Lights out factories utilize fully automated production processes that operate without human intervention, significantly increasing efficiency and reducing labor costs in manufacturing. Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, builds products layer by layer directly from digital models, enabling complex designs and rapid prototyping with minimal waste. Explore how integrating these technologies transforms the future of smart manufacturing and operational excellence.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between lights-out factory and additive manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and cost management. Lights-out factories operate autonomously with minimal human intervention, enhancing scalability and reducing labor costs. Additive manufacturing focuses on layer-by-layer construction, enabling rapid prototyping and customized production. Knowing these distinctions allows manufacturers to select the best technology aligned with their production goals and product complexity.
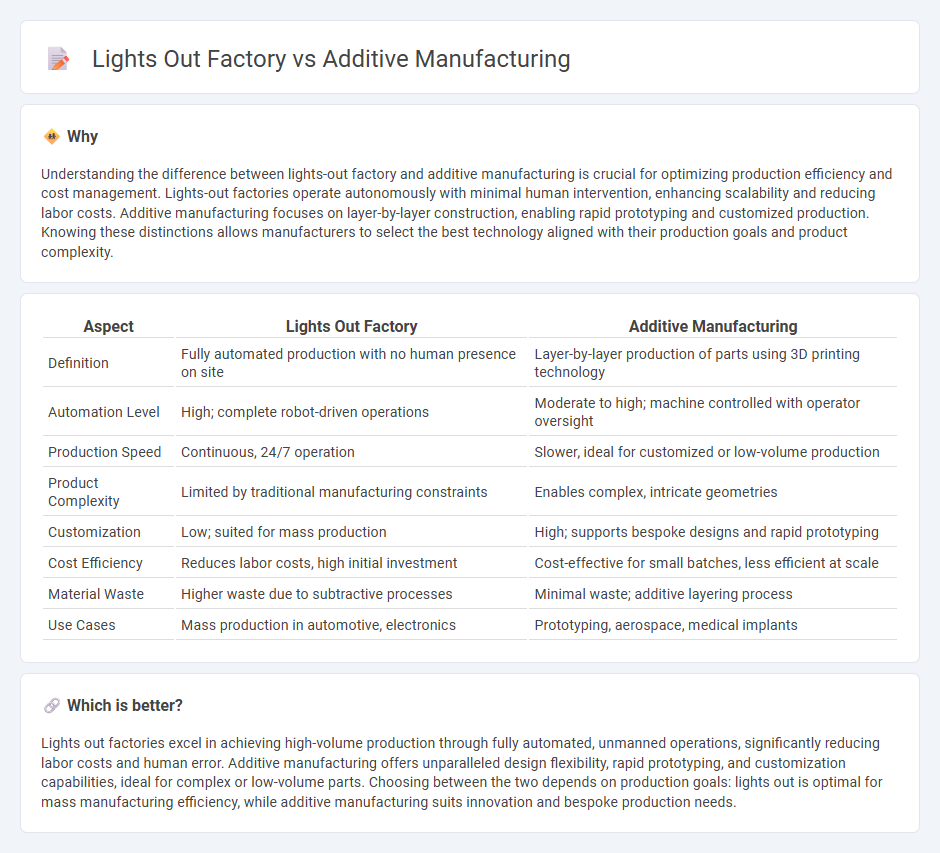
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Lights Out Factory | Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated production with no human presence on site | Layer-by-layer production of parts using 3D printing technology |
| Automation Level | High; complete robot-driven operations | Moderate to high; machine controlled with operator oversight |
| Production Speed | Continuous, 24/7 operation | Slower, ideal for customized or low-volume production |
| Product Complexity | Limited by traditional manufacturing constraints | Enables complex, intricate geometries |
| Customization | Low; suited for mass production | High; supports bespoke designs and rapid prototyping |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces labor costs, high initial investment | Cost-effective for small batches, less efficient at scale |
| Material Waste | Higher waste due to subtractive processes | Minimal waste; additive layering process |
| Use Cases | Mass production in automotive, electronics | Prototyping, aerospace, medical implants |
Which is better?
Lights out factories excel in achieving high-volume production through fully automated, unmanned operations, significantly reducing labor costs and human error. Additive manufacturing offers unparalleled design flexibility, rapid prototyping, and customization capabilities, ideal for complex or low-volume parts. Choosing between the two depends on production goals: lights out is optimal for mass manufacturing efficiency, while additive manufacturing suits innovation and bespoke production needs.
Connection
Lights-out factories rely heavily on additive manufacturing technology to enable fully automated production processes with minimal human intervention. The precision and flexibility of 3D printing techniques allow for rapid prototyping, custom parts fabrication, and tool-less manufacturing in an unmanned environment. Integration of additive manufacturing in lights-out operations enhances efficiency, reduces downtime, and supports continuous production cycles.
Key Terms
**Additive Manufacturing:**
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, revolutionizes production by building parts layer-by-layer directly from digital models, enabling rapid prototyping, complex geometries, and material efficiency. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, additive processes reduce material waste and shorten supply chains, making it ideal for customized and low-volume production. Explore how additive manufacturing transforms the future of manufacturing and integrates with Industry 4.0 technologies.
3D Printing
Additive manufacturing leverages 3D printing technology to build complex parts layer by layer, offering design flexibility and rapid prototyping capabilities that traditional subtractive methods cannot match. Lights out factories emphasize fully automated production environments with minimal human intervention, integrating robotics, AI, and machine learning to maximize operational efficiency and reduce downtime. Explore how combining 3D printing innovations with lights out factory automation is revolutionizing modern manufacturing processes.
Layer-by-Layer Fabrication
Layer-by-layer fabrication in additive manufacturing allows precise, customizable production by building parts directly from digital models, reducing material waste and enabling complex geometries. Lights-out factories optimize this process through automation and minimal human intervention, ensuring continuous, high-throughput production while maintaining quality control. Explore how integrating additive manufacturing with lights-out factory concepts revolutionizes industrial manufacturing efficiency and scalability.
Source and External Links
Additive manufacturing, explained - Additive manufacturing is a process of creating objects layer by layer from digital designs, often referred to as 3-D printing, enabling direct conversion from digital models to physical products using various materials such as polymers, metals, and ceramics.
Additive manufacturing | NIST - Additive manufacturing or 3D printing fabricates products layer-by-layer from digital files, allowing complex designs with less material waste, and is applied in industries from aerospace to biomedical implants.
What Is Additive Manufacturing? | 3D Printing Simulation ... - Additive manufacturing builds physical 3D models by layering materials using multiple print technologies like powder bed fusion and material extrusion, enabling industrial applications from prototypes to production.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com