Circular manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste by reusing materials and designing products for longevity, promoting sustainability throughout the production lifecycle. Lean manufacturing emphasizes efficiency by eliminating non-value-added processes, reducing costs, and improving workflow to maximize productivity. Discover how integrating these strategies can revolutionize your manufacturing operations.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between circular manufacturing and lean manufacturing is crucial for optimizing resource use and minimizing waste in production processes. Circular manufacturing focuses on sustainability by promoting reuse, recycling, and regeneration of materials to create a closed-loop system. Lean manufacturing aims to improve efficiency by eliminating non-value-added activities and reducing operational waste. Recognizing these distinctions enables businesses to implement strategies that align with their environmental and operational goals.
Comparison Table
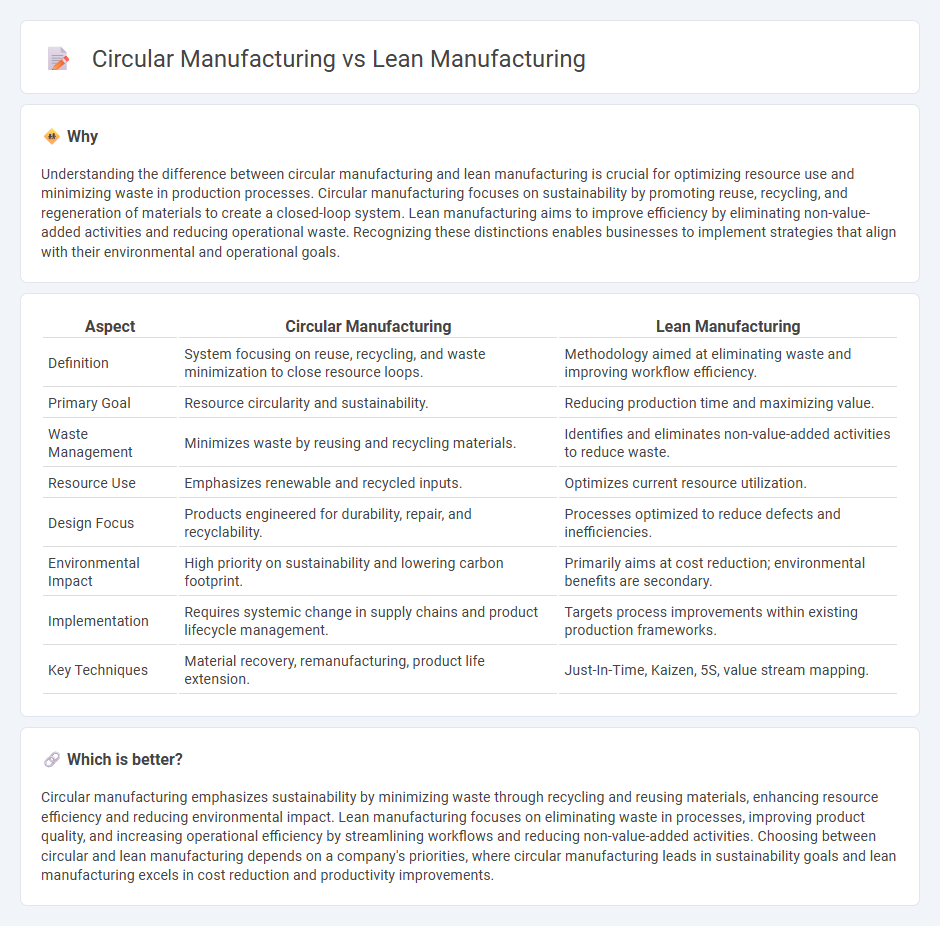
| Aspect | Circular Manufacturing | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | System focusing on reuse, recycling, and waste minimization to close resource loops. | Methodology aimed at eliminating waste and improving workflow efficiency. |
| Primary Goal | Resource circularity and sustainability. | Reducing production time and maximizing value. |
| Waste Management | Minimizes waste by reusing and recycling materials. | Identifies and eliminates non-value-added activities to reduce waste. |
| Resource Use | Emphasizes renewable and recycled inputs. | Optimizes current resource utilization. |
| Design Focus | Products engineered for durability, repair, and recyclability. | Processes optimized to reduce defects and inefficiencies. |
| Environmental Impact | High priority on sustainability and lowering carbon footprint. | Primarily aims at cost reduction; environmental benefits are secondary. |
| Implementation | Requires systemic change in supply chains and product lifecycle management. | Targets process improvements within existing production frameworks. |
| Key Techniques | Material recovery, remanufacturing, product life extension. | Just-In-Time, Kaizen, 5S, value stream mapping. |
Which is better?
Circular manufacturing emphasizes sustainability by minimizing waste through recycling and reusing materials, enhancing resource efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste in processes, improving product quality, and increasing operational efficiency by streamlining workflows and reducing non-value-added activities. Choosing between circular and lean manufacturing depends on a company's priorities, where circular manufacturing leads in sustainability goals and lean manufacturing excels in cost reduction and productivity improvements.
Connection
Circular manufacturing and lean manufacturing both emphasize waste reduction to improve efficiency and sustainability. Circular manufacturing focuses on designing products and processes that enable reuse, recycling, and remanufacturing of materials, while lean manufacturing targets eliminating non-value-added activities and minimizing resource consumption in production. Integrating principles from both approaches results in streamlined operations that reduce environmental impact and enhance resource circularity throughout the product lifecycle.
Key Terms
Waste Reduction (Lean)
Lean manufacturing targets waste reduction by eliminating non-value-added activities and optimizing resource use, focusing on minimizing defects, overproduction, and excess inventory. Circular manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction through material reuse, recycling, and designing products for longevity and remanufacturability, enhancing sustainability and resource efficiency. Explore more to understand how these methodologies complement each other in creating efficient and eco-friendly production systems.
Resource Recirculation (Circular)
Lean manufacturing minimizes waste by improving process efficiency and reducing non-value-added activities, while circular manufacturing prioritizes resource recirculation through recycling, reuse, and regeneration of materials within product life cycles. Circular manufacturing extends product lifespan and supports sustainable resource management by designing products for disassembly and encouraging closed-loop supply chains. Discover how integrating circular manufacturing principles can revolutionize your approach to sustainability and resource optimization.
Continuous Improvement (Lean)
Lean manufacturing emphasizes continuous improvement by systematically eliminating waste and optimizing processes to enhance efficiency and reduce costs in production. Circular manufacturing integrates continuous improvement with sustainable practices, focusing on resource regeneration, waste minimization, and product lifecycle extension for environmental benefits. Explore the differences in continuous improvement strategies between lean and circular manufacturing to boost operational sustainability.
Source and External Links
Lean manufacturing - Wikipedia - Lean manufacturing is a method aimed at reducing production and response times by eliminating wastes and emphasizing continuous improvement, originally developed as the Toyota Production System.
What is Lean Manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - Lean manufacturing minimizes waste while maximizing productivity, with principles like Kaizen, and is widely adopted by companies such as Toyota, Intel, and Nike.
What is Lean Manufacturing and the 5 Principles Used? - TWI - Lean manufacturing is based on five core principles--value, value stream, flow, pull, and perfection--focusing on maximizing productivity by eliminating non-value-adding activities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com