Decentralized manufacturing refers to the strategic placement of production units away from a central facility, allowing localized control and customization to meet regional demand efficiently. Distributed manufacturing involves a network of interconnected production sites that collaborate through digital platforms to optimize resource use and reduce lead times. Explore the advantages and applications of these innovative manufacturing models to enhance operational agility and customer responsiveness.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between decentralized manufacturing and distributed manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and supply chain resilience. Decentralized manufacturing centralizes decision-making within individual facilities, enhancing local autonomy, while distributed manufacturing disperses production geographically to reduce lead times and transportation costs. Knowing these distinctions enables businesses to tailor strategies for scalability, cost reduction, and rapid response to market demands. This knowledge supports improved resource allocation and adoption of advanced technologies like IoT and AI in different manufacturing models.
Comparison Table
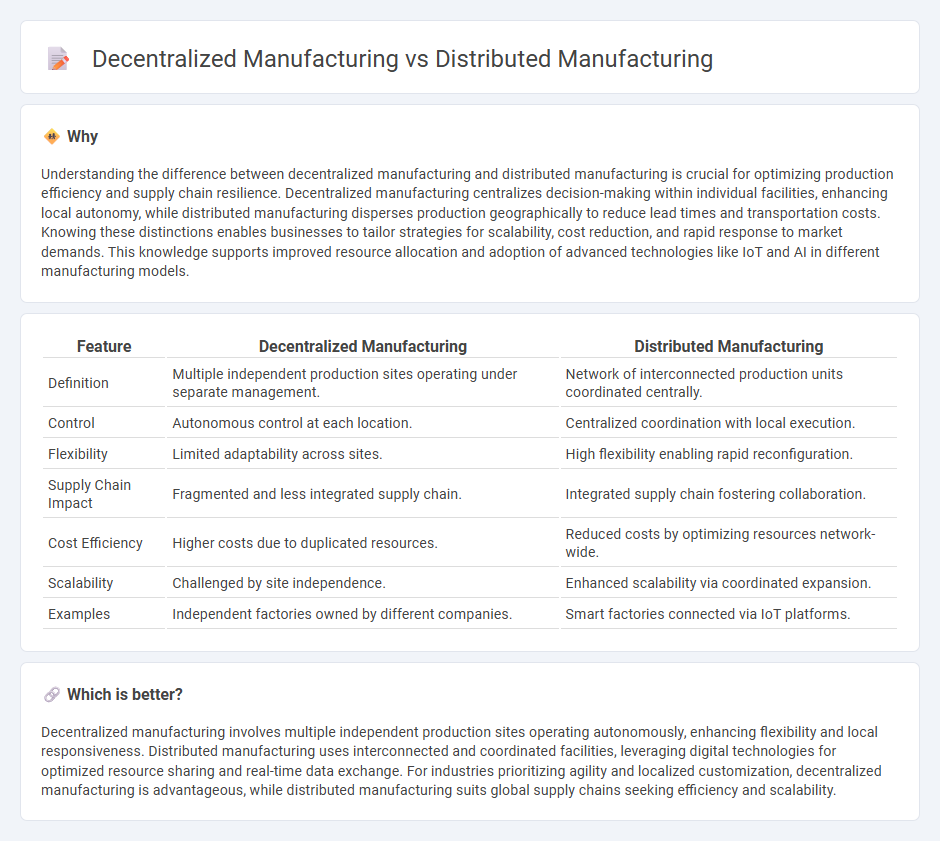
| Feature | Decentralized Manufacturing | Distributed Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple independent production sites operating under separate management. | Network of interconnected production units coordinated centrally. |
| Control | Autonomous control at each location. | Centralized coordination with local execution. |
| Flexibility | Limited adaptability across sites. | High flexibility enabling rapid reconfiguration. |
| Supply Chain Impact | Fragmented and less integrated supply chain. | Integrated supply chain fostering collaboration. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher costs due to duplicated resources. | Reduced costs by optimizing resources network-wide. |
| Scalability | Challenged by site independence. | Enhanced scalability via coordinated expansion. |
| Examples | Independent factories owned by different companies. | Smart factories connected via IoT platforms. |
Which is better?
Decentralized manufacturing involves multiple independent production sites operating autonomously, enhancing flexibility and local responsiveness. Distributed manufacturing uses interconnected and coordinated facilities, leveraging digital technologies for optimized resource sharing and real-time data exchange. For industries prioritizing agility and localized customization, decentralized manufacturing is advantageous, while distributed manufacturing suits global supply chains seeking efficiency and scalability.
Connection
Decentralized manufacturing and distributed manufacturing both involve spreading production processes across multiple locations to enhance flexibility and reduce dependency on a single site. Decentralized manufacturing emphasizes autonomous decision-making at each production node, while distributed manufacturing focuses on strategically locating facilities closer to end consumers to minimize logistics costs and delivery times. Together, they optimize supply chain resilience, enable rapid customization, and support scalability in the manufacturing industry.
Key Terms
Supply Chain Flexibility
Distributed manufacturing enhances supply chain flexibility by leveraging localized production closer to end consumers, reducing lead times and transportation costs. Decentralized manufacturing spreads production across multiple independent facilities, allowing rapid adaptation to demand fluctuations and disruptions. Explore the advantages of each model to optimize supply chain resilience and responsiveness.
Production Location Autonomy
Distributed manufacturing involves multiple interconnected production sites that share resources and coordinate processes, often under centralized control, whereas decentralized manufacturing grants independent autonomy to each production location, enabling localized decision-making and flexibility. The level of production location autonomy is higher in decentralized systems, fostering responsiveness to local market demands and reducing dependency on a central hub. Explore more to understand how production location autonomy impacts operational efficiency and scalability.
Resource Allocation
Distributed manufacturing allocates resources across multiple geographically dispersed production facilities, enhancing flexibility and risk mitigation by localizing supply chains. Decentralized manufacturing, however, emphasizes autonomous decision-making at individual manufacturing sites, optimizing resource utilization based on local demand and conditions. Explore the nuances of resource allocation strategies in these manufacturing paradigms to optimize your production efficiency.
Source and External Links
Distributed manufacturing benefits: Revolutionizing production - Distributed manufacturing is a model where production is spread across smaller, geographically dispersed facilities, locally serving markets with advanced technologies like 3D printing and cloud management, enabling faster delivery, customization, and reduced shipping costs.
Distributed Manufacturing: The Way of the Future? - Distributed manufacturing organizes production across multiple local sites or via on-demand technologies like 3D printing, focusing on localized, modular, and sustainable manufacturing closer to consumption points to reduce waste and supply chain complexity.
What Is Distributed Manufacturing? - MRPeasy Blog - It is a business model emphasizing many small, regional production points managed centrally, producing customized products locally to lower shipping times and costs, increase flexibility, and improve sustainability despite somewhat higher production costs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com