Condition monitoring involves the continuous assessment of equipment health through real-time data collection to predict potential failures and optimize maintenance schedules. Fault diagnosis focuses on identifying the root causes and specific issues once a malfunction or abnormal condition has been detected, enabling targeted repairs and minimizing downtime. Explore the differences and advantages of each method to enhance manufacturing efficiency.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between condition monitoring and fault diagnosis is crucial in manufacturing to enhance equipment reliability and minimize downtime. Condition monitoring involves real-time tracking of equipment health using sensors and data analytics to detect potential issues before they escalate. Fault diagnosis specifically identifies and classifies existing faults to enable targeted maintenance and rapid repairs. Distinguishing these processes optimizes predictive maintenance strategies, reduces operational costs, and improves production efficiency.
Comparison Table
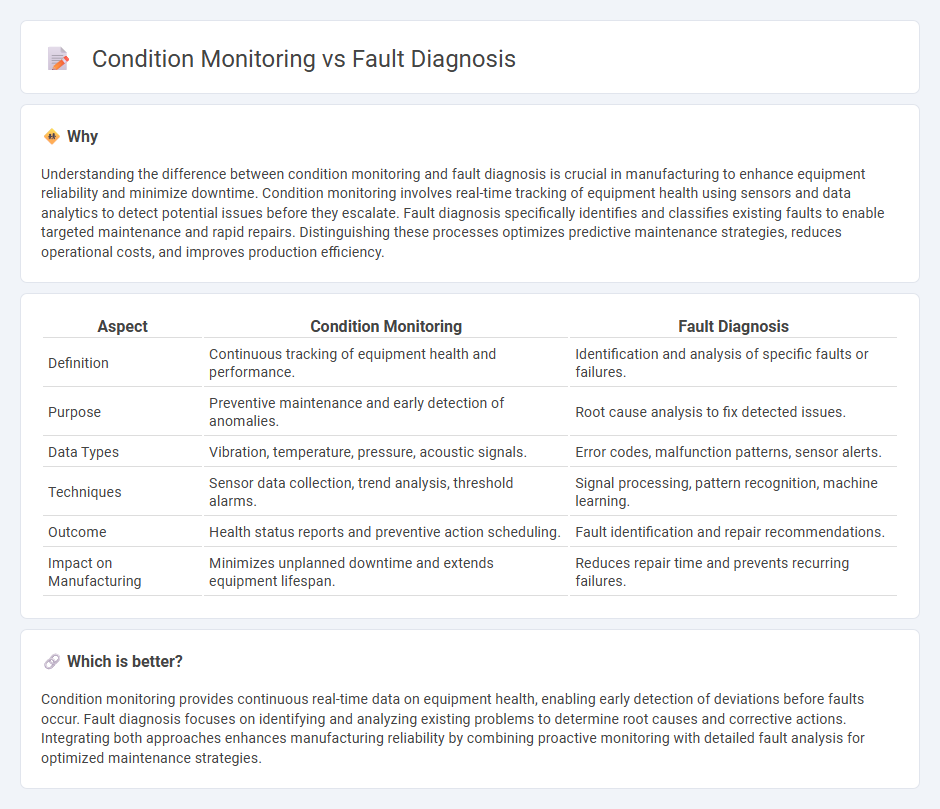
| Aspect | Condition Monitoring | Fault Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous tracking of equipment health and performance. | Identification and analysis of specific faults or failures. |
| Purpose | Preventive maintenance and early detection of anomalies. | Root cause analysis to fix detected issues. |
| Data Types | Vibration, temperature, pressure, acoustic signals. | Error codes, malfunction patterns, sensor alerts. |
| Techniques | Sensor data collection, trend analysis, threshold alarms. | Signal processing, pattern recognition, machine learning. |
| Outcome | Health status reports and preventive action scheduling. | Fault identification and repair recommendations. |
| Impact on Manufacturing | Minimizes unplanned downtime and extends equipment lifespan. | Reduces repair time and prevents recurring failures. |
Which is better?
Condition monitoring provides continuous real-time data on equipment health, enabling early detection of deviations before faults occur. Fault diagnosis focuses on identifying and analyzing existing problems to determine root causes and corrective actions. Integrating both approaches enhances manufacturing reliability by combining proactive monitoring with detailed fault analysis for optimized maintenance strategies.
Connection
Condition monitoring utilizes real-time data from sensors to track equipment performance and identify anomalies, enabling early detection of potential faults. Fault diagnosis interprets this sensor data through advanced algorithms to pinpoint the exact cause and location of equipment malfunctions. Together, these processes reduce downtime and optimize maintenance schedules in manufacturing operations.
Key Terms
Sensors
Fault diagnosis and condition monitoring both rely heavily on sensor technologies such as vibration sensors, temperature sensors, and acoustic sensors to detect anomalies and assess system health. Condition monitoring emphasizes continuous data collection to track equipment performance over time, enabling early intervention, while fault diagnosis involves analyzing sensor data to pinpoint specific faults or malfunctions after deviations occur. Explore the latest advancements in sensor-based diagnostic systems to enhance predictive maintenance strategies.
Predictive Maintenance
Fault diagnosis identifies specific equipment malfunctions by analyzing symptom data, while condition monitoring continuously tracks machinery health parameters such as vibration, temperature, and pressure to detect early signs of deterioration. Predictive maintenance leverages both techniques, integrating real-time sensor data and advanced analytics to forecast failures and optimize maintenance schedules, reducing downtime and operational costs. Explore how combining fault diagnosis and condition monitoring enhances predictive maintenance strategies for improved asset reliability.
Root Cause Analysis
Fault diagnosis involves identifying the specific causes behind equipment malfunctions by analyzing system deviations and failure patterns, whereas condition monitoring continuously tracks machinery health using sensors to detect early signs of deterioration. Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is integral to fault diagnosis, enabling targeted corrective actions by pinpointing fundamental faults rather than symptoms detected during condition monitoring. Explore detailed methodologies and tools in RCA to enhance fault detection and prevention strategies.
Source and External Links
Fault Detection And Diagnostics In Equipment Maintenance - Covers the process of detecting, isolating, identifying, and evaluating faults in equipment to improve maintenance, emphasizing understanding failure modes and assessing fault severity for appropriate tolerance measures.
A Guide to Fault Detection and Diagnosis - Defines fault diagnosis as pinpointing the root cause(s) of system problems so corrective action can be taken, distinguishing between detection (recognizing a problem exists) and isolation (identifying the specific cause).
Fault detection and isolation - Wikipedia - Focuses on monitoring systems to detect and isolate faults, particularly in mechanical engineering where advanced data analysis techniques (e.g., vibration, thermal, oil analysis) are used to diagnose and address root causes of machine failures.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com