Predictive maintenance leverages advanced data analytics and IoT sensors to forecast equipment failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and reducing repair costs. Autonomous maintenance involves empowering operators to perform routine maintenance activities, enhancing equipment reliability and fostering proactive engagement. Discover how these maintenance strategies revolutionize manufacturing efficiency and productivity.
Why it is important
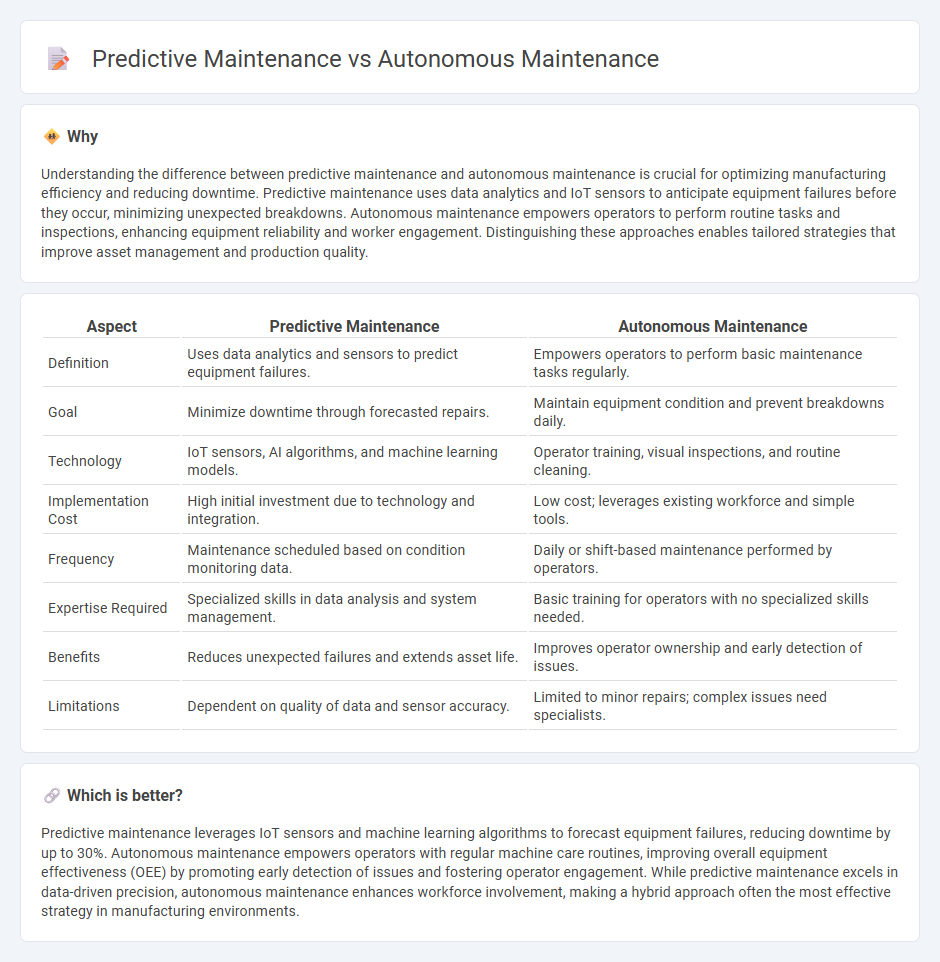
Understanding the difference between predictive maintenance and autonomous maintenance is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and reducing downtime. Predictive maintenance uses data analytics and IoT sensors to anticipate equipment failures before they occur, minimizing unexpected breakdowns. Autonomous maintenance empowers operators to perform routine tasks and inspections, enhancing equipment reliability and worker engagement. Distinguishing these approaches enables tailored strategies that improve asset management and production quality.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Predictive Maintenance | Autonomous Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses data analytics and sensors to predict equipment failures. | Empowers operators to perform basic maintenance tasks regularly. |
| Goal | Minimize downtime through forecasted repairs. | Maintain equipment condition and prevent breakdowns daily. |
| Technology | IoT sensors, AI algorithms, and machine learning models. | Operator training, visual inspections, and routine cleaning. |
| Implementation Cost | High initial investment due to technology and integration. | Low cost; leverages existing workforce and simple tools. |
| Frequency | Maintenance scheduled based on condition monitoring data. | Daily or shift-based maintenance performed by operators. |
| Expertise Required | Specialized skills in data analysis and system management. | Basic training for operators with no specialized skills needed. |
| Benefits | Reduces unexpected failures and extends asset life. | Improves operator ownership and early detection of issues. |
| Limitations | Dependent on quality of data and sensor accuracy. | Limited to minor repairs; complex issues need specialists. |
Which is better?
Predictive maintenance leverages IoT sensors and machine learning algorithms to forecast equipment failures, reducing downtime by up to 30%. Autonomous maintenance empowers operators with regular machine care routines, improving overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) by promoting early detection of issues and fostering operator engagement. While predictive maintenance excels in data-driven precision, autonomous maintenance enhances workforce involvement, making a hybrid approach often the most effective strategy in manufacturing environments.
Connection
Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data and advanced analytics to forecast equipment failures, enabling timely interventions that reduce downtime. Autonomous maintenance empowers operators to perform routine inspections and basic repairs, fostering early detection of anomalies. Together, these strategies create a proactive maintenance ecosystem that enhances manufacturing efficiency and asset reliability.
Key Terms
**Autonomous Maintenance:**
Autonomous Maintenance empowers operators to take full ownership of routine equipment care, enhancing machine reliability and reducing downtime through proactive inspections and basic repairs. This approach fosters a culture of continuous improvement, enabling early detection of potential issues before they escalate into costly failures. Discover how implementing Autonomous Maintenance can transform your maintenance strategy and boost operational efficiency.
Operator-led Equipment Care
Autonomous maintenance emphasizes operator-led equipment care, where operators perform routine maintenance tasks to prevent breakdowns and improve equipment reliability. Predictive maintenance relies on data analytics and sensor technology to forecast equipment failures and schedule interventions just in time. Explore detailed differences and benefits of these maintenance strategies to optimize your maintenance program.
Cleaning and Inspection
Autonomous maintenance emphasizes operator-led regular cleaning and inspection to prevent equipment deterioration, enhancing machine reliability through hands-on attention. Predictive maintenance leverages advanced sensors and data analytics to monitor equipment condition, identifying potential failures before they occur without interrupting operations. Explore the distinct cleaning and inspection strategies in these maintenance approaches for optimized asset management.
Source and External Links
Autonomous Maintenance (AM): 7 Steps to Implement & ... - Autonomous maintenance is a methodology empowering operators to perform routine equipment upkeep like cleaning, inspection, and lubrication, reducing reliance on maintenance technicians and increasing equipment reliability and cost savings.
Autonomous Maintenance: 7 Steps & Benefits - Autonomous maintenance involves seven steps starting with increasing operator knowledge and initial cleaning/inspection to empower operators to manage routine equipment maintenance and prevent contamination.
Autonomous Maintenance: What It Is and Why It Matters - Autonomous maintenance is a strategy where trained operators continuously monitor and maintain their equipment by performing tasks like cleaning, lubricating, and inspecting to keep machines in optimal condition, integral to total productive maintenance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com