Smart dust consists of tiny wireless microelectromechanical sensors that can detect environmental data, offering real-time monitoring in manufacturing processes. RFID technology uses radio waves to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects, streamlining inventory management and supply chain operations. Explore the differences and benefits of smart dust versus RFID for smarter manufacturing solutions.
Why it is important
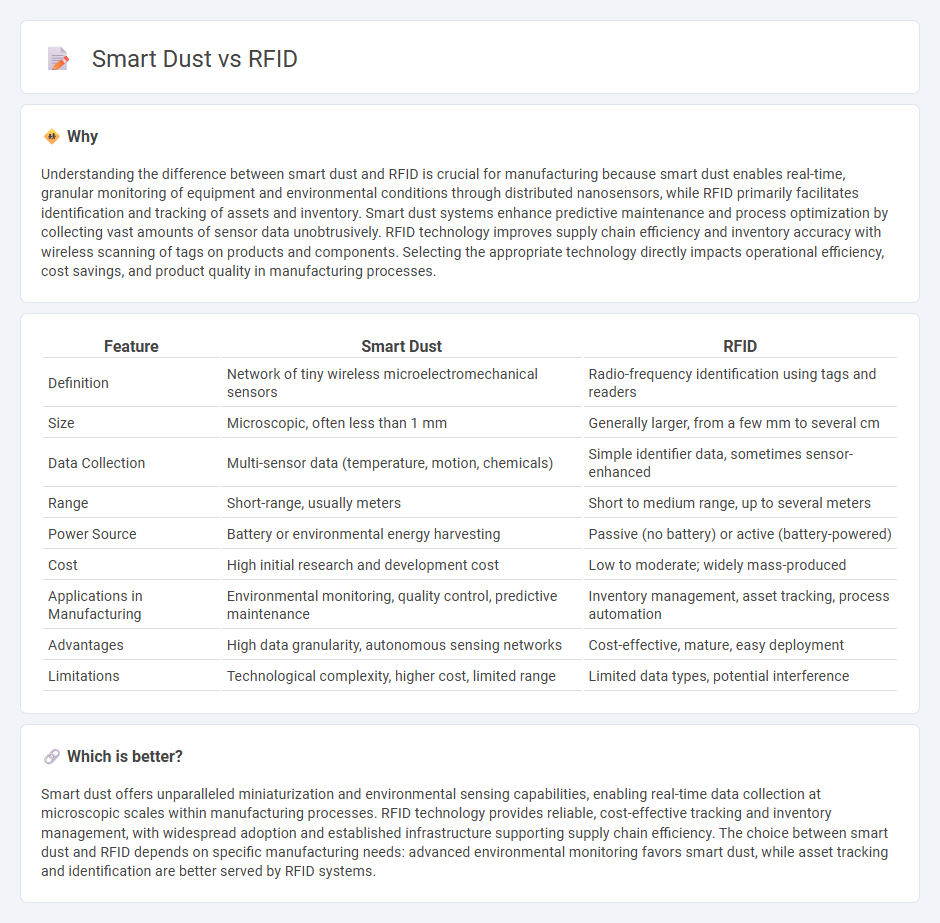
Understanding the difference between smart dust and RFID is crucial for manufacturing because smart dust enables real-time, granular monitoring of equipment and environmental conditions through distributed nanosensors, while RFID primarily facilitates identification and tracking of assets and inventory. Smart dust systems enhance predictive maintenance and process optimization by collecting vast amounts of sensor data unobtrusively. RFID technology improves supply chain efficiency and inventory accuracy with wireless scanning of tags on products and components. Selecting the appropriate technology directly impacts operational efficiency, cost savings, and product quality in manufacturing processes.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Smart Dust | RFID |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network of tiny wireless microelectromechanical sensors | Radio-frequency identification using tags and readers |
| Size | Microscopic, often less than 1 mm | Generally larger, from a few mm to several cm |
| Data Collection | Multi-sensor data (temperature, motion, chemicals) | Simple identifier data, sometimes sensor-enhanced |
| Range | Short-range, usually meters | Short to medium range, up to several meters |
| Power Source | Battery or environmental energy harvesting | Passive (no battery) or active (battery-powered) |
| Cost | High initial research and development cost | Low to moderate; widely mass-produced |
| Applications in Manufacturing | Environmental monitoring, quality control, predictive maintenance | Inventory management, asset tracking, process automation |
| Advantages | High data granularity, autonomous sensing networks | Cost-effective, mature, easy deployment |
| Limitations | Technological complexity, higher cost, limited range | Limited data types, potential interference |
Which is better?
Smart dust offers unparalleled miniaturization and environmental sensing capabilities, enabling real-time data collection at microscopic scales within manufacturing processes. RFID technology provides reliable, cost-effective tracking and inventory management, with widespread adoption and established infrastructure supporting supply chain efficiency. The choice between smart dust and RFID depends on specific manufacturing needs: advanced environmental monitoring favors smart dust, while asset tracking and identification are better served by RFID systems.
Connection
Smart dust and RFID technologies enhance manufacturing by enabling real-time asset tracking and environmental monitoring. Smart dust consists of tiny sensor particles that collect granular data on production conditions, while RFID tags provide identification and location information for inventory and equipment. Integrating both technologies optimizes supply chain management and predictive maintenance by offering comprehensive visibility throughout the manufacturing process.
Key Terms
Wireless Communication
RFID technology utilizes radio waves to identify and track objects through tags and readers, offering reliable wireless communication over short distances. Smart dust comprises tiny wireless sensors capable of sensing, computing, and communicating data within a network, enabling more complex environmental monitoring over wider areas. Explore the differences in wireless communication capabilities and applications between RFID and smart dust to understand their specific use cases.
Real-time Tracking
RFID technology enables real-time tracking by using electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects, providing accurate location data within a limited range. Smart dust consists of tiny wireless sensors that detect and transmit environmental data, offering scalable tracking capabilities with higher granularity and broader coverage in dynamic environments. Explore the advantages and applications of RFID and smart dust for optimal real-time tracking solutions.
Sensor Miniaturization
Sensor miniaturization advancements have propelled RFID technology into versatile applications, leveraging microchips and antennas for efficient wireless data transfer. Smart dust epitomizes extreme miniaturization by integrating nanoscale sensors, processors, and communication units into particles as small as a grain of sand, enabling widespread environmental monitoring. Explore further to understand how these contrasting approaches influence sensor deployment and data collection.
Source and External Links
Radio-frequency identification - Wikipedia - RFID uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects, consisting of a tag, reader, and transmitter; tags can be passive or active and are used widely for tracking inventory, animals, and preventing theft.
RFID (radio frequency identification) - TechTarget - RFID is a wireless communication method using radio waves for unique object identification via tags and readers, with read ranges depending on tag types, power, and environment.
What are RFID Tags, What are They Used for? - Camcode - RFID tags store information and communicate via radio waves, with active tags allowing location tracking up to 300 feet and passive tags requiring closer proximity, used in inventory management, access control, and logistics but subject to hacking and interference risks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com