Lights out factories operate with fully automated production processes, minimizing human intervention to increase efficiency and reduce errors, while lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste and optimizing workflows through continuous improvement and employee involvement. Both methodologies aim to enhance productivity and product quality but differ in their reliance on technology and human factors. Explore the benefits and applications of each approach to identify the best fit for your manufacturing needs.
Why it is important
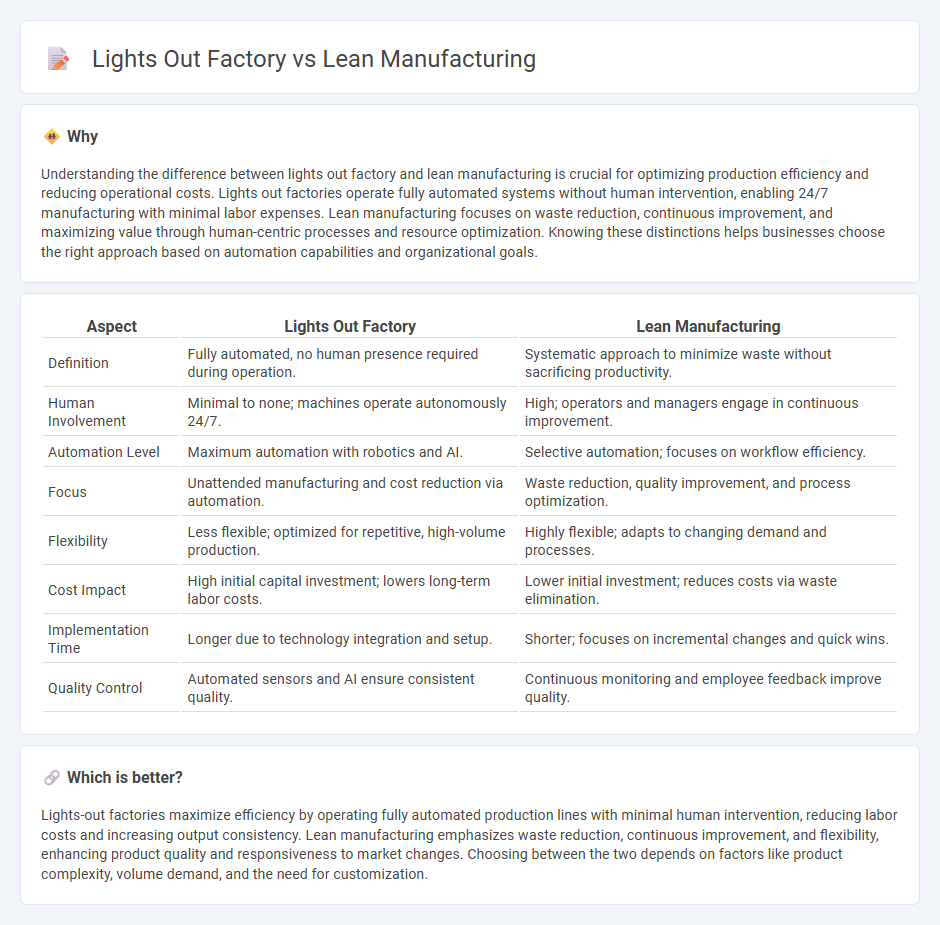
Understanding the difference between lights out factory and lean manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and reducing operational costs. Lights out factories operate fully automated systems without human intervention, enabling 24/7 manufacturing with minimal labor expenses. Lean manufacturing focuses on waste reduction, continuous improvement, and maximizing value through human-centric processes and resource optimization. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses choose the right approach based on automation capabilities and organizational goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Lights Out Factory | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated, no human presence required during operation. | Systematic approach to minimize waste without sacrificing productivity. |
| Human Involvement | Minimal to none; machines operate autonomously 24/7. | High; operators and managers engage in continuous improvement. |
| Automation Level | Maximum automation with robotics and AI. | Selective automation; focuses on workflow efficiency. |
| Focus | Unattended manufacturing and cost reduction via automation. | Waste reduction, quality improvement, and process optimization. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; optimized for repetitive, high-volume production. | Highly flexible; adapts to changing demand and processes. |
| Cost Impact | High initial capital investment; lowers long-term labor costs. | Lower initial investment; reduces costs via waste elimination. |
| Implementation Time | Longer due to technology integration and setup. | Shorter; focuses on incremental changes and quick wins. |
| Quality Control | Automated sensors and AI ensure consistent quality. | Continuous monitoring and employee feedback improve quality. |
Which is better?
Lights-out factories maximize efficiency by operating fully automated production lines with minimal human intervention, reducing labor costs and increasing output consistency. Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction, continuous improvement, and flexibility, enhancing product quality and responsiveness to market changes. Choosing between the two depends on factors like product complexity, volume demand, and the need for customization.
Connection
Lights out factories leverage automation and robotics to operate with minimal or no human intervention, aligning closely with lean manufacturing principles that aim to eliminate waste and maximize efficiency. Both approaches focus on streamlining production processes, reducing labor costs, and improving product quality through continuous improvement and just-in-time production methods. Implementing lights out technology enhances lean manufacturing by enabling 24/7 operations, minimizing downtime, and optimizing resource utilization.
Key Terms
**Lean Manufacturing:**
Lean manufacturing prioritizes minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency through continuous improvement, employing techniques such as Just-In-Time inventory, value stream mapping, and Kaizen events. This methodology enhances product quality and reduces lead times by empowering employees and optimizing workflow. Explore how lean manufacturing transforms operational productivity and cost savings.
Value Stream Mapping
Lean manufacturing emphasizes eliminating waste through continuous improvement and value stream mapping (VSM), which identifies and optimizes every step of the production process. In contrast, lights-out factories prioritize full automation and minimal human intervention, using VSM to streamline robotic operations and reduce downtime. Explore how integrating value stream mapping in these approaches can enhance efficiency and productivity.
Just-In-Time (JIT)
Lean manufacturing emphasizes Just-In-Time (JIT) production to minimize inventory and reduce waste by producing only what is needed, when it is needed. Lights out factories leverage automation and JIT principles to operate with minimal human intervention, ensuring streamlined processes and continuous flow. Explore how integrating JIT within these strategies can optimize efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Source and External Links
Lean manufacturing - A method focused on reducing production and supplier response times by minimizing waste, related to the Toyota Production System and just-in-time manufacturing, targeting seven key wastes like overproduction and defects.
What is Lean Manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - A methodology to minimize waste while maximizing productivity in manufacturing, based on Toyota's system and principles such as Kaizen, with broad application beyond manufacturing.
What is Lean Manufacturing and the 5 Principles Used? - TWI - Defines lean as maximizing productivity and minimizing waste through five core principles: value, value stream, flow, pull, and perfection, emphasizing a trained workforce and supplier network.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com