Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines repetitive manufacturing tasks through software-driven automation, enhancing operational efficiency and accuracy. Additive Manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, builds products layer-by-layer from digital models, enabling rapid prototyping and complex design fabrication. Explore how these innovative technologies are transforming manufacturing workflows and productivity.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Additive Manufacturing (AM) is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and innovation in manufacturing. RPA automates repetitive tasks in digital workflows, enhancing operational speed and accuracy without physical production changes. Additive Manufacturing, or 3D printing, enables the creation of complex physical parts layer-by-layer, reducing material waste and enabling rapid prototyping. Distinguishing these technologies helps businesses allocate resources effectively to improve productivity and product development.
Comparison Table
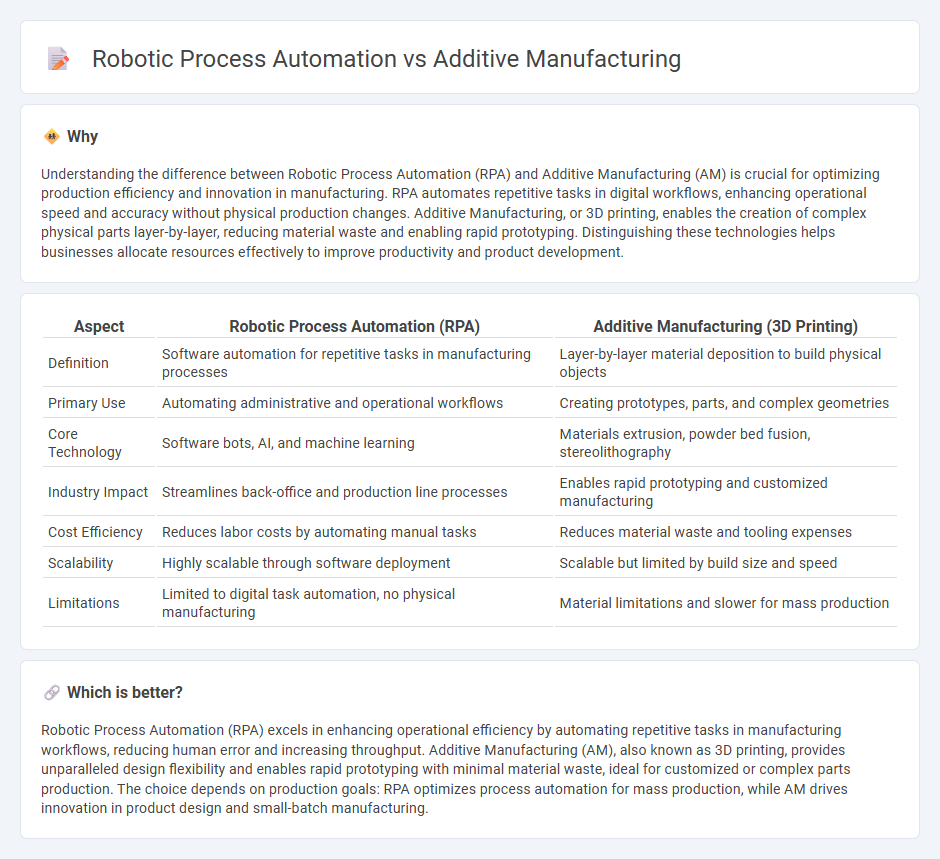
| Aspect | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software automation for repetitive tasks in manufacturing processes | Layer-by-layer material deposition to build physical objects |
| Primary Use | Automating administrative and operational workflows | Creating prototypes, parts, and complex geometries |
| Core Technology | Software bots, AI, and machine learning | Materials extrusion, powder bed fusion, stereolithography |
| Industry Impact | Streamlines back-office and production line processes | Enables rapid prototyping and customized manufacturing |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces labor costs by automating manual tasks | Reduces material waste and tooling expenses |
| Scalability | Highly scalable through software deployment | Scalable but limited by build size and speed |
| Limitations | Limited to digital task automation, no physical manufacturing | Material limitations and slower for mass production |
Which is better?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) excels in enhancing operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks in manufacturing workflows, reducing human error and increasing throughput. Additive Manufacturing (AM), also known as 3D printing, provides unparalleled design flexibility and enables rapid prototyping with minimal material waste, ideal for customized or complex parts production. The choice depends on production goals: RPA optimizes process automation for mass production, while AM drives innovation in product design and small-batch manufacturing.
Connection
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances additive manufacturing by streamlining repetitive tasks such as machine calibration, quality inspection, and data collection, increasing production efficiency. Integration of RPA with additive manufacturing systems facilitates real-time monitoring and adaptive control, reducing errors and downtime. This synergy accelerates product development cycles and improves precision in complex manufacturing processes.
Key Terms
3D Printing
Additive manufacturing revolutionizes production by building objects layer by layer using digital models, primarily through 3D printing technologies such as fused deposition modeling (FDM) and selective laser sintering (SLS). Robotic process automation (RPA) optimizes business workflows by automating repetitive tasks across software systems but does not involve physical object creation. Explore how combining 3D printing with RPA can enhance manufacturing efficiency and innovation in your industry.
Automated Assembly
Additive manufacturing revolutionizes automated assembly by enabling precise layer-by-layer fabrication of complex components, reducing material waste and accelerating prototyping cycles. Robotic process automation streamlines repetitive assembly tasks through software-driven control of robotic arms, enhancing accuracy and operational efficiency. Explore how integrating these technologies transforms automated assembly workflows and boosts manufacturing productivity.
Workflow Optimization
Additive manufacturing enhances workflow optimization by enabling rapid prototyping and customized production, significantly reducing lead times and material waste. Robotic process automation (RPA) optimizes workflows by automating repetitive tasks, increasing process accuracy and efficiency in administrative and manufacturing environments. Discover how integrating both technologies can revolutionize operational workflows and boost productivity.
Source and External Links
Additive manufacturing, explained | MIT Sloan - Additive manufacturing builds objects layer by layer from digital designs, typically using 3D printing, evolving from rapid prototyping in the 1980s to functional production parts today with a wide variety of materials including metals and biomaterials.
Additive manufacturing | NIST - Additive manufacturing (or 3D printing) fabricates complex 3D products by layering materials precisely as directed by digital files, enabling less waste and diverse applications such as aerospace lightweight structures and custom biomedical implants.
The 7 categories of Additive Manufacturing - Loughborough University - Additive manufacturing includes various processes classified into seven categories like vat photopolymerization, material jetting, and binder jetting, each differing by materials used and layer-building technology.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com