Industrial symbiosis focuses on resource sharing between different industries to minimize waste and enhance sustainability, while lean manufacturing aims to eliminate internal process inefficiencies by reducing waste and improving productivity within a single organization. Both strategies prioritize waste reduction but differ in scope, with industrial symbiosis emphasizing inter-industry collaboration and lean manufacturing targeting streamlined internal operations. Explore more to understand how integrating these approaches can revolutionize your manufacturing processes.
Why it is important
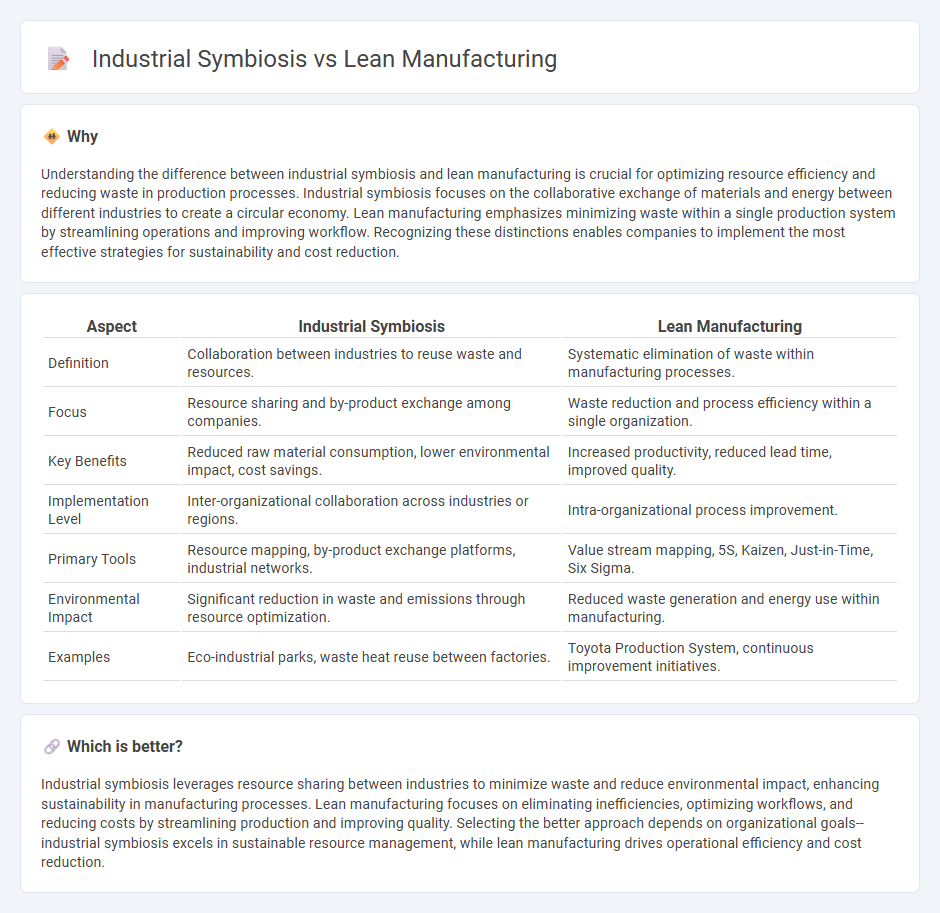
Understanding the difference between industrial symbiosis and lean manufacturing is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and reducing waste in production processes. Industrial symbiosis focuses on the collaborative exchange of materials and energy between different industries to create a circular economy. Lean manufacturing emphasizes minimizing waste within a single production system by streamlining operations and improving workflow. Recognizing these distinctions enables companies to implement the most effective strategies for sustainability and cost reduction.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Industrial Symbiosis | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaboration between industries to reuse waste and resources. | Systematic elimination of waste within manufacturing processes. |
| Focus | Resource sharing and by-product exchange among companies. | Waste reduction and process efficiency within a single organization. |
| Key Benefits | Reduced raw material consumption, lower environmental impact, cost savings. | Increased productivity, reduced lead time, improved quality. |
| Implementation Level | Inter-organizational collaboration across industries or regions. | Intra-organizational process improvement. |
| Primary Tools | Resource mapping, by-product exchange platforms, industrial networks. | Value stream mapping, 5S, Kaizen, Just-in-Time, Six Sigma. |
| Environmental Impact | Significant reduction in waste and emissions through resource optimization. | Reduced waste generation and energy use within manufacturing. |
| Examples | Eco-industrial parks, waste heat reuse between factories. | Toyota Production System, continuous improvement initiatives. |
Which is better?
Industrial symbiosis leverages resource sharing between industries to minimize waste and reduce environmental impact, enhancing sustainability in manufacturing processes. Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating inefficiencies, optimizing workflows, and reducing costs by streamlining production and improving quality. Selecting the better approach depends on organizational goals--industrial symbiosis excels in sustainable resource management, while lean manufacturing drives operational efficiency and cost reduction.
Connection
Industrial symbiosis and lean manufacturing are interconnected through their shared goal of minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency in production processes. Industrial symbiosis promotes the exchange of materials, energy, and by-products between different industries, while lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating non-value-added activities within a single production system. Together, they create a sustainable manufacturing ecosystem that reduces environmental impact and operational costs.
Key Terms
Waste Reduction (Lean Manufacturing)
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction by minimizing non-value-added activities through techniques such as Just-in-Time, 5S, and Kaizen, leading to improved efficiency and lower production costs. Industrial symbiosis focuses on waste reduction by facilitating the exchange of by-products and resources between industries, creating a closed-loop system that minimizes environmental impact. Explore how integrating these approaches can maximize sustainability and operational efficiency.
Resource Sharing (Industrial Symbiosis)
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction through efficient resource utilization within a single production system, while industrial symbiosis extends resource sharing across multiple industries by exchanging materials, energy, and by-products to create a circular economy. Industrial symbiosis enhances sustainability by connecting diverse enterprises to optimize resource flow, reduce environmental impact, and lower costs collectively. Explore how industrial symbiosis drives innovative resource sharing for greater economic and ecological benefits.
Continuous Improvement (Lean Manufacturing)
Lean manufacturing emphasizes continuous improvement by systematically eliminating waste and optimizing processes to enhance efficiency and product quality. Industrial symbiosis focuses on resource sharing and collaboration between industries to maximize sustainability and reduce environmental impact. Explore how integrating these strategies can drive innovation and operational excellence in manufacturing.
Source and External Links
Lean manufacturing - Wikipedia - Lean manufacturing is a method focused on reducing production and supplier response times by eliminating waste, improving efficiency, and continuously enhancing processes, rooted in the Toyota Production System with seven identified wastes to reduce.
What is Lean Manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - Lean manufacturing minimizes waste while maximizing productivity by following principles such as continuous improvement (Kaizen), benefiting industries beyond manufacturing such as healthcare and software.
What is Lean Manufacturing and the 5 Principles Used? - TWI - Lean manufacturing streamlines processes by focusing on five principles: value, value stream, flow, pull, and perfection to maximize productivity and reduce waste throughout production.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com