Microfactories enable localized, flexible manufacturing with lower capital investment and faster response times compared to traditional mass production lines, which focus on high-volume output and economies of scale. Microfactories leverage automation and modular designs to customize small batches efficiently while mass production relies on standardized processes and assembly lines to minimize cost per unit. Explore the benefits and challenges of both manufacturing approaches to determine the best fit for your production needs.
Why it is important
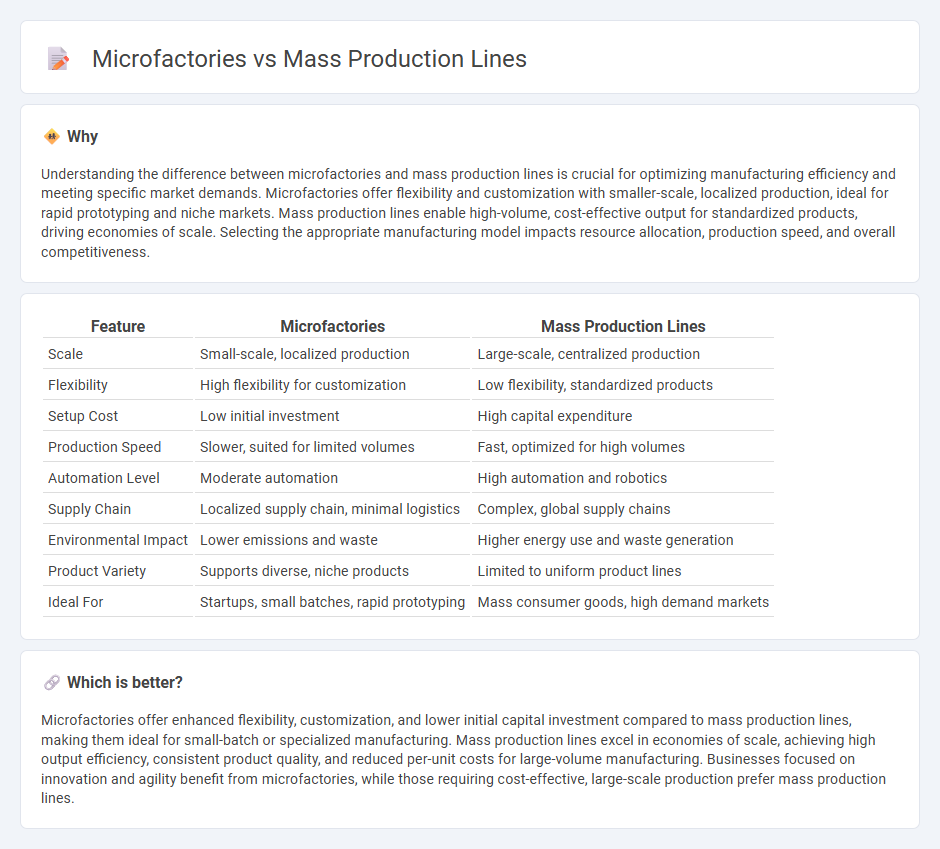
Understanding the difference between microfactories and mass production lines is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and meeting specific market demands. Microfactories offer flexibility and customization with smaller-scale, localized production, ideal for rapid prototyping and niche markets. Mass production lines enable high-volume, cost-effective output for standardized products, driving economies of scale. Selecting the appropriate manufacturing model impacts resource allocation, production speed, and overall competitiveness.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Microfactories | Mass Production Lines |
|---|---|---|
| Scale | Small-scale, localized production | Large-scale, centralized production |
| Flexibility | High flexibility for customization | Low flexibility, standardized products |
| Setup Cost | Low initial investment | High capital expenditure |
| Production Speed | Slower, suited for limited volumes | Fast, optimized for high volumes |
| Automation Level | Moderate automation | High automation and robotics |
| Supply Chain | Localized supply chain, minimal logistics | Complex, global supply chains |
| Environmental Impact | Lower emissions and waste | Higher energy use and waste generation |
| Product Variety | Supports diverse, niche products | Limited to uniform product lines |
| Ideal For | Startups, small batches, rapid prototyping | Mass consumer goods, high demand markets |
Which is better?
Microfactories offer enhanced flexibility, customization, and lower initial capital investment compared to mass production lines, making them ideal for small-batch or specialized manufacturing. Mass production lines excel in economies of scale, achieving high output efficiency, consistent product quality, and reduced per-unit costs for large-volume manufacturing. Businesses focused on innovation and agility benefit from microfactories, while those requiring cost-effective, large-scale production prefer mass production lines.
Connection
Microfactories and mass production lines share a fundamental connection in streamlining manufacturing processes to enhance efficiency and scalability. Microfactories enable localized, flexible production with rapid prototyping, while mass production lines specialize in high-volume output through standardized workflows. Integrating microfactory agility with mass production scale optimizes supply chain responsiveness and reduces time-to-market for diverse manufacturing industries.
Key Terms
Automation
Mass production lines leverage large-scale automation technologies such as robotic arms, conveyor belts, and AI-powered quality control to achieve high output and consistency. Microfactories utilize compact, flexible automation systems tailored for localized, customizable production with rapid reconfiguration capabilities. Explore the evolving automation strategies driving efficiency in both mass production lines and microfactories.
Scalability
Mass production lines excel in scalability by delivering high-volume output through standardized processes and automation. Microfactories offer flexible scalability, allowing rapid adaptation to demand fluctuations and localized production with lower initial investment. Discover how these production models impact manufacturing efficiency and market responsiveness.
Flexibility
Mass production lines offer high output but limited flexibility, making them less suited for customized or rapidly changing products. Microfactories excel in adaptability, allowing for small batch production and quick reconfiguration to meet specific market demands. Explore how microfactories redefine manufacturing agility and responsiveness.
Source and External Links
Mass production - Wikipedia - Mass production is a capital- and energy-intensive manufacturing process using assembly line techniques where workers each perform an individual step, enabling the rapid production of standardized products with machinery and often automation.
What Is Mass Production? A Comprehensive Guide - MRPeasy - Mass production involves designing products with interchangeable parts and standardized processes, procuring raw materials in bulk, planning production for continuous flow, and dividing labor so workers specialize in specific tasks to maximize efficiency.
Manufacturing Assembly Line: Understanding the Set-up - Assembly lines, a key part of mass production, can be continuous flow, cellular, balanced, flexible, or automated, with the choice depending on product type, production volume, and desired automation level.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com