Dark factories leverage advanced automation and robotics to operate with minimal human intervention, maximizing efficiency and reducing labor costs. Cellular manufacturing organizes production into self-contained units or cells, enhancing flexibility, reducing waste, and improving workflow by grouping similar processes. Explore these innovative manufacturing approaches to understand their impact on modern industrial productivity.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dark factory and cellular manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and automation strategies. Dark factories operate fully automated systems with minimal human intervention, reducing labor costs and increasing precision. Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations in close proximity to enhance workflow, flexibility, and team collaboration. Choosing the right manufacturing approach impacts operational scalability and cost management.
Comparison Table
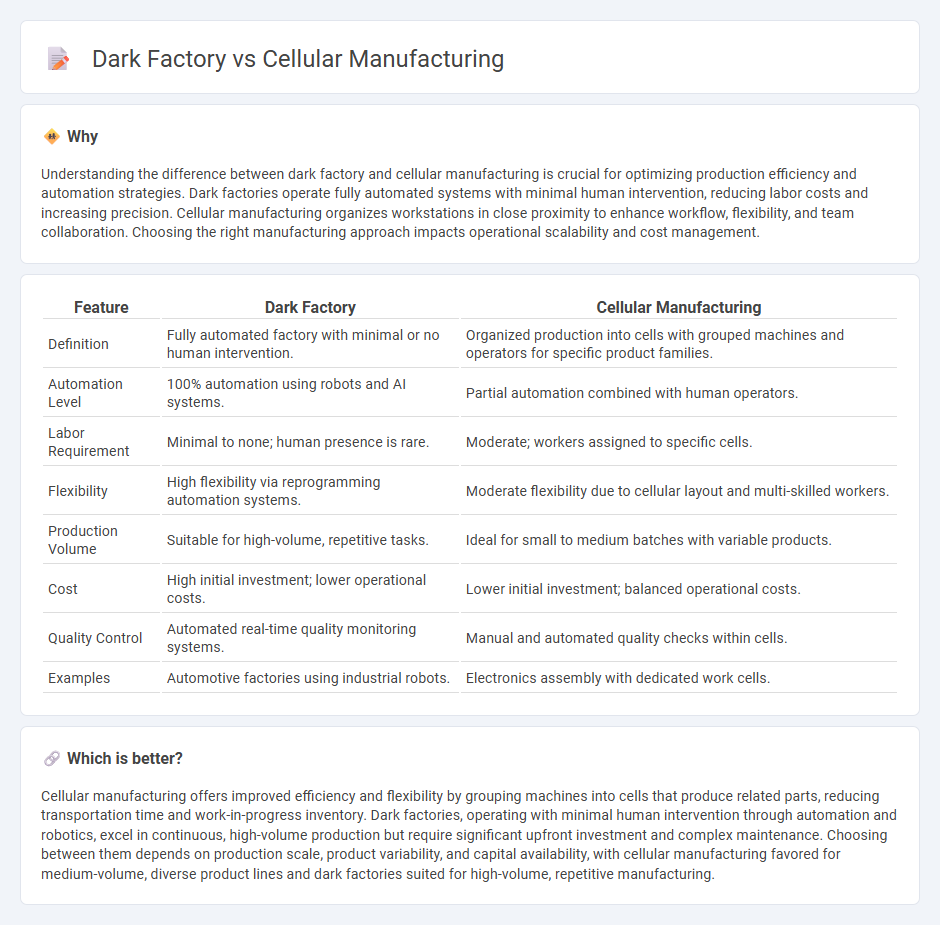
| Feature | Dark Factory | Cellular Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated factory with minimal or no human intervention. | Organized production into cells with grouped machines and operators for specific product families. |
| Automation Level | 100% automation using robots and AI systems. | Partial automation combined with human operators. |
| Labor Requirement | Minimal to none; human presence is rare. | Moderate; workers assigned to specific cells. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility via reprogramming automation systems. | Moderate flexibility due to cellular layout and multi-skilled workers. |
| Production Volume | Suitable for high-volume, repetitive tasks. | Ideal for small to medium batches with variable products. |
| Cost | High initial investment; lower operational costs. | Lower initial investment; balanced operational costs. |
| Quality Control | Automated real-time quality monitoring systems. | Manual and automated quality checks within cells. |
| Examples | Automotive factories using industrial robots. | Electronics assembly with dedicated work cells. |
Which is better?
Cellular manufacturing offers improved efficiency and flexibility by grouping machines into cells that produce related parts, reducing transportation time and work-in-progress inventory. Dark factories, operating with minimal human intervention through automation and robotics, excel in continuous, high-volume production but require significant upfront investment and complex maintenance. Choosing between them depends on production scale, product variability, and capital availability, with cellular manufacturing favored for medium-volume, diverse product lines and dark factories suited for high-volume, repetitive manufacturing.
Connection
Dark factories utilize automated systems and robotics to operate with minimal human intervention, enhancing efficiency and reducing errors. Cellular manufacturing organizes production into small, self-contained units, promoting flexibility and faster response to demand changes. Integrating dark factory technologies within cellular manufacturing cells enables seamless automation and optimization of workflow, boosting productivity and reducing operational costs.
Key Terms
Cellular Manufacturing:
Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations in compact, U-shaped cells to streamline production, reduce waste, and enhance communication, resulting in higher efficiency and flexibility compared to traditional manufacturing methods. Unlike dark factories, which operate fully automated with minimal human intervention and rely heavily on robotics and AI, cellular manufacturing integrates human skills with machinery for customized and adaptable workflows. Discover more about how cellular manufacturing boosts productivity and supports lean manufacturing principles by exploring its methodologies and benefits.
Work Cells
Cellular manufacturing organizes production into work cells, grouping machines and processes to enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and streamline workflow. Dark factories operate with minimal or no human presence, relying heavily on automation and robotics to maintain continuous production around the clock. Explore the distinctions between work cell configurations in cellular manufacturing and the automation strategies deployed in dark factories to optimize industrial output.
Lean Production
Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations in a sequence to optimize material flow and reduce waste, enabling efficient Lean Production by minimizing cycle time and inventory. Dark factories, operating fully automated with minimal human intervention, further enhance Lean principles through continuous production and reduced labor costs. Explore how integrating these approaches revolutionizes Lean Production strategies and operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
Cellular manufacturing - Cellular manufacturing is a lean production process grouping machines into cells that manufacture a product or part through sequential steps to reduce waste and increase efficiency, often arranged in U-shapes for flexibility and supervision.
Cellular Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide - This method integrates multiple production processes into unified cells, designed based on production assessment and flow charts, to enhance efficiency by monitoring and optimizing performance in a lean manufacturing context.
What Is Cellular Manufacturing? - Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations and equipment into self-sufficient cells with cross-trained workers, optimizing continuous flow and improving communication, quality, and lead times across industries like automotive and electronics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com