Edge computing processes data locally on devices or nearby servers, reducing latency and enhancing real-time decision-making in manufacturing environments. Cloud computing offers scalable storage and powerful analytics by centralizing data processing, enabling extensive historical data analysis and resource optimization. Explore the differences and benefits of edge versus cloud computing to enhance your manufacturing operations.
Why it is important
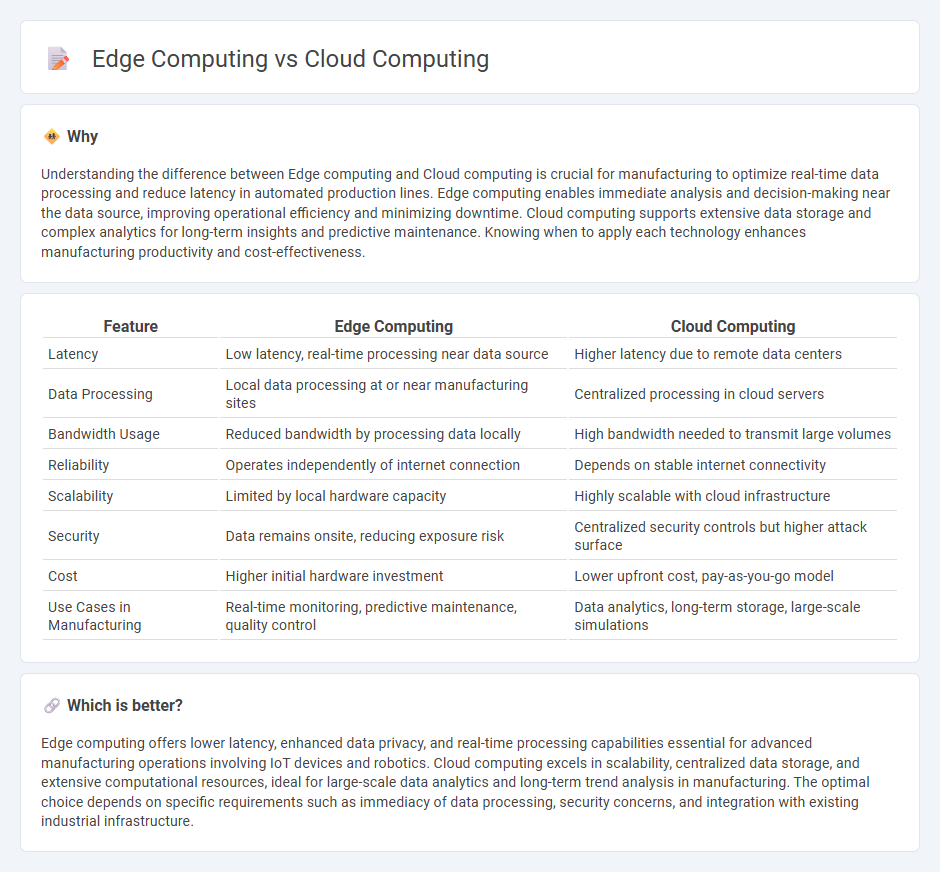
Understanding the difference between Edge computing and Cloud computing is crucial for manufacturing to optimize real-time data processing and reduce latency in automated production lines. Edge computing enables immediate analysis and decision-making near the data source, improving operational efficiency and minimizing downtime. Cloud computing supports extensive data storage and complex analytics for long-term insights and predictive maintenance. Knowing when to apply each technology enhances manufacturing productivity and cost-effectiveness.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | Low latency, real-time processing near data source | Higher latency due to remote data centers |
| Data Processing | Local data processing at or near manufacturing sites | Centralized processing in cloud servers |
| Bandwidth Usage | Reduced bandwidth by processing data locally | High bandwidth needed to transmit large volumes |
| Reliability | Operates independently of internet connection | Depends on stable internet connectivity |
| Scalability | Limited by local hardware capacity | Highly scalable with cloud infrastructure |
| Security | Data remains onsite, reducing exposure risk | Centralized security controls but higher attack surface |
| Cost | Higher initial hardware investment | Lower upfront cost, pay-as-you-go model |
| Use Cases in Manufacturing | Real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, quality control | Data analytics, long-term storage, large-scale simulations |
Which is better?
Edge computing offers lower latency, enhanced data privacy, and real-time processing capabilities essential for advanced manufacturing operations involving IoT devices and robotics. Cloud computing excels in scalability, centralized data storage, and extensive computational resources, ideal for large-scale data analytics and long-term trend analysis in manufacturing. The optimal choice depends on specific requirements such as immediacy of data processing, security concerns, and integration with existing industrial infrastructure.
Connection
Edge computing processes data locally at manufacturing sites for real-time decision-making, while cloud computing offers centralized storage and advanced analytics capabilities. This integration enables seamless data exchange, enhances operational efficiency, and supports predictive maintenance in smart factories. Combining both technologies optimizes production workflows and reduces latency in Industry 4.0 environments.
Key Terms
Data Processing Location
Cloud computing centralizes data processing in remote data centers, providing scalable storage and computational power ideal for large-scale analytics and global accessibility. Edge computing processes data locally at the source device or nearby edge servers, reducing latency and bandwidth usage for real-time applications such as IoT and autonomous systems. Explore the benefits and use cases of both architectures to optimize your data processing strategy.
Latency
Cloud computing centralizes data processing in remote data centers, often causing higher latency due to longer transmission distances. Edge computing processes data closer to the data source, reducing latency significantly and enabling real-time analytics and faster decision-making. Explore the benefits of low-latency solutions and how edge computing enhances performance for latency-sensitive applications.
Real-Time Analytics
Real-time analytics in cloud computing leverages scalable centralized data centers to process vast amounts of data but may face latency issues due to bandwidth constraints. Edge computing processes data locally near the source, significantly reducing latency and improving response times for real-time analytics in IoT and autonomous systems. Explore more about how these computing paradigms impact real-time decision-making and efficiency.
Source and External Links
What is Cloud Computing? Types, Examples and Benefits - Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of hosted computing and IT services over the internet, where remote data centers managed by providers handle storage, security, and processing, enabling users to access resources like data, analytics, and applications without owning the underlying infrastructure.
Cloud computing - Wikipedia - Cloud computing is a paradigm that provides scalable, elastic access to a pool of shareable computing resources over the network, characterized by on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service.
The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing - According to NIST, cloud computing is a model offering ubiquitous, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal effort or service provider interaction.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com