Additive manufacturing builds objects layer by layer using digital models, enabling intricate designs and rapid prototyping with minimal material waste. Injection molding injects molten material into molds for mass production, offering high precision and fast cycle times at scale. Explore the advantages and applications of both technologies to determine the best fit for your manufacturing needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between additive manufacturing and injection molding is crucial for selecting the optimal production method based on cost, complexity, and volume requirements. Additive manufacturing excels in producing complex, customized parts with minimal waste, while injection molding is ideal for high-volume, consistent output with low per-unit cost. Knowledge of these methods impacts lead times, material selection, and scalability in manufacturing processes. Making informed decisions enhances product quality, reduces production costs, and accelerates time-to-market.
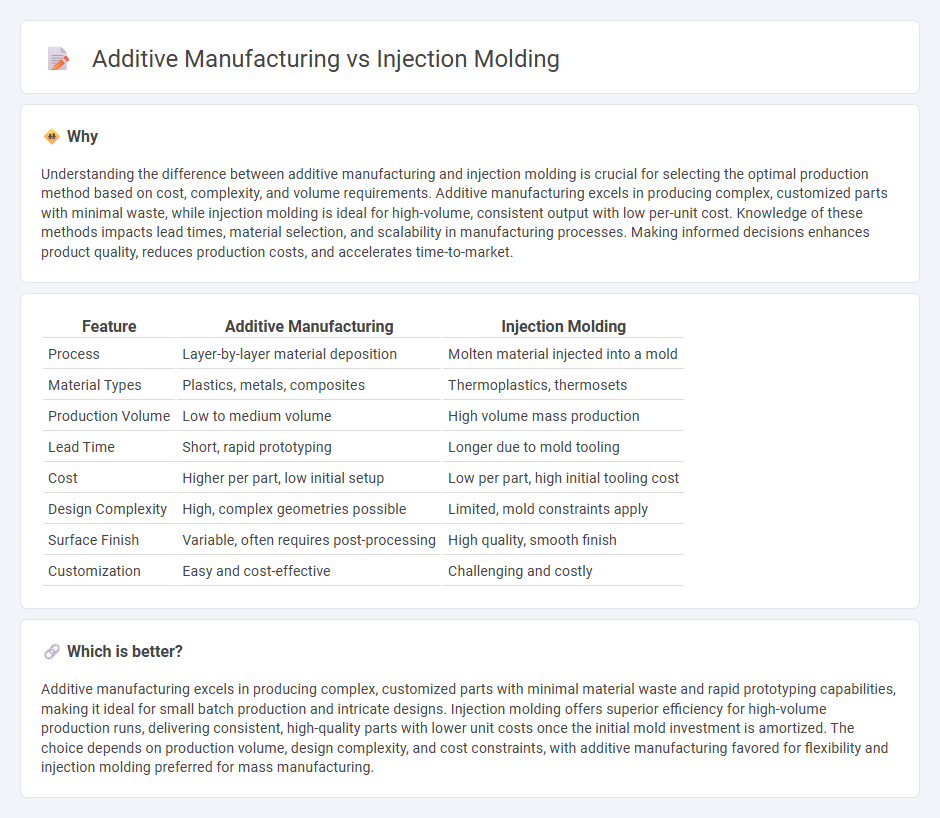
Comparison Table
| Feature | Additive Manufacturing | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Layer-by-layer material deposition | Molten material injected into a mold |
| Material Types | Plastics, metals, composites | Thermoplastics, thermosets |
| Production Volume | Low to medium volume | High volume mass production |
| Lead Time | Short, rapid prototyping | Longer due to mold tooling |
| Cost | Higher per part, low initial setup | Low per part, high initial tooling cost |
| Design Complexity | High, complex geometries possible | Limited, mold constraints apply |
| Surface Finish | Variable, often requires post-processing | High quality, smooth finish |
| Customization | Easy and cost-effective | Challenging and costly |
Which is better?
Additive manufacturing excels in producing complex, customized parts with minimal material waste and rapid prototyping capabilities, making it ideal for small batch production and intricate designs. Injection molding offers superior efficiency for high-volume production runs, delivering consistent, high-quality parts with lower unit costs once the initial mold investment is amortized. The choice depends on production volume, design complexity, and cost constraints, with additive manufacturing favored for flexibility and injection molding preferred for mass manufacturing.
Connection
Additive manufacturing and injection molding are connected through their shared role in producing complex, high-precision parts, with additive manufacturing often used to create prototypes or molds for injection molding. Injection molding relies on molds that can be quickly developed and iterated using 3D-printed tooling from additive manufacturing, reducing lead times and costs. This synergy enhances manufacturing efficiency by combining the rapid design flexibility of additive processes with the high-volume production capability of injection molding.
Key Terms
Mold (Injection Molding)
Injection molding relies on precision-engineered molds made from durable materials like steel or aluminum to produce high volumes of identical parts with exceptional surface finish and dimensional accuracy. These molds involve significant upfront costs and lead times but ensure rapid cycle times and consistent quality for mass production. Explore the advantages and detailed design considerations of injection molding molds to optimize your manufacturing process.
Layer-by-Layer (Additive Manufacturing)
Injection molding produces parts by forcing molten material into a mold cavity, offering high-volume production with excellent surface finish and consistent mechanical properties. Layer-by-layer additive manufacturing builds components by depositing material sequentially, allowing for complex geometries, customization, and reduced material waste. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which manufacturing process suits your specific application needs.
Cycle Time
Injection molding offers significantly faster cycle times, often ranging from 15 to 60 seconds per part, making it ideal for high-volume production. Additive manufacturing, depending on the technology used, typically requires minutes to hours per part due to layer-by-layer material deposition, resulting in slower throughput. Discover detailed comparisons and process optimizations to choose the best technique for your production needs.
Source and External Links
Injection moulding - Wikipedia - Injection molding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, suitable for materials like plastics, metals, and elastomers, widely used for producing a variety of parts from small components to car body panels.
The outline of injection molding - Polyplastics - Injection molding involves melting plastic materials, injecting the molten plastic into a mold where it cools and solidifies, and is ideal for mass producing products with complex shapes through a cycle of clamping, injection, dwelling, cooling, mold opening, and product removal.
Custom Plastic Injection Molding | Order Parts Online - Protolabs - Plastic injection molding produces custom prototypes and production parts by melting resin pellets and injecting the hot resin into a mold cavity, with automated quality control processes to ensure dimensional accuracy and part consistency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com