Remanufacturing restores used products to like-new condition through disassembly, cleaning, and replacement of components, extending product life and reducing waste. Reuse involves employing products or parts again without major alterations, preserving original materials and energy consumption. Discover how these sustainable manufacturing practices impact industry efficiency and environmental goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between remanufacturing and reuse is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and minimizing environmental impact in manufacturing. Remanufacturing involves restoring used products to like-new condition through extensive disassembly and replacement of parts, while reuse simply extends the life of products without significant alteration. Accurate knowledge helps manufacturers implement sustainable practices that reduce waste and lower production costs. This distinction also influences quality control, regulatory compliance, and customer satisfaction in the industrial sector.
Comparison Table
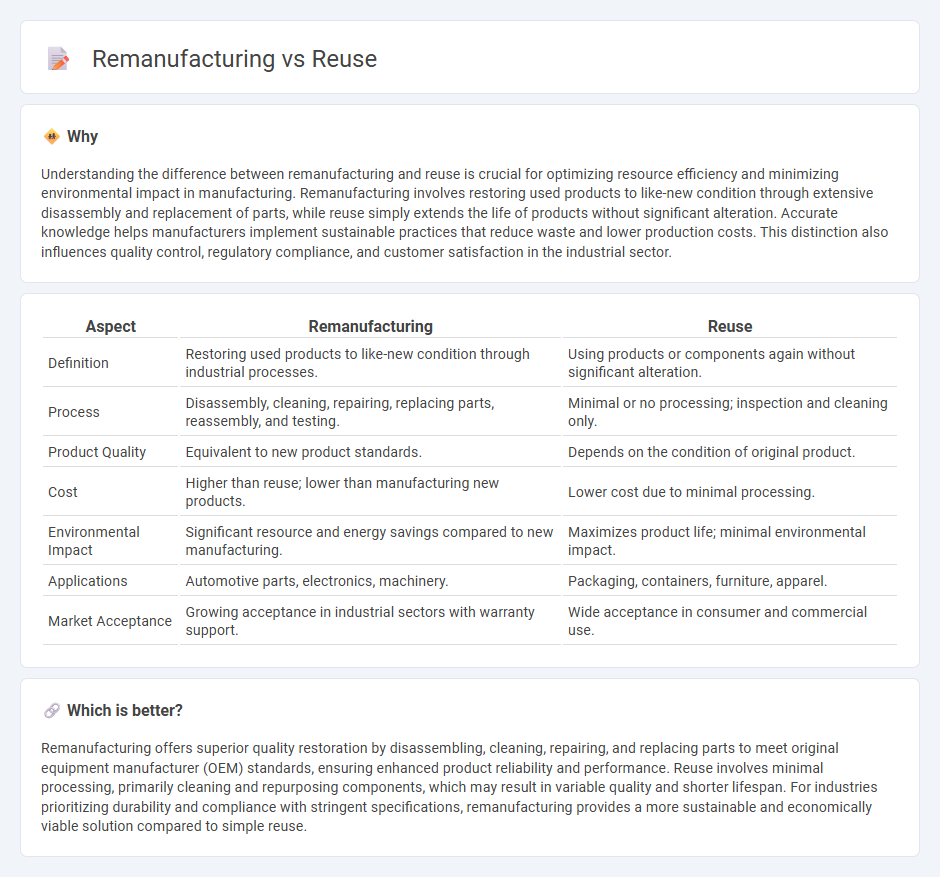
| Aspect | Remanufacturing | Reuse |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Restoring used products to like-new condition through industrial processes. | Using products or components again without significant alteration. |
| Process | Disassembly, cleaning, repairing, replacing parts, reassembly, and testing. | Minimal or no processing; inspection and cleaning only. |
| Product Quality | Equivalent to new product standards. | Depends on the condition of original product. |
| Cost | Higher than reuse; lower than manufacturing new products. | Lower cost due to minimal processing. |
| Environmental Impact | Significant resource and energy savings compared to new manufacturing. | Maximizes product life; minimal environmental impact. |
| Applications | Automotive parts, electronics, machinery. | Packaging, containers, furniture, apparel. |
| Market Acceptance | Growing acceptance in industrial sectors with warranty support. | Wide acceptance in consumer and commercial use. |
Which is better?
Remanufacturing offers superior quality restoration by disassembling, cleaning, repairing, and replacing parts to meet original equipment manufacturer (OEM) standards, ensuring enhanced product reliability and performance. Reuse involves minimal processing, primarily cleaning and repurposing components, which may result in variable quality and shorter lifespan. For industries prioritizing durability and compliance with stringent specifications, remanufacturing provides a more sustainable and economically viable solution compared to simple reuse.
Connection
Remanufacturing and reuse are interconnected processes that extend the lifecycle of products by recovering value from used components. Remanufacturing involves restoring equipment to like-new condition through disassembly, cleaning, repairing, and reassembly, which supports sustainable manufacturing practices by reducing waste and conserving raw materials. Reuse complements remanufacturing by directly employing recovered parts or products in new production cycles, enhancing resource efficiency and lowering environmental impact.
Key Terms
Product Lifecycle
Reuse extends product lifecycle by directly repurposing components without significant processing, maintaining original material integrity and reducing waste generation. Remanufacturing involves disassembling, restoring, and upgrading products to like-new condition, significantly enhancing product lifespan and performance while conserving resources. Explore deeper insights into how each approach optimizes product lifecycle management and sustainability.
Value Retention
Reuse maximizes value retention by extending a product's lifecycle with minimal processing, preserving its original condition and functionality. Remanufacturing involves restoring used products to like-new condition through extensive refurbishment, enhancing performance and reliability while sustaining value. Explore deeper insights into how reuse and remanufacturing strategies impact circular economy and resource efficiency.
Component Recovery
Reuse involves directly employing components in their original form without significant alteration, maximizing the lifespan of parts while minimizing waste generation. Remanufacturing entails disassembling, cleaning, repairing, and restoring components to a like-new condition, which requires advanced processes but significantly enhances product reliability and performance. Explore detailed insights on component recovery strategies to optimize sustainability and cost-efficiency in manufacturing.
Source and External Links
Reuse - Reuse involves using items again either for their original purpose or for a different function, helping to conserve resources and reduce waste.
NY State - How to Reuse More - This webpage provides tips and strategies for incorporating reuse into daily life to conserve resources and protect the environment.
Reuse Alliance - An organization advocating for a circular economy by focusing on reuse infrastructure and promoting collaborative efforts to reduce overconsumption.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com