Remanufacturing involves restoring used products to like-new condition, focusing on disassembly, cleaning, repairing, and reassembling components. Reverse logistics manages the movement of goods from customers back to manufacturers for returns, repairs, recycling, or disposal, optimizing supply chain efficiency and sustainability. Explore how remanufacturing and reverse logistics drive cost savings and environmental benefits in manufacturing.
Why it is important
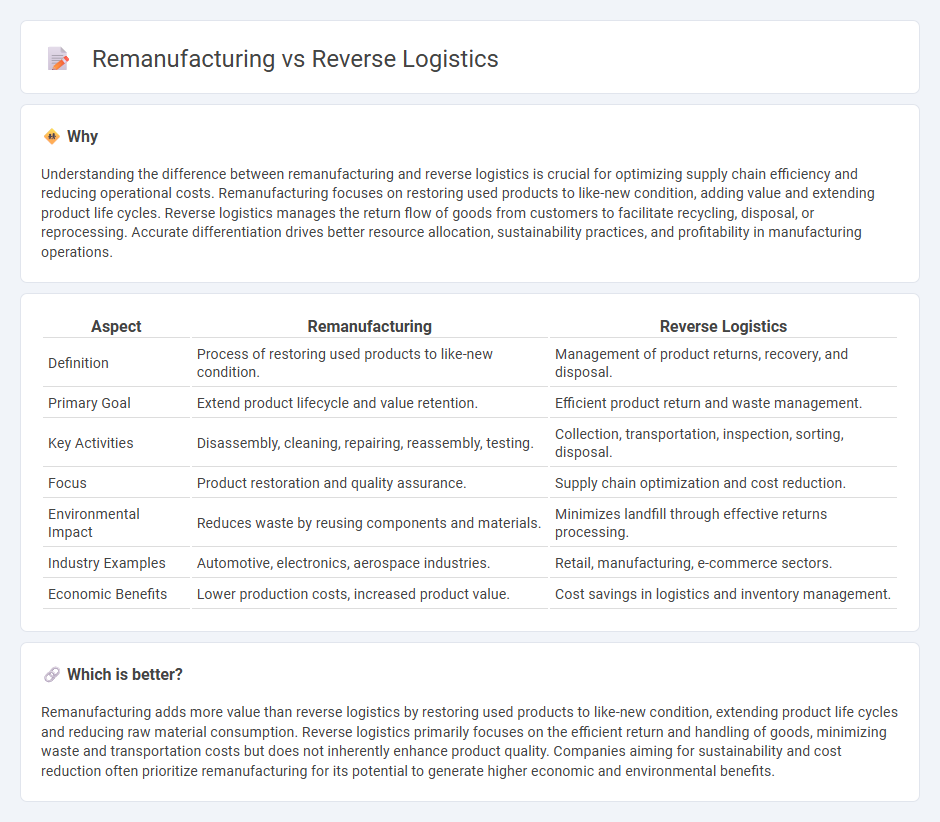
Understanding the difference between remanufacturing and reverse logistics is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing operational costs. Remanufacturing focuses on restoring used products to like-new condition, adding value and extending product life cycles. Reverse logistics manages the return flow of goods from customers to facilitate recycling, disposal, or reprocessing. Accurate differentiation drives better resource allocation, sustainability practices, and profitability in manufacturing operations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Remanufacturing | Reverse Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of restoring used products to like-new condition. | Management of product returns, recovery, and disposal. |
| Primary Goal | Extend product lifecycle and value retention. | Efficient product return and waste management. |
| Key Activities | Disassembly, cleaning, repairing, reassembly, testing. | Collection, transportation, inspection, sorting, disposal. |
| Focus | Product restoration and quality assurance. | Supply chain optimization and cost reduction. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste by reusing components and materials. | Minimizes landfill through effective returns processing. |
| Industry Examples | Automotive, electronics, aerospace industries. | Retail, manufacturing, e-commerce sectors. |
| Economic Benefits | Lower production costs, increased product value. | Cost savings in logistics and inventory management. |
Which is better?
Remanufacturing adds more value than reverse logistics by restoring used products to like-new condition, extending product life cycles and reducing raw material consumption. Reverse logistics primarily focuses on the efficient return and handling of goods, minimizing waste and transportation costs but does not inherently enhance product quality. Companies aiming for sustainability and cost reduction often prioritize remanufacturing for its potential to generate higher economic and environmental benefits.
Connection
Remanufacturing relies heavily on reverse logistics to efficiently collect, transport, and process used products and components for refurbishment or restoration. This supply chain integration minimizes raw material consumption, reduces production costs, and supports sustainable manufacturing practices. Effective reverse logistics systems enable timely returns, quality inspection, and inventory management, driving the overall success of remanufacturing operations.
Key Terms
Product Recovery
Reverse logistics involves the process of returning products from consumers back to manufacturers for reuse, recycling, or proper disposal, emphasizing efficient transportation and handling. Remanufacturing is a subset of product recovery within reverse logistics, where used products are disassembled, restored to like-new condition, and tested for quality assurance. Explore further to understand how these processes optimize supply chains and sustainability.
Returns Management
Reverse logistics encompasses the entire process of managing product returns, including transportation, inspection, and disposition. Remanufacturing specifically involves restoring returned products to like-new condition through disassembly and refurbishment. Explore the distinctions and benefits within returns management to optimize your supply chain efficiency.
Component Reuse
Component reuse in reverse logistics emphasizes the efficient recovery and redistribution of used parts to minimize waste and reduce production costs. Remanufacturing prioritizes the restoration and refurbishment of components to original specifications, extending product lifespan and enhancing sustainability. Explore how integrating both strategies can maximize value and environmental benefits in supply chain management.
Source and External Links
What is Reverse Logistics? - c3controls - Reverse logistics involves moving goods from the customer back to the manufacturer for return, repair, recycling, or remanufacturing, and is essential for a leaner, more efficient supply chain aligned with sustainability goals.
A Guide to Reverse Logistics: How It Works, Types and Strategies - Reverse logistics manages returns, surplus goods, and refurbishments, varying by industry, and involves processes such as return authorization, scheduling shipments, and refunds.
Reverse logistics - Wikipedia - Reverse logistics is the upstream movement of products for recapturing value or proper disposal, including activities like remanufacturing and refurbishing, and is a growing global market estimated at nearly $1 trillion as of 2023.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com