Machine vision technology leverages advanced cameras and image processing algorithms to inspect, monitor, and guide manufacturing processes, ensuring high precision and quality control. RFID technology uses radio frequency identification to track and manage inventory, assets, and production workflows efficiently without direct line-of-sight scanning. Explore the advantages and applications of machine vision and RFID technology in modern manufacturing to enhance operational effectiveness.
Why it is important
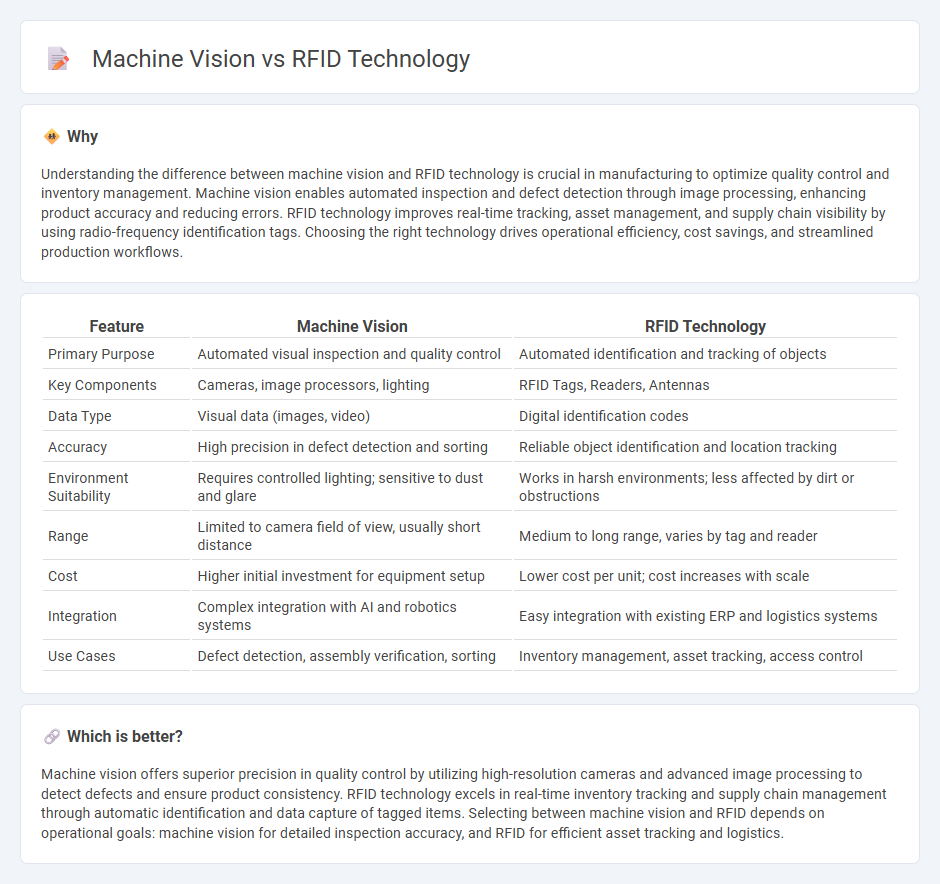
Understanding the difference between machine vision and RFID technology is crucial in manufacturing to optimize quality control and inventory management. Machine vision enables automated inspection and defect detection through image processing, enhancing product accuracy and reducing errors. RFID technology improves real-time tracking, asset management, and supply chain visibility by using radio-frequency identification tags. Choosing the right technology drives operational efficiency, cost savings, and streamlined production workflows.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Machine Vision | RFID Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Automated visual inspection and quality control | Automated identification and tracking of objects |
| Key Components | Cameras, image processors, lighting | RFID Tags, Readers, Antennas |
| Data Type | Visual data (images, video) | Digital identification codes |
| Accuracy | High precision in defect detection and sorting | Reliable object identification and location tracking |
| Environment Suitability | Requires controlled lighting; sensitive to dust and glare | Works in harsh environments; less affected by dirt or obstructions |
| Range | Limited to camera field of view, usually short distance | Medium to long range, varies by tag and reader |
| Cost | Higher initial investment for equipment setup | Lower cost per unit; cost increases with scale |
| Integration | Complex integration with AI and robotics systems | Easy integration with existing ERP and logistics systems |
| Use Cases | Defect detection, assembly verification, sorting | Inventory management, asset tracking, access control |
Which is better?
Machine vision offers superior precision in quality control by utilizing high-resolution cameras and advanced image processing to detect defects and ensure product consistency. RFID technology excels in real-time inventory tracking and supply chain management through automatic identification and data capture of tagged items. Selecting between machine vision and RFID depends on operational goals: machine vision for detailed inspection accuracy, and RFID for efficient asset tracking and logistics.
Connection
Machine vision and RFID technology are connected in manufacturing through their combined ability to enhance automation and tracking processes. Machine vision systems capture and analyze visual data for quality control and object recognition, while RFID technology provides real-time inventory tracking and identification using radio frequency signals. Together, they streamline production lines by ensuring accurate product verification and efficient asset management, reducing errors and increasing operational efficiency.
Key Terms
Tagging (RFID)
RFID technology offers efficient automated tagging through radio frequency identification, enabling real-time inventory tracking and minimizing manual scanning errors. Machine vision systems use image recognition to identify and verify items visually, which requires clear line-of-sight and can be affected by lighting conditions. Explore the advantages and applications of RFID and machine vision in tagging to optimize your asset management strategy.
Image Processing (Machine Vision)
Machine vision utilizes advanced image processing algorithms to analyze visual data from cameras and sensors, enabling precise object detection, quality inspection, and pattern recognition in industrial automation. RFID technology, on the other hand, relies on radio frequency signals to identify and track tags attached to objects, offering efficient inventory management but limited in detailed visual analysis. Discover how leveraging image processing in machine vision can enhance accuracy and operational insights beyond RFID capabilities.
Automation
RFID technology streamlines automation by enabling real-time asset tracking and inventory management through wireless identification, reducing human error and labor costs. Machine vision enhances automation by providing detailed image analysis for quality control, object recognition, and sorting in manufacturing processes. Explore how integrating RFID and machine vision can revolutionize your automation systems.
Source and External Links
Radio-frequency identification - Wikipedia - RFID uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects, with applications in inventory management, asset tracking, and access control, without requiring line of sight.
Introduction of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) - GeeksforGeeks - RFID is a wireless technology that employs radio waves to uniquely identify objects or people, enabling efficient and accurate tracking in logistics, inventory, and security systems without direct physical contact.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID): What is it? | Homeland Security - RFID technology reads information from wireless tags via radio waves, facilitating contactless identification for applications like border management, employee badges, and toll collection, with data linked securely to external databases rather than stored on the tag itself.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com