Generative design uses AI algorithms to create optimized product models based on specific constraints, improving efficiency and innovation in manufacturing. Reverse engineering focuses on analyzing existing products to reproduce or enhance designs, enabling rapid iteration and quality control. Explore how both approaches transform manufacturing processes and drive competitive advantage.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between generative design and reverse engineering is crucial in manufacturing because generative design uses algorithms to optimize product innovation, while reverse engineering focuses on replicating or improving existing parts. Generative design accelerates prototyping by exploring multiple design possibilities based on performance criteria, reducing material usage and production costs. Reverse engineering enables manufacturers to capture legacy product data, ensuring compatibility and quality in redesign or replacement scenarios. Mastery of both techniques enhances manufacturing efficiency, innovation, and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Generative Design | Reverse Engineering |
|---|---|---|
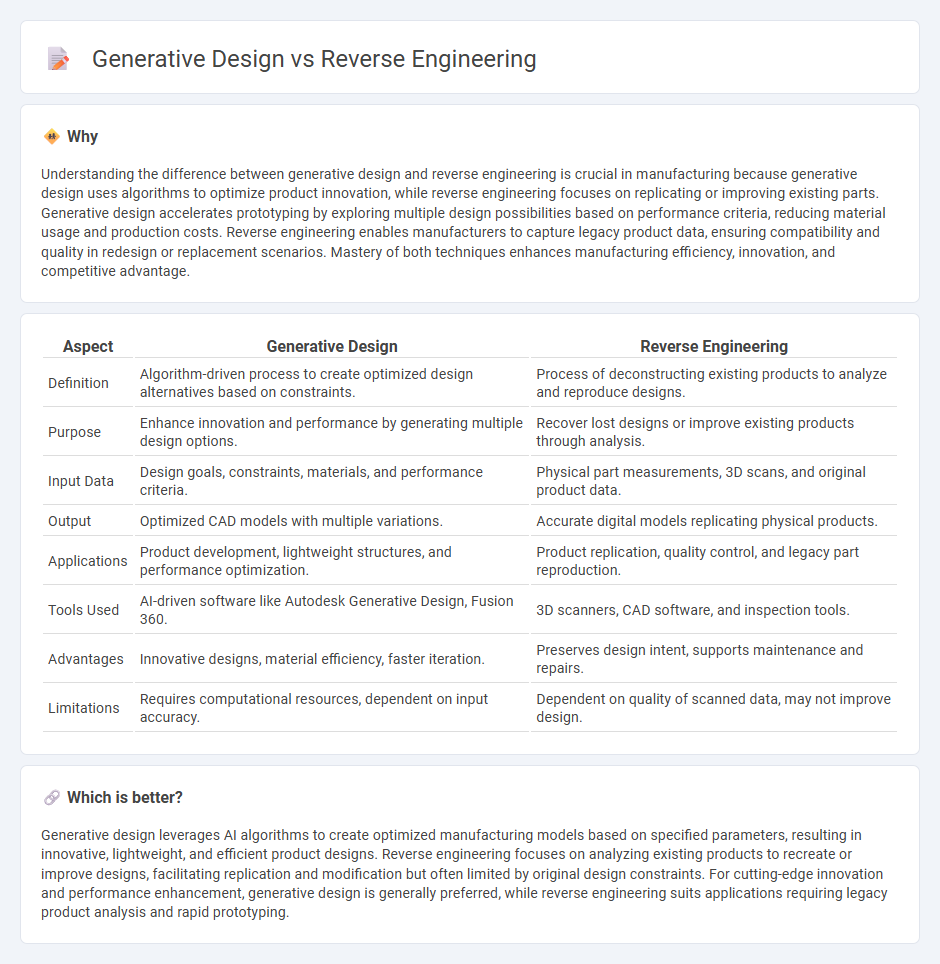
| Definition | Algorithm-driven process to create optimized design alternatives based on constraints. | Process of deconstructing existing products to analyze and reproduce designs. |
| Purpose | Enhance innovation and performance by generating multiple design options. | Recover lost designs or improve existing products through analysis. |
| Input Data | Design goals, constraints, materials, and performance criteria. | Physical part measurements, 3D scans, and original product data. |
| Output | Optimized CAD models with multiple variations. | Accurate digital models replicating physical products. |
| Applications | Product development, lightweight structures, and performance optimization. | Product replication, quality control, and legacy part reproduction. |
| Tools Used | AI-driven software like Autodesk Generative Design, Fusion 360. | 3D scanners, CAD software, and inspection tools. |
| Advantages | Innovative designs, material efficiency, faster iteration. | Preserves design intent, supports maintenance and repairs. |
| Limitations | Requires computational resources, dependent on input accuracy. | Dependent on quality of scanned data, may not improve design. |
Which is better?
Generative design leverages AI algorithms to create optimized manufacturing models based on specified parameters, resulting in innovative, lightweight, and efficient product designs. Reverse engineering focuses on analyzing existing products to recreate or improve designs, facilitating replication and modification but often limited by original design constraints. For cutting-edge innovation and performance enhancement, generative design is generally preferred, while reverse engineering suits applications requiring legacy product analysis and rapid prototyping.
Connection
Generative design leverages algorithms to create optimized manufacturing components based on performance criteria, while reverse engineering captures existing product geometries and functional data. These technologies intersect by using reverse-engineered digital models as input for generative design processes, enabling improved product iterations and innovation. The integration accelerates development cycles and enhances manufacturing efficiency by combining detailed physical insights with AI-driven design optimization.
Key Terms
CAD Modeling
Reverse engineering in CAD modeling involves extracting precise digital representations from existing physical objects to enable modifications, analysis, or reproduction, using tools like 3D scanners and mesh processing software. Generative design leverages advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence to create optimized CAD models based on predefined constraints, performance goals, and material properties, resulting in innovative and efficient structures often unattainable through traditional design methods. Explore the nuances and applications of these cutting-edge CAD modeling approaches to enhance product development workflows.
Topology Optimization
Topology optimization is a critical aspect that distinguishes generative design from reverse engineering, focusing on enhancing material layout within a given design space for improved performance and reduced weight. Generative design leverages topology optimization algorithms to create innovative shapes and structures that meet specified constraints and objectives, whereas reverse engineering primarily replicates and analyzes existing designs without inherently optimizing material distribution. Explore detailed insights on how topology optimization integrates with these methodologies to revolutionize product development.
Digital Twin
Reverse engineering captures existing physical assets by extracting precise geometric and functional data, enabling accurate digital twin creation for simulation and analysis. Generative design leverages algorithm-driven models to optimize component performance and innovate within the digital twin framework, enhancing design efficiency and adaptability. Explore how combining reverse engineering and generative design can revolutionize digital twin development in your projects.
Source and External Links
Reverse engineering - Wikipedia - Reverse engineering is a process of understanding how a device, process, or piece of software works by analyzing its structure and behavior, often without access to its original design documentation.
What is Reverse Engineering? - Autodesk - Reverse engineering involves taking something apart to discover how it works, and is commonly used in design, manufacturing, and biomedical fields to replicate, improve, or interoperate with existing products.
Reverse Engineering - DLA - Reverse engineering is the process of replicating a design by physically examining and measuring an existing item to develop the technical data needed to reproduce it functionally and dimensionally.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com