Remanufacturing involves restoring used products to like-new condition through comprehensive disassembly, cleaning, and replacement of worn components, ensuring performance and quality standards comparable to new items. Repurposing transforms existing products or materials into new uses that differ from their original intent, often without extensive restoration, emphasizing creativity and resourcefulness. Explore the key differences, benefits, and applications of remanufacturing versus repurposing to optimize sustainability and cost efficiency in manufacturing.
Why it is important
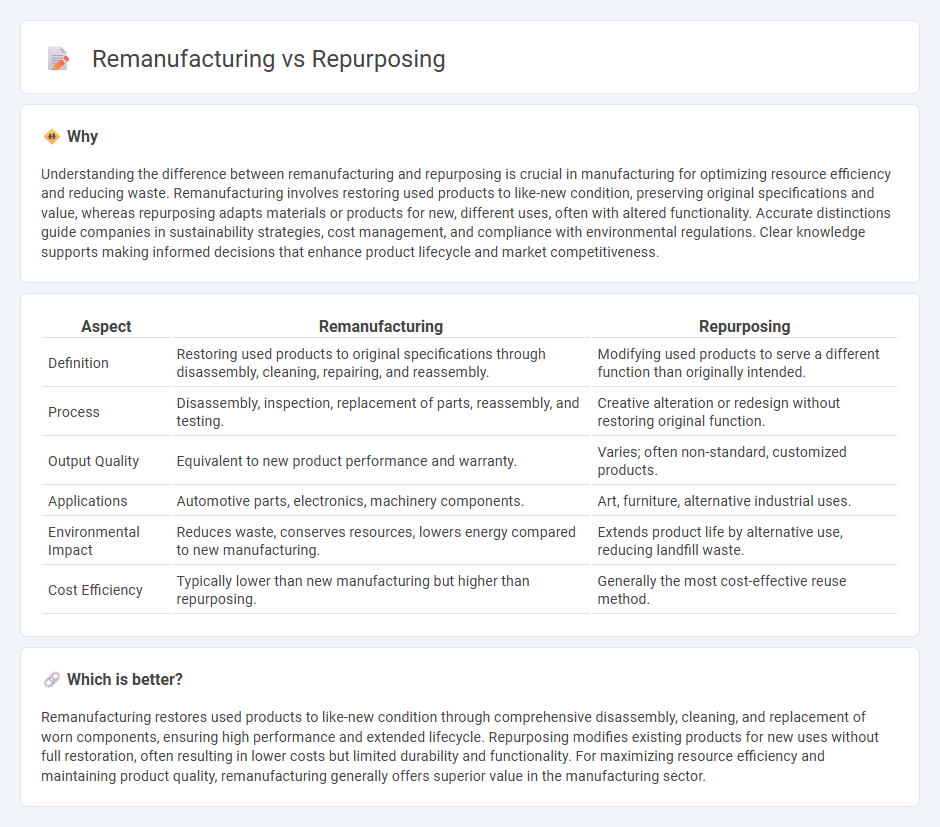
Understanding the difference between remanufacturing and repurposing is crucial in manufacturing for optimizing resource efficiency and reducing waste. Remanufacturing involves restoring used products to like-new condition, preserving original specifications and value, whereas repurposing adapts materials or products for new, different uses, often with altered functionality. Accurate distinctions guide companies in sustainability strategies, cost management, and compliance with environmental regulations. Clear knowledge supports making informed decisions that enhance product lifecycle and market competitiveness.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Remanufacturing | Repurposing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Restoring used products to original specifications through disassembly, cleaning, repairing, and reassembly. | Modifying used products to serve a different function than originally intended. |
| Process | Disassembly, inspection, replacement of parts, reassembly, and testing. | Creative alteration or redesign without restoring original function. |
| Output Quality | Equivalent to new product performance and warranty. | Varies; often non-standard, customized products. |
| Applications | Automotive parts, electronics, machinery components. | Art, furniture, alternative industrial uses. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste, conserves resources, lowers energy compared to new manufacturing. | Extends product life by alternative use, reducing landfill waste. |
| Cost Efficiency | Typically lower than new manufacturing but higher than repurposing. | Generally the most cost-effective reuse method. |
Which is better?
Remanufacturing restores used products to like-new condition through comprehensive disassembly, cleaning, and replacement of worn components, ensuring high performance and extended lifecycle. Repurposing modifies existing products for new uses without full restoration, often resulting in lower costs but limited durability and functionality. For maximizing resource efficiency and maintaining product quality, remanufacturing generally offers superior value in the manufacturing sector.
Connection
Remanufacturing and repurposing are connected through their shared goal of extending product life cycles by transforming used materials into functional goods. Remanufacturing involves restoring products to like-new condition with OEM standards, while repurposing adapts components for new uses, reducing waste and conserving resources. Both processes support sustainable manufacturing by minimizing raw material consumption and lowering environmental impact.
Key Terms
Product Lifecycle
Repurposing extends a product's lifecycle by adapting existing materials or components for new uses without extensive alteration, reducing waste and conserving resources. Remanufacturing involves disassembling, restoring, and upgrading used products to meet original specifications, significantly prolonging their functional lifespan within the circular economy. Explore the distinctions and benefits of these processes to optimize product lifecycle management.
Value Recovery
Repurposing transforms used products into new items with different functions, maximizing value recovery by extending product life cycles and reducing waste. Remanufacturing restores used products to their original specifications through comprehensive disassembly, cleaning, and replacement of worn components, preserving brand value and reliability. Explore how these strategies drive sustainability and profitability in circular economies.
Quality Standards
Repurposing involves converting used products into new items with different functions, often with less stringent quality standards compared to remanufacturing, which restores products to like-new condition adhering to original manufacturer's specifications and rigorous quality controls. Remanufacturing requires comprehensive inspection, component replacement, and testing to ensure performance and reliability equivalent to new products, aligning with ISO 9001 quality standards. Explore more about how quality frameworks impact repurposing and remanufacturing processes to optimize sustainability and product lifecycle management.
Source and External Links
Repurposing - Wikipedia - Repurposing is the process of transforming an object with one use value into an object with an alternative use value, often using items considered junk or obsolete.
Repurpose - UNEP circularity platform - Repurposing involves reusing discarded goods or components for new functions, giving them a distinct new life cycle and reducing waste generation.
Repurposed Furniture Projects and more - Offers hundreds of creative repurposed furniture projects, including upcycling pallets, cribs, and chairs into new functional items.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com