Smart dust consists of tiny wireless sensors equipped with microprocessors, cameras, and environmental sensors that collect real-time data across manufacturing facilities. Digital twin technology creates a virtual replica of physical assets, processes, or systems to simulate, analyze, and optimize production in real time. Discover how integrating smart dust and digital twin technologies can revolutionize manufacturing efficiency and decision-making.
Why it is important
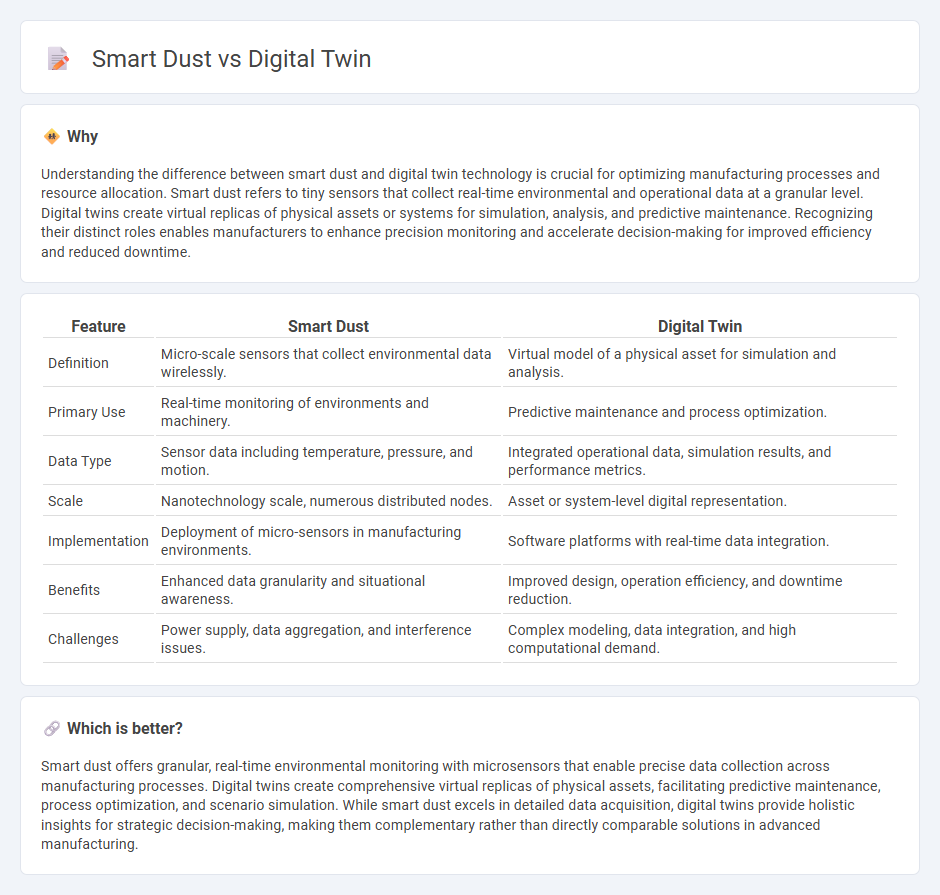
Understanding the difference between smart dust and digital twin technology is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes and resource allocation. Smart dust refers to tiny sensors that collect real-time environmental and operational data at a granular level. Digital twins create virtual replicas of physical assets or systems for simulation, analysis, and predictive maintenance. Recognizing their distinct roles enables manufacturers to enhance precision monitoring and accelerate decision-making for improved efficiency and reduced downtime.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Smart Dust | Digital Twin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Micro-scale sensors that collect environmental data wirelessly. | Virtual model of a physical asset for simulation and analysis. |
| Primary Use | Real-time monitoring of environments and machinery. | Predictive maintenance and process optimization. |
| Data Type | Sensor data including temperature, pressure, and motion. | Integrated operational data, simulation results, and performance metrics. |
| Scale | Nanotechnology scale, numerous distributed nodes. | Asset or system-level digital representation. |
| Implementation | Deployment of micro-sensors in manufacturing environments. | Software platforms with real-time data integration. |
| Benefits | Enhanced data granularity and situational awareness. | Improved design, operation efficiency, and downtime reduction. |
| Challenges | Power supply, data aggregation, and interference issues. | Complex modeling, data integration, and high computational demand. |
Which is better?
Smart dust offers granular, real-time environmental monitoring with microsensors that enable precise data collection across manufacturing processes. Digital twins create comprehensive virtual replicas of physical assets, facilitating predictive maintenance, process optimization, and scenario simulation. While smart dust excels in detailed data acquisition, digital twins provide holistic insights for strategic decision-making, making them complementary rather than directly comparable solutions in advanced manufacturing.
Connection
Smart dust, composed of tiny sensors, collects real-time data on manufacturing environments, enabling precise monitoring of machinery and processes. Digital twins utilize this sensor data to create accurate virtual replicas of physical assets, facilitating simulation, predictive maintenance, and process optimization. The integration of smart dust with digital twin technology enhances operational efficiency, reduces downtime, and supports proactive decision-making in manufacturing.
Key Terms
Simulation
Digital twins create high-fidelity simulations by replicating real-world systems through continuous data integration and advanced modeling techniques. Smart dust consists of miniature sensors that collect real-time environmental data for distributed monitoring but lacks the comprehensive simulation capabilities of digital twins. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how simulation impacts applications in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and urban planning.
Sensor networks
Digital twin technology utilizes extensive sensor networks to create real-time digital replicas of physical assets, enabling precise monitoring and predictive maintenance in industries like manufacturing and urban planning. Smart dust consists of ultra-miniaturized sensors dispersed in environments to collect granular data on factors such as temperature, humidity, and pollution, facilitating pervasive environmental sensing and IoT applications. Discover more about how these advanced sensor networks are transforming data collection and asset management across sectors.
Real-time monitoring
Digital twin technology enables real-time monitoring by creating virtual replicas of physical assets, allowing continuous data analysis and predictive maintenance through IoT sensors and AI algorithms. Smart dust consists of tiny wireless sensors that collect environmental data in real time, offering granular monitoring in hard-to-reach locations but with limited processing capabilities compared to digital twins. Explore how integrating both technologies can revolutionize real-time monitoring across industries.
Source and External Links
Definition of a Digital Twin - A digital twin is an integrated data-driven virtual representation of real-world entities and processes with synchronized interaction, built on real-time and historical data to simulate and predict physical system behavior for better decision-making and interventions.
What Is a Digital Twin? - A digital twin is a virtual model reflecting a physical object accurately using real-time sensor data and simulations to analyze performance, diagnose issues, and optimize operations throughout the object's lifecycle.
Digital twin - A digital twin is a digital model of a physical product, system, or process that continuously updates with real-time data to predict failures and optimize performance, extending from product design to manufacturing processes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com