Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data and advanced analytics to anticipate equipment failures before they occur, reducing unplanned downtime and maintenance costs. Reliability-centered maintenance (RCM) focuses on identifying critical systems and establishing maintenance priorities based on their function and potential failure modes to optimize asset reliability and safety. Explore how integrating predictive maintenance with RCM strategies can transform manufacturing efficiency and asset management.
Why it is important
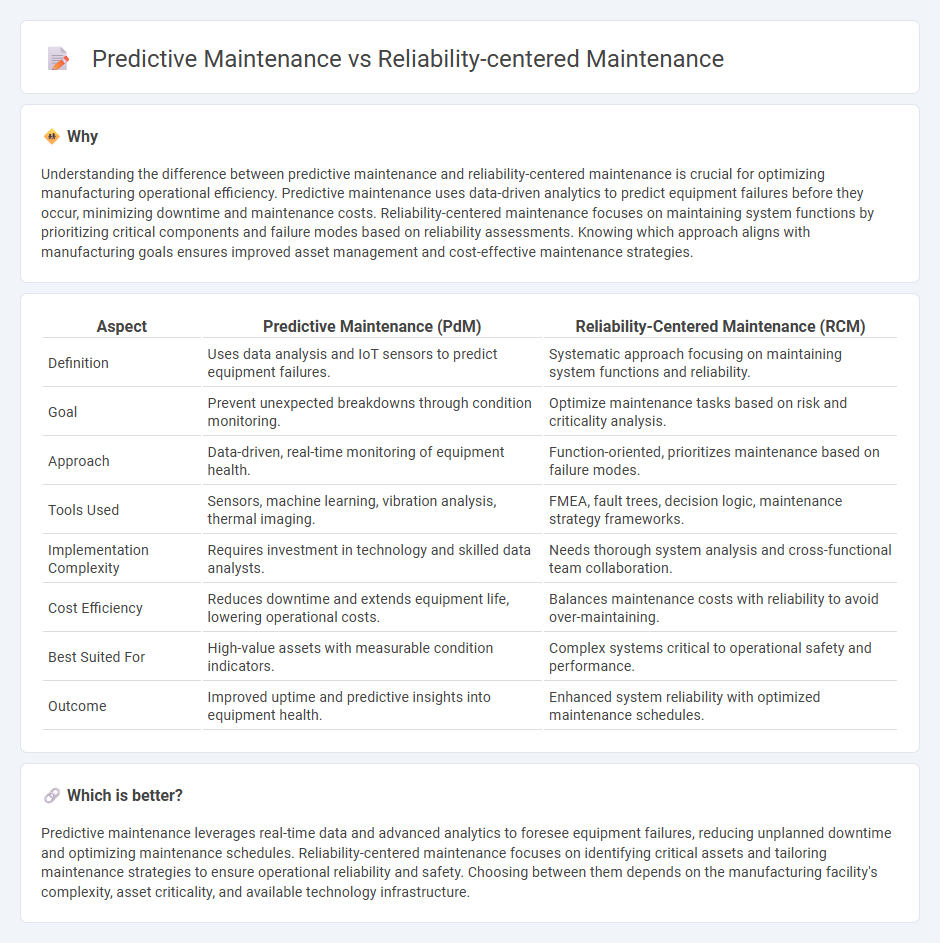
Understanding the difference between predictive maintenance and reliability-centered maintenance is crucial for optimizing manufacturing operational efficiency. Predictive maintenance uses data-driven analytics to predict equipment failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. Reliability-centered maintenance focuses on maintaining system functions by prioritizing critical components and failure modes based on reliability assessments. Knowing which approach aligns with manufacturing goals ensures improved asset management and cost-effective maintenance strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Predictive Maintenance (PdM) | Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses data analysis and IoT sensors to predict equipment failures. | Systematic approach focusing on maintaining system functions and reliability. |
| Goal | Prevent unexpected breakdowns through condition monitoring. | Optimize maintenance tasks based on risk and criticality analysis. |
| Approach | Data-driven, real-time monitoring of equipment health. | Function-oriented, prioritizes maintenance based on failure modes. |
| Tools Used | Sensors, machine learning, vibration analysis, thermal imaging. | FMEA, fault trees, decision logic, maintenance strategy frameworks. |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires investment in technology and skilled data analysts. | Needs thorough system analysis and cross-functional team collaboration. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces downtime and extends equipment life, lowering operational costs. | Balances maintenance costs with reliability to avoid over-maintaining. |
| Best Suited For | High-value assets with measurable condition indicators. | Complex systems critical to operational safety and performance. |
| Outcome | Improved uptime and predictive insights into equipment health. | Enhanced system reliability with optimized maintenance schedules. |
Which is better?
Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data and advanced analytics to foresee equipment failures, reducing unplanned downtime and optimizing maintenance schedules. Reliability-centered maintenance focuses on identifying critical assets and tailoring maintenance strategies to ensure operational reliability and safety. Choosing between them depends on the manufacturing facility's complexity, asset criticality, and available technology infrastructure.
Connection
Predictive maintenance leverages data analytics and real-time monitoring to forecast equipment failures, enhancing operational reliability by addressing issues before they escalate. Reliability-centered maintenance (RCM) focuses on identifying critical assets and prioritizing maintenance tactics to optimize equipment performance and safety. Together, these approaches create a comprehensive maintenance strategy that maximizes uptime, reduces costs, and ensures long-term manufacturing efficiency.
Key Terms
**Reliability-Centered Maintenance:**
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) emphasizes identifying critical assets and prioritizing maintenance tasks to ensure system reliability and safety, often using failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) to guide decisions. Unlike Predictive Maintenance, which relies on real-time condition monitoring and data analytics, RCM integrates both preventive and corrective strategies based on asset importance and risk assessment. Discover how RCM can optimize asset performance and reduce downtime by exploring its comprehensive framework.
Failure Modes
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) prioritizes identifying and addressing critical failure modes through systematic analysis to ensure system reliability and safety, while Predictive Maintenance (PdM) uses real-time data and condition-monitoring technologies to detect early signs of failure in components. RCM develops maintenance strategies based on failure impact, frequency, and consequences, targeting high-risk failure modes, whereas PdM focuses on predicting specific failure events using sensors and analytics for timely maintenance actions. Explore more about how understanding failure modes enhances maintenance effectiveness in both RCM and PdM frameworks.
Criticality Analysis
Reliability-centered maintenance (RCM) prioritizes maintenance tasks based on criticality analysis to ensure system reliability and safety by identifying failure modes that impact operations the most. Predictive maintenance (PdM) uses real-time data and condition monitoring to predict failures, focusing on equipment health but often less on overall criticality within the system. Explore detailed comparisons and methodologies to optimize maintenance strategies effectively.
Source and External Links
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) - RCM is the optimal mix of reactive, time-based, condition-based, and proactive maintenance practices designed to maximize equipment reliability while minimizing lifecycle costs by understanding system functions, failure modes, and boundaries.
Reliability-Centered Maintenance: What It Is & How ... - RCM is a preventive maintenance strategy aimed at identifying potential failure modes and preventing them, optimizing reliability and cost-effectiveness by tailoring maintenance techniques to each asset's criticality and failure risk.
Reliability-centered maintenance - RCM systematically defines maintenance tasks focusing on preserving critical functions by assessing failure causes and consequences to prioritize cost-effective interventions, often combining predictive maintenance with traditional methods.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com