Biofabrication employs advanced techniques such as 3D bioprinting to create living tissues layer by layer, offering precise control over cell placement and scaffold design. Casting involves pouring liquid material into a mold to set into a desired shape, commonly used for metals, plastics, and ceramics in traditional manufacturing. Explore the unique advantages and applications of biofabrication versus casting to understand their roles in modern manufacturing.
Why it is important
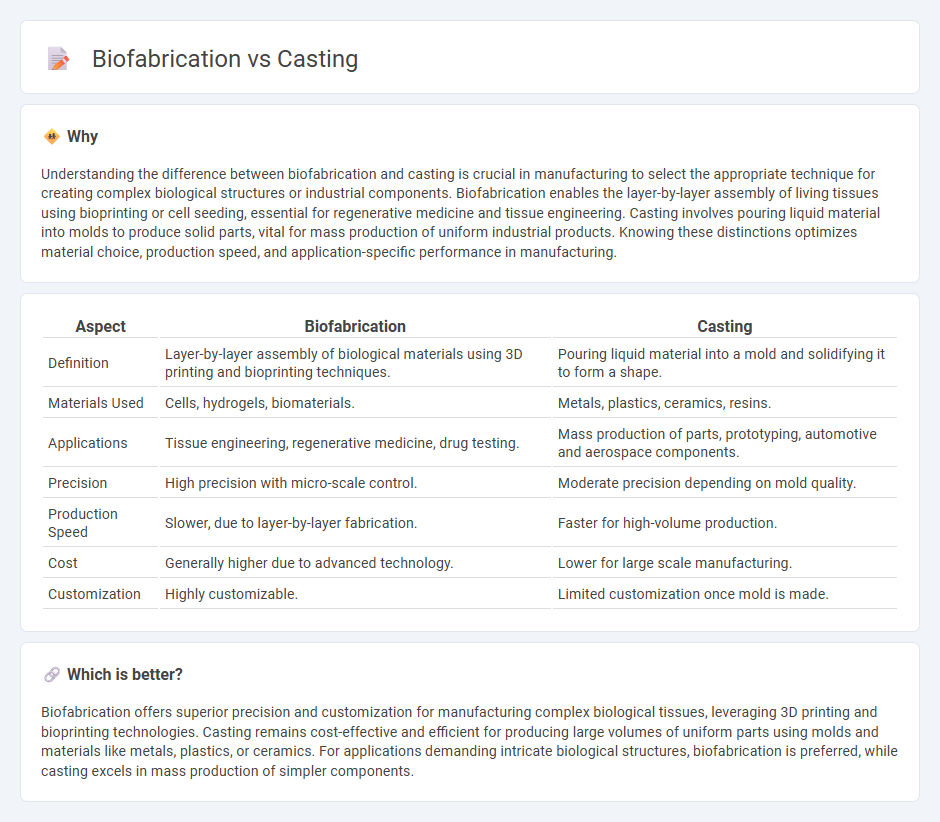
Understanding the difference between biofabrication and casting is crucial in manufacturing to select the appropriate technique for creating complex biological structures or industrial components. Biofabrication enables the layer-by-layer assembly of living tissues using bioprinting or cell seeding, essential for regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. Casting involves pouring liquid material into molds to produce solid parts, vital for mass production of uniform industrial products. Knowing these distinctions optimizes material choice, production speed, and application-specific performance in manufacturing.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Biofabrication | Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Layer-by-layer assembly of biological materials using 3D printing and bioprinting techniques. | Pouring liquid material into a mold and solidifying it to form a shape. |
| Materials Used | Cells, hydrogels, biomaterials. | Metals, plastics, ceramics, resins. |
| Applications | Tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, drug testing. | Mass production of parts, prototyping, automotive and aerospace components. |
| Precision | High precision with micro-scale control. | Moderate precision depending on mold quality. |
| Production Speed | Slower, due to layer-by-layer fabrication. | Faster for high-volume production. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to advanced technology. | Lower for large scale manufacturing. |
| Customization | Highly customizable. | Limited customization once mold is made. |
Which is better?
Biofabrication offers superior precision and customization for manufacturing complex biological tissues, leveraging 3D printing and bioprinting technologies. Casting remains cost-effective and efficient for producing large volumes of uniform parts using molds and materials like metals, plastics, or ceramics. For applications demanding intricate biological structures, biofabrication is preferred, while casting excels in mass production of simpler components.
Connection
Biofabrication and casting intersect in manufacturing by enabling the production of complex, high-precision components through layer-by-layer construction and mold-based shaping techniques. Biofabrication utilizes biocompatible materials and 3D printing technologies to create living tissues or biomaterials, while casting involves pouring liquid materials into molds to form solid structures. Combining these methods enhances the creation of customized biomedical implants and scaffolds with improved structural integrity and biological functionality.
Key Terms
Mold
Casting involves shaping materials by pouring them into molds, enabling precise replication of complex geometries in tissue engineering and biomaterial production. Biofabrication using molds incorporates living cells with biomaterials, allowing the creation of functional tissues with enhanced biological relevance and structural fidelity. Explore further to understand how mold design influences the effectiveness of casting and biofabrication techniques.
Scaffold
Casting involves shaping scaffolds by pouring biomaterial solutions into molds, creating structures with controlled geometries and porosities essential for tissue engineering. Biofabrication utilizes techniques like 3D bioprinting to precisely position cells and biomaterials, enabling the creation of complex, functional scaffolds mimicking native extracellular matrices. Explore how advancements in scaffold fabrication are revolutionizing regenerative medicine and tissue engineering outcomes.
Cell-laden bioink
Casting methods often struggle with precise control over cell distribution and architecture in tissue constructs. In contrast, biofabrication utilizing cell-laden bioink enables high-resolution spatial patterning and enhanced cell viability through tailored bioink formulations and extrusion techniques. Explore more about advancements in biofabrication technologies and their impact on regenerative medicine.
Source and External Links
Casting Frontier - A comprehensive online platform where actors can create profiles, upload media, search and apply for casting calls, and connect directly with casting directors for film, TV, commercials, and more.
Central Casting - The leading U.S. background actor casting company, offering daily opportunities for extras, stand-ins, and specialty roles across major film and TV productions.
Backstage Casting - A trusted resource for actors to find casting calls, auditions, and acting jobs, with a long-standing reputation for connecting talent to professional opportunities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com