safety | Maintains human oversight; risks depend on environment | Reduces human exposure to hazardous environments |
| Scalability | Limited to workforce size and augmentation devices | Highly scalable with robotic fleet expansion |
| Impact on Workforce | Enhances worker productivity and skillset | May reduce manual labor jobs, shift to higher-skilled roles |
Which is better?
Human augmentation enhances worker capabilities by integrating advanced technologies such as exoskeletons and neural interfaces, improving precision and reducing fatigue while maintaining human creativity and decision-making. Robotic automation excels in repetitive, high-volume tasks, increasing efficiency and consistency with minimal error rates but lacks the adaptability and problem-solving skills of humans. Combining both approaches in manufacturing can optimize productivity, leveraging human intuition and machine precision for superior operational outcomes.
Connection
Human augmentation enhances worker capabilities through wearable exoskeletons and neural interfaces, improving precision and endurance in manufacturing tasks. Robotic automation integrates these augmented human inputs with autonomous machines to optimize production efficiency and reduce error rates. The synergy between augmented humans and robots drives adaptive, flexible manufacturing systems that increase output and safety.
Key Terms
Robotic Automation:
Robotic automation refers to the use of robots and AI-driven machines to perform repetitive and precise tasks traditionally done by humans, significantly enhancing productivity and reducing operational costs. Industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics benefit from automated systems that improve accuracy, speed, and safety while minimizing human error and fatigue. Explore the latest advancements in robotic automation to understand its transformative impact on diverse sectors.
Industrial Robots
Industrial robots enhance manufacturing efficiency by automating repetitive and hazardous tasks, reducing human error and operational costs. Human augmentation, through wearable exoskeletons and advanced interfaces, empowers workers with increased strength and precision while maintaining cognitive control. Explore more to understand the impact of these technologies on industry productivity and workforce dynamics.
Automated Production Lines
Automated production lines leverage robotic automation to enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and maintain consistent output, often outperforming human capabilities in repetitive tasks and hazardous environments. Human augmentation integrates wearable technology and AI-powered tools to amplify workers' physical and cognitive functions, ensuring greater precision and adaptability in complex manufacturing processes. Explore the evolving impact of these technologies on industrial productivity and workforce dynamics.
Source and External Links
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)? - IBM - Robotic Process Automation (RPA) uses intelligent automation technologies and software robots to perform repetitive office tasks by emulating human actions, enabling organizations to increase efficiency and free human workers for more complex work, with advances expanding into intelligent automation including AI and machine learning integration.
Robot Automation | Rockwell Automation | US - Robot automation involves programmable robots performing repetitive, high-precision manufacturing tasks like assembly, welding, and packaging to boost efficiency, accuracy, safety, and reduce costs in industrial settings.
What is Robotic Process Automation - RPA Software - UiPath - RPA software robots emulate human interactions with digital systems to automate repetitive tasks faster and more reliably, increasingly incorporating AI technologies such as machine learning and natural language processing to enable broader automation capabilities beyond simple rule-based operations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com